What is the ICD-10-CM code for recurring canker sore in the mouth?
ICD-10 code K12. 0 for Recurrent oral aphthae is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the ICD 10 code for mouth sores?
Unspecified lesions of oral mucosa K13. 70 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K13. 70 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the main term for the diagnosis recurrent canker sore in the mouth?
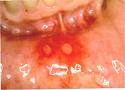
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (canker sores, or aphthous ulcers) is the presence of small, painful sores (ulcers) inside the mouth that typically begin in childhood and recur frequently. Mouth injury, stress, and some foods may trigger an attack.
What is K13 79 code?
Other lesions of oral mucosaK13. 79 - Other lesions of oral mucosa | ICD-10-CM.
Are canker sores mouth ulcers?
The difference between a Mouth ulcer and a Canker Sore lies in its underlying cause. Quite simply: Mouth Ulcers are either caused by trauma to the mouth, or by a viral infection (most commonly Oral Herpes). Canker Sores, on the other hand, are caused by an underlying condition called Aphthous Stomatitis.
What is the diagnosis for ICD 10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What causes mouth canker sores?
Canker sore causes include stress, acidic foods and minor injuries to the inside of your mouth. Treatments include over-the-counter or prescription gels, ointments and rinses. Even without treatment, canker sores usually go away within two weeks.
What is the differential diagnosis of aphthous ulcer?
The differential diagnosis for recurrent aphthous ulcerations is extensive and ranges from idiopathic benign causes to inherited fever syndromes, to connective tissue disease, or even inflammatory bowel diseases.
What causes aphthous stomatitis?
Aphthous stomatitis can be related to a weakened immune system, eating certain foods, having increased levels of stress, and nutritional deficiencies. Canker sores often recur, and prevention involves managing stress, maintaining a healthy diet, and practicing good oral hygiene.
What are the types of oral lesions?
Large-scale, population-based screening studies have identified the most common oral lesions as candidiasis, recurrent herpes labialis, recurrent aphthous stomatitis, mucocele, fibroma, mandibular and palatal tori, pyogenic granuloma, erythema migrans, hairy tongue, lichen planus, and leukoplakia.
What is oral mucosal lesions?
Broadly speaking, oral pathology can present as a mucosal surface lesion (white, red, brown, blistered or verruciform), swelling present at an oral subsite (lips/buccal mucosa, tongue, floor of mouth, palate and jaws; discussed in an accompanying article by these authors)1 or symptoms related to teeth (pain, mobility).
What is the oral mucosa?
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining or “skin” inside of the mouth, including cheeks and lips. People with oral mucosal diseases may develop painful mouth sores or ulcers on this lining.
What is oral mucositis?
Mucositis is when your mouth or gut is sore and inflamed. It's a common side effect of chemotherapy and radiotherapy for cancer. Although mucositis is usually painful, it can be treated. It should get better within a few weeks of finishing cancer treatment.
What is oral mucositis ulcerative?
Oral mucositis is a debilitating condition, and it presents as erythema, edema, and ulceration of the oral mucosa with subsequent pain and restriction in oral intake. The lesions can also break the skin barrier resulting in local or systemic infection.
What do you mean by stomatitis?
Stomatitis, a general term for an inflamed and sore mouth, can disrupt a person's ability to eat, talk, and sleep. Stomatitis can occur anywhere in the mouth, including the inside of the cheeks, gums, tongue, lips, and palate.
What is the oral mucosa?
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining or “skin” inside of the mouth, including cheeks and lips. People with oral mucosal diseases may develop painful mouth sores or ulcers on this lining.
The ICD code K12 is used to code Mouth ulcer
A mouth ulcer (also termed an oral ulcer, or a mucosal ulcer) is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanisms, but usually there is no serious underlying cause.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #011-013 - Tracheostomy for face, mouth and neck diagnoses with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K12.30 - Oral mucositis (ulcerative), unspecified'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K12.30. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code K12.30 and a single ICD9 code, 528.00 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the ICd 9 code for canker sores?
Specialty: Oral Medicine, Dermatology. MeSH Code: D013281. ICD 9 Code: 528.2. Canker sore on the lower lip.
What is aphthous stomatitis?
Aphthous stomatitis (also termed recurrent aphthous stomatitis, recurring oral aphthae or recurrent aphthous ulceration; from Greek: ἄφθα aphtha, "mouth ulcer") is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benign and non-contagious mouth ulcers (aphthae) in otherwise healthy individuals.
What is the ICd 10 code for aphthae?
K12.0 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Recurrent oral aphthae . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also: Aphthae, aphthous see also condition.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hepatic congestion
- 2. icd 10 code for atypical ductal hyperplasia
- 3. icd 10 code for myelophthisis
- 4. icd 10 cm code for peripheral neuropathy of feet
- 5. icd 10 code for meniscus tear right knee
- 6. icd 10 code for ddd lumbar spin
- 7. icd 9 code for history of herpes
- 8. icd 10 code for postpartum depression
- 9. icd 9 code for saurday night paralysis
- 10. icd 10 code for fluid collection