Which is more likely to cause caudal equina syndrome?
Which is more likely to cause caudal equina syndrome? The most common cause of cauda equina syndrome is A ruptured or herniated disk in the lower spine, especially in people who are born with a narrow spinal canal Other causes include the following: Birth defects of the spinal cord (such as spina bifida)
What happens if cauda equina syndrome is not treated?
What happens if cauda equina is not treated? If left untreated, cauda equina syndrome can lead to permanent paralysis in the muscle of one or both legs and permanent loss of bladder/bowel control. An important thing to note is that following surgery, bladder function may take longer to improve than muscle function.
Can cauda equina symptoms come and go?
This can make it feel as though the symptoms of cauda equina syndrome are coming and going. The symptoms of cauda equina can also come and go because of changes in the back. For instance, if any of your discs begin to bulge, it can press upon your already damaged nerves and symptoms can return.
Can cauda equina happen without disk herniation?
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a rare neurologic condition that is caused by compression of the cauda equina. Cauda equina consists of spinal nerves L2-L5, S1-S5 and the coccygeal nerve. The compression of these nerve roots can be caused mainly by lumbar disc herniation (45% of all causes).
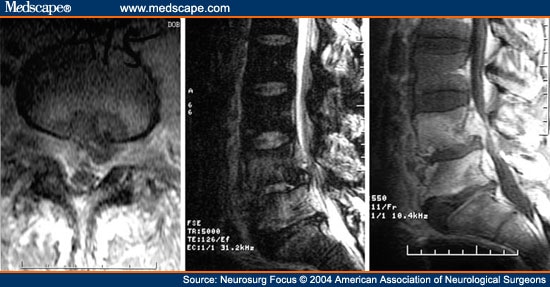
What is cauda equina?
The cauda equina is the continuation of these nerve roots in the lumbar and sacral region. These nerves send and receive messages to and from the lower limbs and pelvic organs. Cauda equina syndrome (CES) occurs when there is dysfunction of multiple lumbar and sacral nerve roots of the cauda equina.
What and where is the cauda equina?
The cauda equina is the sack of nerve roots (nerves that leave the spinal cord between spaces in the bones of the spine to connect to other parts of the body) at the lower end of the spinal cord. These nerve roots provide the ability to move and feel sensation in the legs and the bladder.
What is saddle anesthesia ICD-10?
R20. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R20.
Is cauda equina a neurological condition?
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a rare but serious neurological condition affecting the bundle of nerve roots at the lower end of the spinal cord.
What is conus and cauda equina?
The most distal bulbous part of the spinal cord is called the conus medullaris, and its tapering end continues as the filum terminale. Distal to this end of the spinal cord is a collection of nerve roots, which are horsetail-like in appearance and hence called the cauda equina (Latin for horse's tail).
What spinal nerves are part of the cauda equina?
The cauda equina (from Latin horse's tail) is a bundle of spinal nerves and spinal nerve rootlets, consisting of the second through fifth lumbar nerve pairs, the first through fifth sacral nerve pairs, and the coccygeal nerve, all of which arise from the lumbar enlargement and the conus medullaris of the spinal cord.
Is saddle anesthesia the same as cauda equina?
Saddle anaesthesia in particular is a red flag symptom of cauda equina syndrome. A patient may have symptoms such as lower back pain for a long period of time. But when saddle anaesthesia appears as well, alarm bells should start ringing as it indicates that the condition may have progressed to cauda equina syndrome.
How is cauda equina syndrome different?
Symptoms of cauda equina syndrome include the following:Low back pain.Unilateral or bilateral sciatica.Saddle and perineal hypoesthesia or anesthesia.Bowel and bladder disturbances.Lower extremity motor weakness and sensory deficits.Reduced or absent lower extremity reflexes.
Is cauda equina upper motor neuron?
A lower motor neuron (LMN) injury can result from a cauda equina injury or conus injury. In the lumbar region of the spine, there is a spray of spinal nerve roots called the cauda equina. Cauda equina in Latin means the horse's tail. The LMN lesion presents with flaccid or no tone and minimal or nil reflexes (floppy).
What is the most common cause of cauda equina syndrome?
Causes of Cauda Equina Syndrome A severe ruptured disk in the lumbar area (the most common cause) Narrowing of the spinal canal (stenosis) A spinal lesion or malignant tumor. A spinal infection, inflammation, hemorrhage, or fracture.
Is cauda equina syndrome a spinal cord injury?
Sometimes a cauda equina injury is said to not be a “true” spinal cord injury because they affect the peripheral nerves very close to, but not part of, the spinal cord.
Is cauda equina a radiculopathy?
Cauda equina syndrome bilateral lower limb radicular pain. perianal sensory loss. insensate urinary retention and subsequent incontinence. Often the first symptom is the radiculopathy, followed later by the addition of perianal sensory loss and then finally the triad completed by episodes of incontinence.
The ICD code G834 is used to code Cauda equina syndrome
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a serious neurologic condition in which damage to the cauda equina causes loss of function of the lumbar plexus, (nerve roots) of the spinal canal below the termination (conus medullaris) of the spinal cord. CES is a lower motor neuron lesion.
Coding Notes for G83.4 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'G83.4 - Cauda equina syndrome'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code G83.4. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Codes GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code G83.4 and a single ICD9 code, 344.61 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for history of superficial femoral artery occlusion
- 2. icd 10 code for flat foot bilateral
- 3. icd 10 code for basilar rhonchi
- 4. icd 10 cm code for polycythemia
- 5. icd 10 code for right shoulder subcutaneous fluid collection
- 6. icd 10 code for low white blood cell count unspecified
- 7. icd-10 code for dexa scan postmenopausal
- 8. icd 10 code external cause for auto
- 9. icd-9 code for pms
- 10. icd 10 cm code for hit by baseball