What is the difference between hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. Some people with hepatitis B are sick for only a few weeks (known as “acute” infection), but for others, the disease progresses to a serious, lifelong illness known as chronic hepatitis B.
What is ICD 10 code B18?
Chronic viral hepatitis B18-
What is the ICD 10 code for screening for hepatitis B?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z11. 59: Encounter for screening for other viral diseases.
What is chronic hepatitis unspecified?
Chronic hepatitis is inflammation of the liver that lasts at least 6 months. Common causes include hepatitis B and C viruses and certain drugs. Most people have no symptoms, but some have vague symptoms, such as a general feeling of illness, poor appetite, and fatigue.
Why is hepatitis B chronic?
Most people who get hepatitis B as adults have an acute infection, but it can lead to chronic infection. Chronic hepatitis B infection lasts six months or longer. It lingers because your immune system can't fight off the infection.
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic liver disease?
ICD-10-CM Code for Liver disease, unspecified K76. 9.
What ICD 10 code covers hepatitis panel?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B18 B18.
How do you code hepatitis B?
The ICD-10-CM diagnosis code required for billing is: Z23 - Encounter for immunization.Providers must bill with HCPCS code: 90759 - Hepatitis B vaccine (HepB), 3-antigen (S, Pre-S1, Pre-S2), 10 mcg dosage, 3 dose schedule, for intramuscular use.One Medicaid and NC Health Choice unit of coverage is: 10 mcg.More items...•
What is hepatitis B screening?
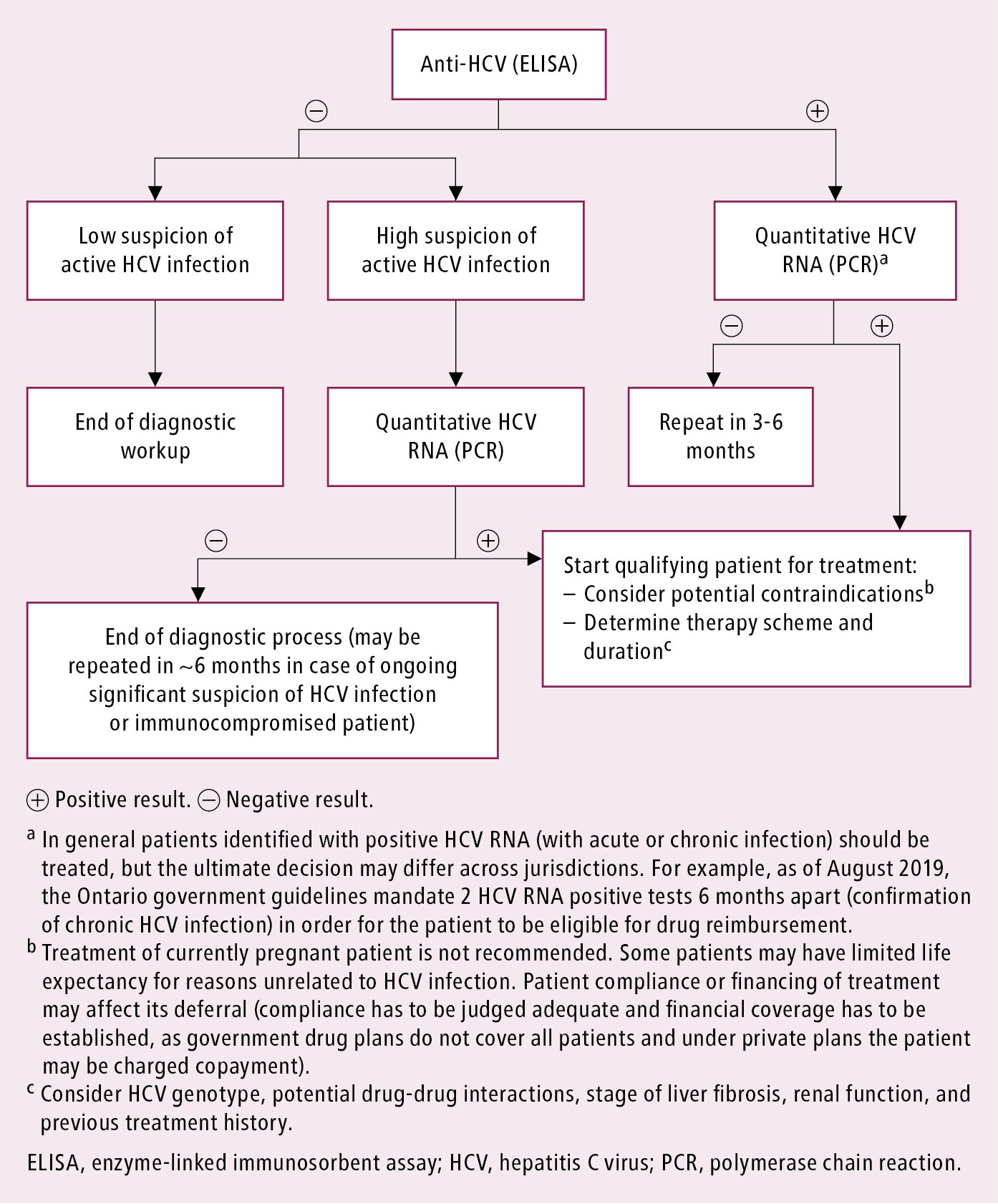
Screening for hepatitis B involves blood tests that measure HBV antigens and antibodies. The test for hepatitis B surface antigen detects the presence of HBV. A positive result means the person is currently infected and can pass the infection to others.
What are types of chronic hepatitis?
Chronic hepatitis is hepatitis that lasts > 6 months. Common causes include hepatitis B and C viruses, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), alcohol-related liver disease, and autoimmune liver disease (autoimmune hepatitis).
How is chronic hepatitis B diagnosed?
Blood tests can detect signs of the hepatitis B virus in your body and tell your doctor whether it's acute or chronic. A simple blood test can also determine if you're immune to the condition. Liver ultrasound. A special ultrasound called transient elastography can show the amount of liver damage.
How do I know if I have chronic hepatitis B?
If you test positive for the hepatitis B virus for more than six months, your infection is considered to be chronic. This means that your immune system is not able to get rid of the hepatitis B virus and it still remains in your blood and liver.
What is Delta agent in hepatitis B?
The delta agent seems to be a defective RNA virus which is dependent on a helper function provided by hepatitis B-virus. Delta agent infection occurs by parenteral transmission either together with hepatitis B-virus, or superimposed on chronic HBV infection.
What is the code for chronic viral hepatitis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Chronic viral hepatitis C B18. 2.
What is the ICD-10 code for portal hypertension?
ICD-10 code K76. 6 for Portal hypertension is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the ICD-10 code for liver fibrosis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Hepatic fibrosis K74. 0.
What is chronic hepatitis?
Chronic hepatitis. Clinical Information. An active inflammatory process affecting the liver for more than six months. Causes include viral infections, autoimmune disorders, drugs, and metabolic disorders. Inflammation of the liver with ongoing hepatocellular injury for 6 months or more, characterized by necrosis of hepatocytes ...
What causes hepatitis in the liver?
Chronic hepatitis can be caused by viruses, medications, autoimmune diseases, and other unknown factors.
What is K71?
drug-induced hepatitis (chronic) ( K71.-) An active inflammatory process affecting the liver for more than six months. Causes include viral infections, autoimmune disorders, drugs, and metabolic disorders. Inflammation of the liver with ongoing hepatocellular injury for 6 months or more, characterized by necrosis of hepatocytes ...
What is the code for hepatitis?
code to identify resistance to antimicrobial drugs ( Z16.-) Chronic hepatitis caused by viruses, most commonly hepatitis viruses b and c. 441 Disorders of liver except malignancy, cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis with mcc. 442 Disorders of liver except malignancy, cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis with cc.
What are the 441 disorders of the liver?
441 Disorders of liver except malignancy, cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis with mcc. 442 Disorders of liver except malignancy, cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis with cc. 443 Disorders of liver except malignancy, cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis without cc/mcc. 791 Prematurity with major problems.
What are the causes of hepatitis?
The most common causes of viral hepatitis are the five unrelated hepatotropic viruses Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C , Hepatitis D , and Hepatitis E. In addition to the nominal hepatitis viruses, other viruses that can also cause liver inflammation include Herpes simplex, Cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, and Yellow fever.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code B19.10 and a single ICD9 code, 070.30 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for ltbi
- 2. icd 10 code for cronic migraine
- 3. icd 10 code for exposed scleral buckle
- 4. what is the icd 10 cm code for acute bronchitis with bronchospasm
- 5. icd 10 code for contusion of left shoulder initial encounter
- 6. icd 10 code for right toe osteomyelitis
- 7. icd 10 code for lamisil therapy
- 8. icd 10 code for wart right hand
- 9. icd 10 code for bilateral pressure ulcer of feet unstageable
- 10. what is the icd 10 code for intraosse cyst