What is the ICD 10 code for congenital malformations of diaphragm?
Other congenital malformations of diaphragm. Q79.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM Q79.1 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for diaphragm injury?
ICD Code S27.80 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the four child codes of S27.80 that describes the diagnosis 'injury of diaphragm' in more detail.
What is the new ICD 10 for diaphragmatic hernia?
Diaphragmatic hernia. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM K44 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K44 - other international versions of ICD-10 K44 may differ.
What is the latest ICD 10 version for lung disorders?
Other disorders of lung. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM J98.4 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J98.4 - other international versions of ICD-10 J98.4 may differ.
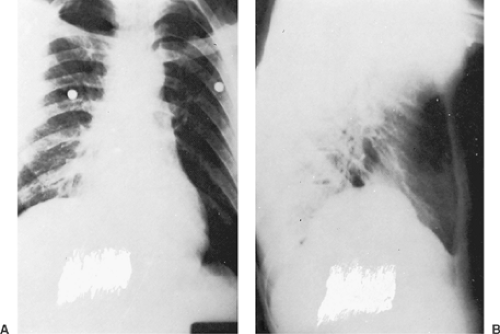
What is diaphragmatic Eventration?
Diaphragmatic eventration (DE) is the abnormal elevation of a portion or entire hemidiaphragm due to a lack of muscle or nerve function while maintaining its anatomical attachments. The abnormality can be congenital or acquired, thus presenting in both the pediatric and adult populations.
What is DX code J98 4?
ICD-10 code J98. 4 for Other disorders of lung is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is elevated diaphragm?
[1] Elevated hemidiaphragm occurs when one side of the diaphragm becomes weak from muscular disease or loss of innervation due to phrenic nerve injury. Patients may present with difficulty breathing, but more commonly elevated hemidiaphragm is found on imaging as an incidental finding, and patients are asymptomatic.
What is paralyzed diaphragm?
Patients with a paralyzed diaphragm experience weakness of the diaphragm and have reduced breathing capabilities or are unable to control their voluntary breathing. They also have difficulty maintaining adequate gas exchange, as the lungs are not able to inhale and exhale outside air as efficiently.
What is diagnosis code R91 8?
Other nonspecific abnormal finding of lung fieldICD-10 code R91. 8 for Other nonspecific abnormal finding of lung field is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
ICD-10 Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris- I25. 10- Codify by AAPC.
What is the left Hemidiaphragm?
Hemidiaphragm: Half of the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdomen and that serves as the main muscle of respiration. Both hemidiaphragms are visible on X-ray studies from the front or back. The right hemidiaphragm is protected by the liver and is stronger than the left.
Where is diaphragm located?
The diaphragm, located below the lungs, is the major muscle of respiration. It is a large, dome-shaped muscle that contracts rhythmically and continually, and most of the time, involuntarily. Upon inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens and the chest cavity enlarges.
What causes diaphragm elevation?
Temporary elevation of the diaphragm occurs in pneumonia, lung abscess, subphrenic abscess, liver abscess, diabetes, Banti's disease, during digestion, and normally at full expiration.
What is diaphragm dysfunction?
The diaphragm is the main respiratory muscle. Its dysfunction can be associated with the presence of respiratory symptoms, exercise intolerance, sleep disturbances and, in the more severe cases, have a negative impact on survival.
What happens if the diaphragm is damaged?
Symptoms of significant, usually bilateral diaphragm weakness or paralysis are shortness of breath when lying flat, with walking or with immersion in water up to the lower chest. Bilateral diaphragm paralysis can produce sleep-disordered breathing with reductions in blood oxygen levels.
How is diaphragm paralysis diagnosis?
Diagnosis of Diaphragmatic Paralysis Pulmonary function testing while lying down and again while upright. Sniff Test: With fluoroscopy, the radiologist watches he diaphragm as the patient sniffs. A normal lung moves down and the lung expands. A paralyzed lung moves up to compress the lung.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. code to identify any retained foreign body, if applicable ( Z18.-)
When will the ICD-10-CM S27.80 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S27.80 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the cause of the elevation of the diaphragm?
A congenital abnormality characterized by the elevation of the diaphragm dome. It is the result of a thinned diaphragmatic muscle and injured phrenic nerve, allowing the intra-abdominal viscera to push the diaphragm upward against the lung.
When will the ICD-10-CM Q79.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q79.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
The ICD code S278 is used to code Diaphragmatic rupture
Diaphragmatic rupture (also called diaphragmatic injury or tear) is a tear of the diaphragm, the muscle across the bottom of the ribcage that plays a crucial role in respiration. Most commonly, acquired diaphragmatic tears result from physical trauma.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'S27.80 - Injury of diaphragm'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code S27.80. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for etoh use dis sever
- 2. icd 10 code for neoplastic pleural effusion
- 3. icd 10 code for chest ain
- 4. icd 10 code for radial scar of breast
- 5. icd 10 code for carotid stenosis unspecified
- 6. icd 10 code for atherosclerosis vascular disease
- 7. icd 10 code for polypoidal choiroidal vasculopathy
- 8. icd 10 code for lump left breast
- 9. icd 10 code for rle wound
- 10. icd 10 code for left upper extremity dvt