What is the diagnosis code for lung cancer?
Oct 01, 2021 · This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C34.90 - other international versions of ICD-10 C34.90 may differ. Applicable To Lung cancer NOS The following code (s) above C34.90 contain annotation back-references that may be applicable to C34.90 : C00-D49 Neoplasms C30-C39 Malignant neoplasms of respiratory and intrathoracic organs C34
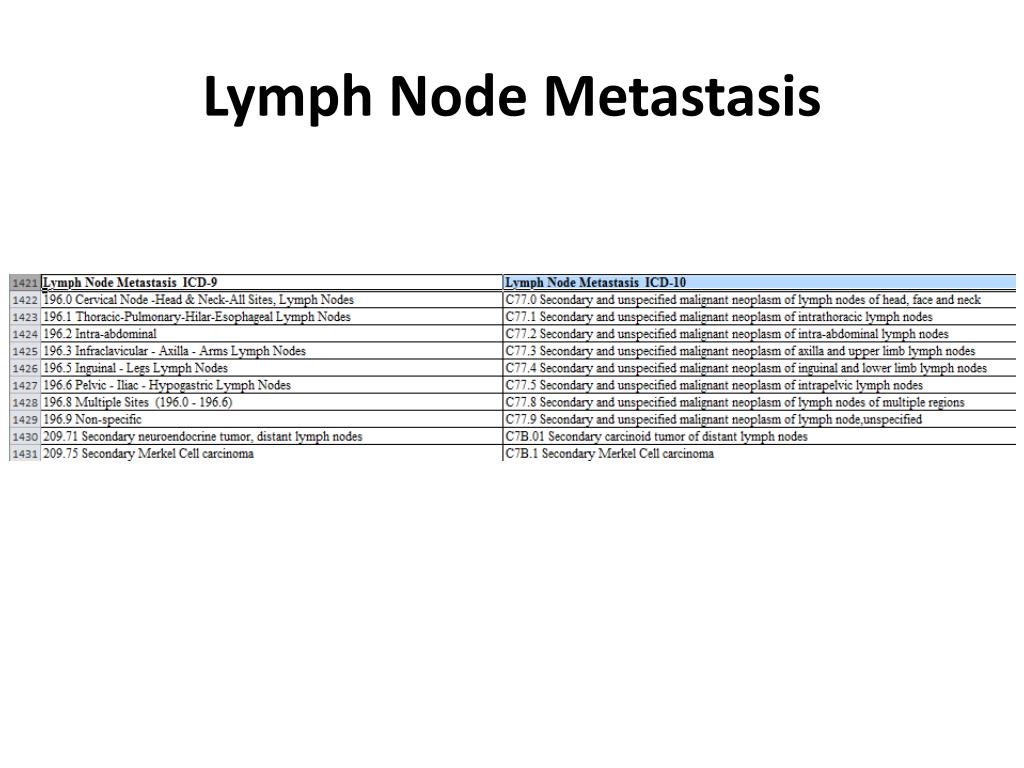
What is the ICD 10 code for secondary lung cancer?
malignant carcinoid tumor of the bronchus and lung (. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C7A.090. Malignant carcinoid tumor of the bronchus and lung. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code.
How do you code metastatic lung cancer?
Oct 01, 2021 · Squamous cell carcinoma of left lung Squamous cell carcinoma, bilateral lungs ICD-10-CM C34.92 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 180 Respiratory neoplasms with mcc 181 Respiratory neoplasms with cc 182 Respiratory neoplasms without cc/mcc Convert C34.92 to ICD-9-CM Code History
What is the diagnosis code for cancer?
Oct 01, 2021 · Carcinoma in situ of unspecified bronchus and lung 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code D02.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D02.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.

What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the Z77.22?
exposure to environmental tobacco smoke ( Z77.22) exposure to tobacco smoke in the perinatal period ( P96.81) history of tobacco dependence ( Z87.891) occupational exposure to environmental tobacco smoke ( Z57.31) tobacco dependence ( F17.-) tobacco use ( Z72.0) Carcinoma in situ of middle ear and respiratory system.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the only test for lung cancer?
The only recommended screening test for lung cancer is low-dose computed tomography (also called a low-dose CT scan, or LDCT). During an LDCT scan, you lie on a table and an X-ray machine uses a low dose (amount) of radiation to make detailed images of your lungs. How much does it cost to check for lung cancer? A spiral CT scan costs $300 or more.
Does Medicare cover LDCT?
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) covers lung cancer screenings with Low Dose Computed Tomography (LDCT) once per year if you meet all of these conditions: You're age 55-77. You don't have signs or symptoms of lung cancer (asymptomatic).
How much does a spiral CT cost?
A spiral CT scan costs $300 or more . Insurance usually pays for the test for lung cancer screening only if you have a very high risk for developing lung cancer. And the test often leads to other costs. Many people have false alarms that lead to more tests and procedures.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the ICd 10 code for bronchus carcinoma?
D02.20 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of carcinoma in situ of unspecified bronchus and lung. The code D02.20 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code D02.20 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like carcinoma in situ of bronchus, carcinoma in situ of bronchus and lung, carcinoma in situ of carina of bronchus, carcinoma in situ of hilus of lung, carcinoma in situ of lower lobe bronchus and lung , carcinoma in situ of lung, etc.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like D02.20 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
What is lung cancer?
Information for Patients. Lung Cancer. Also called: Bronchogenic carcinoma. Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world. It is a leading cause of cancer death in men and women in the United States. Cigarette smoking causes most lung cancers.
When to use unspecified code?
Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition.
What is the most common cancer in the world?
Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world. It is a leading cause of cancer death in men and women in the United States. Cigarette smoking causes most lung cancers. The more cigarettes you smoke per day and the earlier you started smoking, the greater your risk of lung cancer .
What is the most common cause of lung cancer?
It is a leading cause of cancer death in men and women in the United States. Cigarette smoking causes most lung cancers. The more cigarettes you smoke per day and the earlier you started smoking, the greater your risk of lung cancer. High levels of pollution, radiation and asbestos exposure may also increase risk.
Does smoking cigarettes cause cancer?
Cigarette smoking causes most lung cancers. The more cigarettes you smoke per day and the earlier you started smoking, the greater your risk of lung cancer. High levels of pollution, radiation and asbestos exposure may also increase risk. Common symptoms of lung cancer include.
How do doctors diagnose lung cancer?
Doctors diagnose lung cancer using a physical exam, imaging, and lab tests. Treatment depends on the type, stage, and how advanced it is. Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy. Targeted therapy uses substances that attack cancer cells without harming normal cells.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for advanced copd
- 2. 2016 icd 10 code for breast cancer metastises to bone
- 3. icd 10 code for left scrotum hematoma
- 4. icd 10 code for precocious sexual development
- 5. icd 9 code for b12
- 6. icd 10 code for left inguinal hernia unspecified
- 7. icd 10 code for i96
- 8. icd 10 code for malignant neoplasm of esophagus
- 9. icd 10 code for breast scar
- 10. what is the icd 10 code for dvt of right popiteal vein