What is Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome?
Collapse Section. Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome is a disorder that affects many parts of the body, particularly the heart (cardio-), facial features (facio-), and the skin and hair (cutaneous). People with this condition also have delayed development and intellectual disability, usually ranging from moderate to severe.
How is Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome caused?
CFC syndrome is a dominant disorder often caused by de novo (new) mutations in one of four genes called BRAF, MAP2K1 (MEK1), MAP2K2 (MEK2), and KRAS. Some affected individuals do not have a mutation in one of these genes, suggesting that other genes are also associated with CFC syndrome.
What Does CFC mean medical?
Cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome (CFC) is a multiple congenital anomaly disorder that belongs to a group of syndromes known as RASopathies.
How do you say Cardiofaciocutaneous?
0:261:07Pronunciation of the word(s) "Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome".YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipCardiofaciocutaneous syndrome cardio faciocutaneous syndrome cardiofaciocutaneous syndromeMoreCardiofaciocutaneous syndrome cardio faciocutaneous syndrome cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome cardio faciocutaneous syndrome cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome
What does charge syndrome stand for?
CHARGE is an abbreviation for several of the features common in the disorder: coloboma, heart defects, atresia choanae (also known as choanal atresia), growth retardation, genital abnormalities, and ear abnormalities.
What is Rasopathy?
Listen to pronunciation. (ras-AH-puh-thee SIN-drome) A group of rare conditions caused by mutations (changes) in certain genes that make proteins involved in the Ras/MAPK cell signaling pathway.
What are the characteristics of Williams syndrome?
Newborns with Williams syndrome have characteristic “elfin-like” facial features including an unusually small head (microcephaly), full cheeks, an abnormally broad forehead, puffiness around the eyes and lips, a depressed nasal bridge, broad nose, and/or an unusually wide and prominent open mouth.
What causes Cornelia de Lange syndrome?
What causes Cornelia de Lange syndrome? Cornelia de Lange syndrome is genetic condition that is caused by mutations in at least five genes (NIPBL, RAD21, SMC3, HDAC8, and SMC1A). The severity of the condition can vary greatly depending on the type of mutation and which gene is affected.
Is Legius syndrome hereditary?
Inheritance. This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern , which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder.
What causes Coffin Lowry Syndrome?
Causes. Coffin-Lowry syndrome is caused by changes (mutations) in the RPS6KA3 gene on the X chromosome. Some individuals with Coffin-Lowry syndrome do not have a detectable mutation in the RPS6KA3 gene. Coffin-Lowry syndrome is inherited in an X-linked dominant pattern.
What causes Cornelia de Lange syndrome?
What causes Cornelia de Lange syndrome? Cornelia de Lange syndrome is genetic condition that is caused by mutations in at least five genes (NIPBL, RAD21, SMC3, HDAC8, and SMC1A). The severity of the condition can vary greatly depending on the type of mutation and which gene is affected.
Who discovered Russell Silver syndrome?
Henry Silver discovered certain features of Russell-Silver syndrome in 1953. Dr. Alexander Russell discovered additional features of the condition in 1954. For almost 20 years, researchers thought Silver and Russell had found two separate conditions.
When will the ICD-10-CM Q87.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q87.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can Q87.1 be used for reimbursement?
Q87.1 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
Attention
Only comments seeking to improve the quality and accuracy of information on the Orphanet website are accepted. For all other comments, please send your remarks via contact us. Only comments written in English can be processed.
Epidemiology
Around 300 cases have been published in the literature to date. Prevalence has been estimated at 1/810,000 people in Japan. However prevalence is believed to be higher.
Clinical description
Cardiofaciocutaneous (CFC) syndrome displays wide phenotypic variability. Polyhydramnios is often reported. Neonates present at birth with relative macrocephaly, short webbed neck and distinctive dysmorphic craniofacial features (i.e.
Etiology
CFC syndrome is considered a RASopathy and is due to mutations in one of the 4 genes: BRAF (7q34) (in 75% of CFC cases), MAP2K1 (15q22.1-q22.33), MAP2K2 (19p13.3), and KRAS (12p12.1), which encode proteins of the sarcoma/mitogen-activated protein kinase (RAS/MAPK) signaling pathway.
Diagnostic methods
Clinical diagnosis is based mainly on the presence and frequency of the characteristic clinical traits and the sporadic occurrence of the disease. Molecular genetic testing, preferably multigene panel testing, including all known RASopathy genes, is preferable.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnoses include Costello Syndrome (CS) and Noonan Syndrome, which have overlapping phenotypes with CFC syndrome. CFC syndrome, unlike CS, does not appear to have an increased risk of malignancies.
Genetic counseling
All bona fide cases reported to date are due to de novo dominant mutations. Due to sporadic nature of the disease, the sibling recurrence risk is very small.
What are the different types of heart failure?
Types of Heart Failure. Type of heart failure. Description. Left-sided heart failure. Fluid may back up in your lungs, causing shortness of breath. Right-sided heart failure. Fluid may back up into your abdomen, legs and feet, causing swelling. Systolic heart failure.
What is the best treatment for congestive heart failure?
There are several medications that can be used to treat CHF. The first is ACE inhibitors. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) open up narrowed blood vessels to improve blood flow. Vasodilators are another option if you cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors.
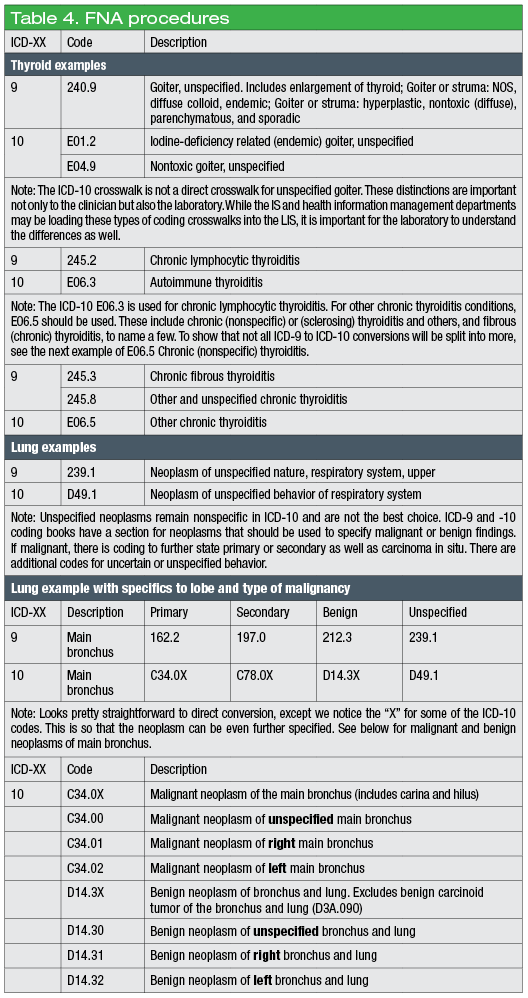
What is the best ICD-10 code?
When selecting the appropriate ICD-10, you should choose the code that accurately reflects the initial confirmed diagnosis. The best code is the actual disease. Without a confirmed diagnosis, the next best is a sign or symptom. After that, other is the best option. The least appropriate code is unspecified.
When to use unspecified code?
The least appropriate code is unspecified. Only use unspecified when there is not a more definitive code. Code the diagnosis you know. Do not code probable, suspected, or questionable diagnoses, do not you rule out conditions until they are confirmed. These principles are relevant when coding for uveitis cases.
What is the least appropriate code for uveitis?
The least appropriate code is unspecified. Only use unspecified when there is not a more definitive code. Reviewing the principles of ICD-10 and the classifications of uveitis will help ensure correct ...
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for multiple etiology
- 2. icd 10 code for post traumatic stress disorder, acute
- 3. icd 10 code for bursitis of right knee
- 4. _______ is the correct icd-10-cd code(s) for localized swelling of the neck.
- 5. icd 10 code for hernia incision right upper quadrant
- 6. icd 9 procedure code for fracturedislocation right femur
- 7. icd 10 code for right diabetic foot ulcer
- 8. icd code for screening mammogram
- 9. icd 9 code for blood clot of knee
- 10. icd 10 external cause code for car hit by another car that went off the road into a ditch