What is the ICD 10 code for cellulitis?
Cellulitis, unspecified. L03.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for colostomy?
Colostomy infection 1 K94.02 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM K94.02 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K94.02 - other international versions of ICD-10 K94.02 may differ. More ...
What is the ICD 10 code for cellulitis of the left leg?
Cellulitis of left lower limb 1 L03.116 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM L03.116 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L03.116 - other international versions of ICD-10 L03.116 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for incontinent external stoma?
Infection of incontinent external stoma of urinary tract. N99.521 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM N99.521 became effective on October 1, 2019.
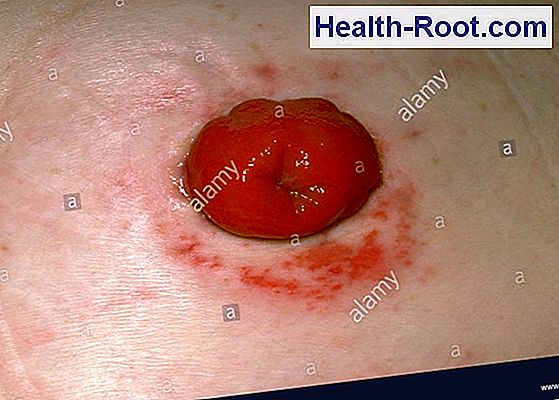
What is the ICD-10 code for abdominal Cellulitis?
311.
What is abdominal wall Cellulitis?
Abdominal cellulitis is a rare sign of acute appendicitis that presents as aggressive intra-abdominal inflammation (1). The chief complaint of patients with appendicitis is abdominal pain.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for colostomy?
Z93.3ICD-10 code Z93. 3 for Colostomy status is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What causes cellulitis of abdominal wall?
Cellulitis is caused when bacteria, most commonly streptococcus and staphylococcus, enter through a crack or break in the skin. The incidence of a more serious staphylococcus infection called methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is increasing.
How do you treat cellulitis in the stomach?
Cellulitis treatment usually includes a prescription oral antibiotic. Within three days of starting an antibiotic, let your health care provider know whether the infection is responding to treatment. You'll need to take the antibiotic for the full course, usually 5 to 10 days, even if you start to feel better.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code R06 2?
ICD-10 code R06. 2 for Wheezing is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What is the ICD-10 code for sepsis?
Septicemia – There is NO code for septicemia in ICD-10. Instead, you're directed to a combination 'A' code for sepsis to indicate the underlying infection, such A41. 9 (Sepsis, unspecified organism) for septicemia with no further detail.
What is ICD-10 code for colostomy closure?
Z93. 3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z93.
What is the CPT code for colostomy?
44146You should report CPT code 44146 (see Table 1). Although the CPT descriptor includes the term “colostomy,” the Medicare physician fee schedule work relative value unit (RVU) for this code is based on creation of either a colostomy or an ileostomy.
What is the ICD-10 code for high ostomy output?
K91.49K91. 49 Malfunction of stoma of the digestive system (which includes high output ileostomy in the tabular) is the new code in tenth edition.
Can you get cellulitis in your abdomen?
Cellulitis is a deep infection of the skin caused by bacteria. It often affects the arms and legs. It can also develop around the eyes, mouth, and anus, or on the belly (abdomen). Normal skin can be affected by cellulitis.
What is abdominal wall?
The abdominal wall is defined cranially by the xiphoid process of the sternum and the costal margins and caudally by the iliac and pubic bones of the pelvis. It extends to the lumbar spine, which joins the thorax and pelvis and is a point of attachment for some abdominal wall structures [1].
How long does it take cellulitis to heal?
With treatment, a small patch of cellulitis in a healthy person can resolve in 5 days or so. The more severe the cellulitis and the more medical problems the person has, the longer it can take to resolve. Very severe cellulitis may last 2 weeks or more, even with treatment in the hospital.
What are the symptoms of cellulitis gets into the bloodstream?
Complications of severe cellulitis include the spread of the infection from the affected area into the bloodstream or to other body tissues....Things to know about cellulitisredness,pain and tenderness,swelling,enlarged lymph nodes, and.the warmth of the affected area.
When will the ICD-10-CM L03.90 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L03.90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is cellulitis a serious disease?
cellulitis can be serious, and possibly even deadly, so prompt treatment is important. The goal of treatment is to control infection and prevent related problems. Treatment usually includes antibiotics. Inflammation that may involve the skin and or subcutaneous tissues, and or muscle.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for subdural hematome
- 2. icd 9 code for nonconvulsive status epilepticus
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for left upper chest hematoma
- 4. 2017 icd 10 code for ventriculomegaly
- 5. icd 10 code for acute superficial venous thrombosis left saphenous
- 6. icd-10 code for left total hip replacement
- 7. icd 10 code for acquired iodine deficient hypothyroidism
- 8. icd-9-cm code for gray syndrome from chloramphenicol administration in newborn
- 9. icd 10 code for sigmoid wall thickening and luminal constriction
- 10. icd 10 code for abnormal periods