What is CIN 3 stage 0 cervical cancer?
cervical intraepithelial glandular neoplasia cervical intraepithelial neoplasia III [CIN III] Stage 0 includes: (tis, n0, m0). Tis: carcinoma in situ. N0: no regional lymph node metastasis.
What is the ICD 10 code for cervical neoplasia II?
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia II [CIN II] ( N87.1) cytologic evidence of malignancy of cervix without histologic confirmation ( R87.614) high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HGSIL) of cervix ( R87.613) melanoma in situ of cervix ( D03.5) moderate cervical dysplasia ( N87.1) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R87.61.
What is the ICD 10 code for dysplasia of cervix?
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2; Dysplasia of cervix, high grade cin 2; Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia II [CIN II] ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z87.410 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Personal history of cervical dysplasia
What is dysplasia of cervix high grade CIN 2?
Dysplasia of cervix, high grade cin 2; Clinical Information. A condition in which moderately abnormal cells grow on the thin layer of tissue that covers the cervix. These abnormal cells are not malignant (cancer) but may become cancer. ICD-10-CM N87.1 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 38.0):
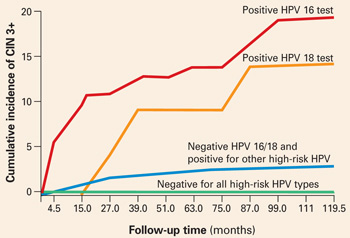
What is CIN III?
Listen to pronunciation. Severely abnormal cells are found on the surface of the cervix. CIN 3 is usually caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) and is found when a cervical biopsy is done. CIN 3 is not cancer, but may become cancer and spread to nearby normal tissue if not treated.
Is CIN the same as cervical cancer?
Cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia (CIN) is a term that describes abnormal changes of the cells that line the cervix. CIN is not cancer. But if the abnormal cells are not treated, over time they may develop into cancer of the cervix (cervical cancer). CIN does not cause any symptoms.
Is cervical dysplasia the same as CIN?
Cervical dysplasia is a precancerous condition in which abnormal cells grow on the surface of your cervix. The cervix is the opening to your uterus that's attached to the top portion of your vagina. Another name for cervical dysplasia is cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, or CIN.
Is CIN 3 a Hsil?
HSIL (CIN3) involves the presence of dysplastic cells in greater than two thirds of the entire thickness of the epithelium but with no signs of invasion into the stroma. Almost all HSIL (CIN3) lesions can be attributed to persistent infection by high risk HPV types.
What is the difference between CIN 2 and CIN 3?
CIN2 – indicates moderate changes; affecting two-thirds of the thickness of the surface layer of the cervix. CIN3 – indicates more severe changes (not cancer); affecting the full thickness of the surface layer of the cervix. Even with CIN2 or CIN3 grade changes, the cell changes are unlikely to be cancer.
What percentage of CIN 3 is cancer?
However, it is estimated that 5% of CIN 2 and 12% of CIN 3 cases will progress to invasive cancer if untreated. In general, it takes 10 to 20 years for CIN to progress to cancer, allowing a significant time period for detection and treatment. Progression from CIN to cancer requires persistent HPV infection.
What is the ICD 10 code for CIN 2?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N87. 1: Moderate cervical dysplasia.
Can you have CIN3 without HPV?
Nearly all CIN3 lesions are associated with hrHPV types, with a very small proportion associated only with low risk HPV types [24].
Is CIN and HPV the same?
We know that CIN is caused by the wart virus, the Human Papilloma Virus. The high risk Human Papilloma Virus. Now this is not the same virus that causes genital warts. It's a slightly different virus; it's of the same family.
Is CIN3 CIS?
Historically, precancerous changes of the cervix have been histologically defined as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), identified at varying levels of severity: CIN1, CIN2, and CIN3. The latter includes carcinoma in situ (CIS), a preinvasive carcinomatous change of the cervix.
What is the difference between CIN and HSIL?
LAST: lower anogenital squamous terminology; LSIL: low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions; HSIL: high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions; CIN: cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. * CIN 2 that is p16-positive is classified as HSIL. CIN 2 that is p16-negative is classified as LSIL.
What is the treatment for CIN3?
The typical treatment procedure for CIN2 or CIN3 involves removing a cone-shaped piece of the cervix, called a LEEP or a cone. This results in scarring and a shortened cervix, which can cause problems during childbirth and lead to increased risk of caesarean section.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for wound drainage
- 2. icd-10 code for alcoholic gastritis with bleeding
- 3. icd 10 code for pain of left ankle
- 4. icd 10 code for acute on chronic blood loss anemia
- 5. icd 10 code for fitting and adjustment of breast prosthesis
- 6. icd-10 code for back strain
- 7. icd 10 code for gastric pacemaker status
- 8. icd-10 code for fall risk assessment
- 9. 2017 icd 10 code for granulomatous disease present within the left hilus.
- 10. icd 10 code for synthetic cannabis