What is the CPT code for cholesteatoma of middle ear?
To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the five child codes of H71 that describes the diagnosis 'cholesteatoma of middle ear' in more detail. Cholesteatoma is a destructive and expanding growth consisting of keratinizing squamous epithelium in the middle ear and/or mastoid process.
What is the ICD 10 code for cholesteatoma?
The ICD code H71 is used to code Cholesteatoma. Cholesteatoma is a destructive and expanding growth consisting of keratinizing squamous epithelium in the middle ear and/or mastoid process.
What causes cholesteatoma in the ear?
Acquired cholesteatoma is the most common. It is caused by accumulation of keratin in a pouch of tympanic membrane extending into the middle ear space. Cholesteatoma may also result from trauma, or metaplasia of the middle ear mucosa (metaplasia is the replacement of one differentiated cell type with another mature differentiated cell).
What is the pathophysiology of cholesteatoma?
Cholesteatoma is a destructive and expanding growth consisting of keratinizing squamous epithelium in the middle ear and/or mastoid process.
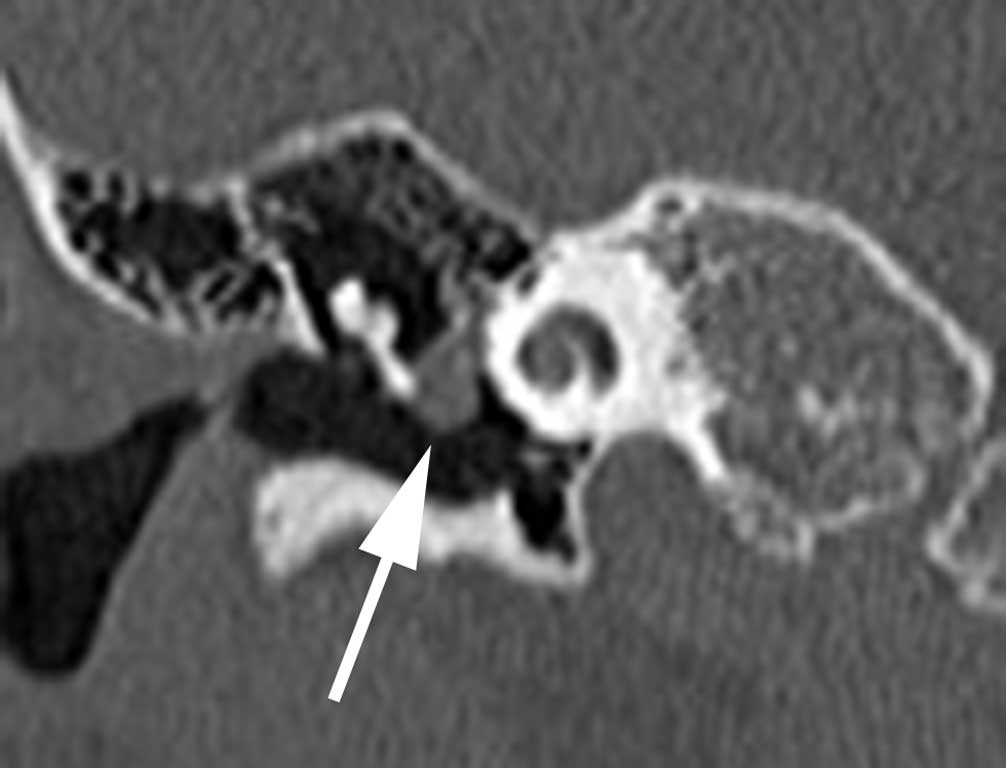
What is the ICD-10-CM code for cholesteatoma middle ear and attic?
Cholesteatoma of attic, bilateral H71. 03 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H71. 03 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is cholesteatoma?
A cholesteatoma is an abnormal collection of skin cells deep inside your ear. They're rare but, if left untreated, they can damage the delicate structures inside your ear that are essential for hearing and balance. A cholesteatoma can also lead to: an ear infection – causing discharge from the ear.
What is the ICD-10 code for middle ear infection?
ICD-10-CM Code for Otitis media, unspecified H66. 9.
How is cholesteatoma formed?
Cholesteatoma can be a birth defect (congenital). It more commonly occurs as a result of chronic ear infection. The eustachian tube helps equalize pressure in the middle ear. When it is not working well, negative pressure can build up and pull part of the eardrum (tympanic membrane) inward.
What is cholesteatoma of external ear?
A cholesteatoma is a non-neoplastic lesion of the petrous temporal bone commonly described as “skin in the wrong place.” It typically arises within the middle ear cavity, may drain externally via tympanic membrane (mural type), or may originate in the external auditory canal (EAC).
What is cholesteatoma and mastoiditis?
Cholesteatoma, a keratinized mass in the middle ear or mastoid, may occur either as a primary lesion or secondary to tympanic membrane perforation. Mastoiditis may occur as a complication of acute otitis media (AOM) or COM.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for otitis media left ear?
ICD-10 Code for Otitis media, unspecified, left ear- H66. 92- Codify by AAPC.
What is acute serous otitis media?
Acute Serous Otitis Media Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common ear infection, causing pain and swelling in the ear. A doctor can diagnose AOM simply by looking into your child's ears with an otoscope.
What is one of the most common symptoms of a cholesteatoma?
SymptomsConstant sound inside your ear (tinnitus)Dizziness (or vertigo)Ear infection.Earache.Feeling of "fullness" in one ear.Fluid that smells bad and leaks from your ears.Trouble hearing in one ear.Weakness in half your face.
What is cholesteatoma surgery called?
Combined approach tympanoplasty (CAT) or canal wall up (CWU) mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure performed for the removal of a cholesteatoma in which the wall of the ear canal is left intact. Cholesteatoma is an abnormal growth of skin in the middle ear behind the eardrum.
What type of hearing loss is cholesteatoma?
Typically, cholesteatomata patients suffer from conductive hearing loss, i.e., a hearing disorder that only affects the outer ear. If the cholesteatoma is so far advanced that the inner ear is already affected, a so-called sensorineural hearing loss is present.
What is the disease of the ear and mastoid process?
Clinical Information. A mass of keratin-producing squamous epithelium that resembles an inverted (suck-in) bag of skin in the middle ear. It arises from the eardrum (tympanic membrane) and grows into the middle ear causing erosion of ear ossicles and mastoid that contains the inner ear. Code History.
Is H71 a reimbursement code?
Cholesteatoma of middle ear. H71 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H71 became effective on October 1, 2020.
Why does cholesteatoma occur?
Typically, a cholesteatoma occurs because of Eustachian tube dysfunction, as well as infection in the middle ear, and can lead to deafness. There are two types of cholesteatoma: Acquired cholesteatoma is the most common.
What causes a keratin pouch in the middle ear?
It is caused by accumulation of keratin in a pouch of tympanic membrane extending into the middle ear space. Cholesteatoma may also result from trauma, or metaplasia of the middle ear mucosa (metaplasia is the replacement of one differentiated cell type with another mature differentiated cell).
What is the ICD code for middle ear?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code H71 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the five child codes of H71 that describes the diagnosis 'cholesteatoma of middle ear' in more detail.
Is cholesteatoma a tumor?
Although cholesteatomas are not classified as either tumors or cancers, they can still cause significant problems because of their erosive and expansile properties resulting in the destruction of the bones of the middle ear (ossicles), as well as their possible spread through the base of the skull into the brain.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for unspecified person
- 2. icd ten code for hypothyroidism
- 3. icd 10 code for subcapsular hematoma
- 4. what is the icd-10-cm code for past history of anxiety?
- 5. icd-10 code for flouextine
- 6. icd 9 code for thalassemia
- 7. icd 10 code for recheck wound
- 8. icd 10 code for t5 fracture
- 9. icd 10 cm code for joint injection
- 10. icd 10cm code for diabestes type l out of control