Dependence on renal dialysis. Z99.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM Z99.2 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What are the common ICD 10 codes?
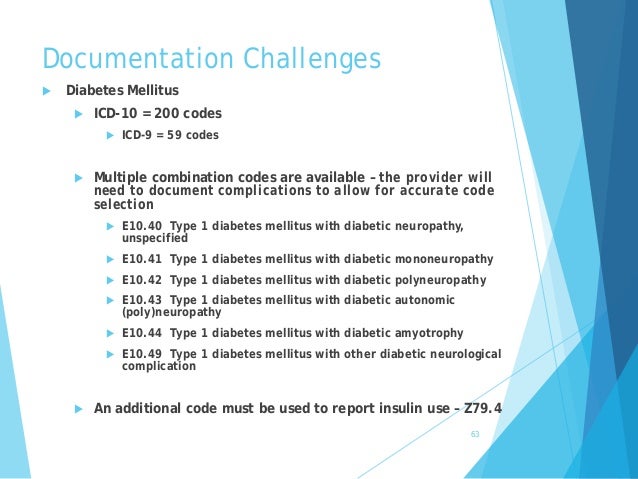
ICD-10-CM CATEGORY CODE RANGE SPECIFIC CONDITION ICD-10 CODE Diseases of the Circulatory System I00 –I99 Essential hypertension I10 Unspecified atrial fibrillation I48.91 Diseases of the Respiratory System J00 –J99 Acute pharyngitis, NOS J02.9 Acute upper respiratory infection J06._ Acute bronchitis, *,unspecified J20.9 Vasomotor rhinitis J30.0
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Search the full ICD-10 catalog by:
- Code
- Code Descriptions
- Clinical Terms or Synonyms
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The new codes are for describing the infusion of tixagevimab and cilgavimab monoclonal antibody (code XW023X7), and the infusion of other new technology monoclonal antibody (code XW023Y7).
How to code a patient on dialysis?
• This situation should be coded using the ESRD-related services G codes for a home dialysis patient per full month. • Physicians and practitioners should use G0320 through G0323 when billing for outpatient ESRD-
What is the ICD-10 code for CKD on dialysis?
Z99. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z99. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is chronic dialysis?
Chronic (long-term) hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are used to treat children with chronic kidney failure. Acute hemodialysis is also used to treat children who have ingested certain toxins (poisons) that must be removed from the body quickly.
What is the ICD-10 code for dependent on dialysis?
ICD-10 code: Z99. 2 Dependence on renal dialysis | gesund.bund.de.
What is the ICD-10 PCS code for dialysis treatment?
Hemodialysis, single encounter, is classified to ICD-10-PCS code 5A1D00Z, which is located in the Extracorporeal Assistance and Performance section. Multiple encounters of hemodialysis is classified to code 5A1D60Z. Peritoneal dialysis is classified to code 3E1M39Z, which is located in the Administration section.
What are the 3 types of dialysis?
There are 3 main types of dialysis: in-center hemodialysis, home hemodialysis, and peritoneal dialysis. Each type has pros and cons. It's important to remember that even once you choose a type of dialysis, you always have the option to change, so you don't have to feel "locked in" to any one type of dialysis.
What stage is chronic kidney disease dialysis?
It is important to start getting ready for dialysis or a transplant well in advance — when your kidney disease reaches Stage 4 (severe, with glomerular filtration rate, or GFR, less than 30 mL/min).
How do you code dialysis?
CPT code 90935 is used to report inpatient dialysis and includes one E/M evaluation provided to that patient on the day of dialysis. Inpatient dialysis requiring repeated evaluations on the same day is reported with code 90937.
What is the ICD-9 code for dialysis?
39.95 Hemodialysis - ICD-9-CM Vol.
Can you code ESRD without dialysis?
A patient with the diagnosis of ESRD requires chronic dialysis. Per the Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting, Section I.C. 14a.
What is being on dialysis?
Dialysis is a treatment for people whose kidneys are failing. When you have kidney failure, your kidneys don't filter blood the way they should. As a result, wastes and toxins build up in your bloodstream. Dialysis does the work of your kidneys, removing waste products and excess fluid from the blood.
What is procedure code 36800?
CPT® Code 36800 - Hemodialysis Access, Intervascular Cannulation for Extracorporeal Circulation, or Shunt Insertion Procedures on Arteries and Veins - Codify by AAPC.
When is hemodialysis used?
When is dialysis needed? You need dialysis if your kidneys no longer remove enough wastes and fluid from your blood to keep you healthy. This usually happens when you have only 10 to 15 percent of your kidney function left. You may have symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, swelling and fatigue.
What causes renal failure?
Gradual and usually permanent loss of kidney function resulting in renal failure. Causes include diabetes, hypertension, and glomerulonephritis. Impairment of health or a condition of abnormal functioning of the kidney. Impairment of the renal function due to chronic kidney damage.
Why is my kidney unable to remove waste?
This damage may leave kidneys unable to remove wastes. Causes can include genetic problems, injuries, or medicines. You are at greater risk for kidney disease if you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or a close family member with kidney disease. chronic kidney disease damages the nephrons slowly over several years.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for congenital coronary artery anomaly
- 2. icd 9 code for pulmonary embolism and infarction
- 3. 2019 icd 10 code for vertigo
- 4. icd code for aki
- 5. icd 10 code for hardware infection elbow
- 6. icd 10 code for acute hepatitis panel screening
- 7. icd 10 code for kidney donor
- 8. icd 9 code for wellness
- 9. icd 9 code for osteomalacia
- 10. icd code for lbp