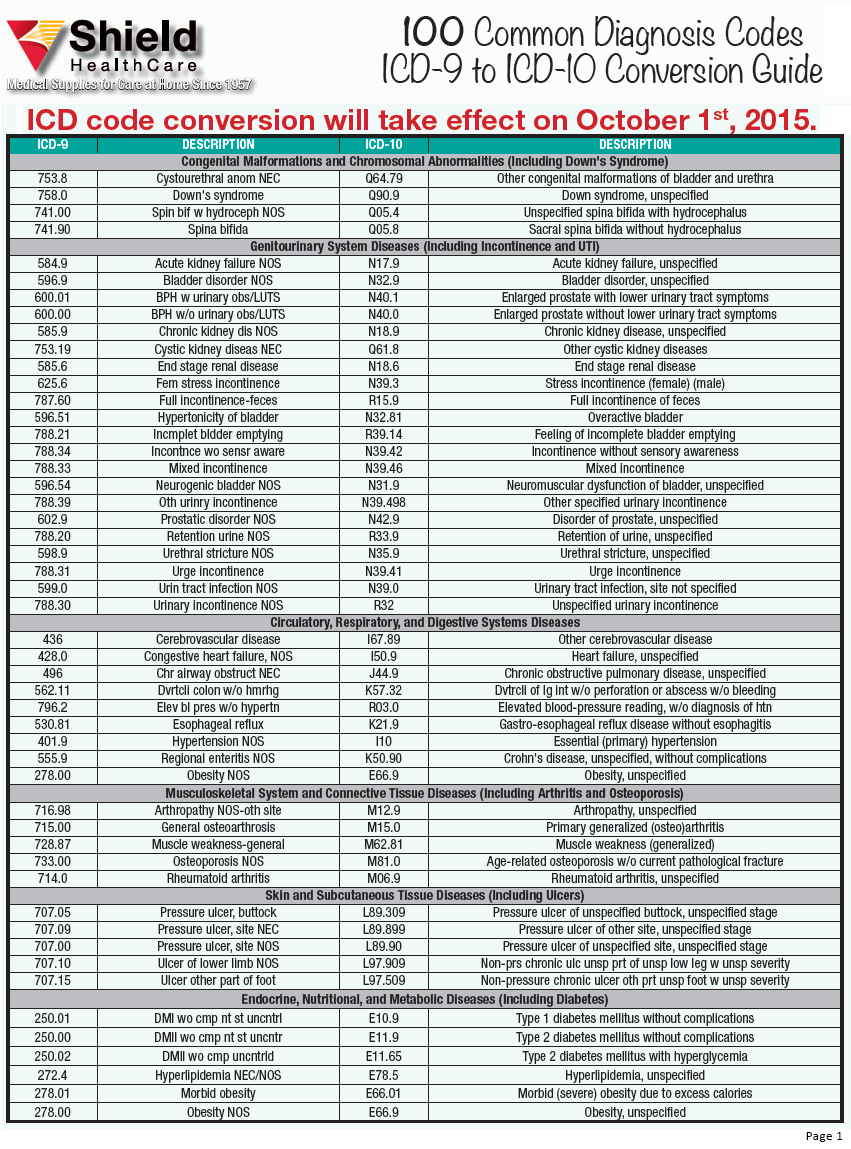
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic kidney disease?
Oct 01, 2021 · R74.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R74.8 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R74.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 R74.8 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic total occlusion?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R97.0 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Elevated carcinoembryonic antigen [CEA] Elevated cea; High carcinoembryonic antigen level. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R97.0. Elevated carcinoembryonic antigen [CEA] 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R74.0.
What is the significance of total CK in acute myositis?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R97.0 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Elevated carcinoembryonic antigen [CEA] Elevated cea; High carcinoembryonic antigen level. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R97.0. Elevated carcinoembryonic antigen [CEA] 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code.
What is the ICD 10 code for signs and symptoms?
Oct 01, 2021 · Chronic total occlusion of coronary artery. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. I25.82 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I25.82 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What ICD 10 code covers creatine kinase?
| ICD-10: | R74.8 |
|---|---|
| Short Description: | Abnormal levels of other serum enzymes |
| Long Description: | Abnormal levels of other serum enzymes |
What does diagnosis code R79 89 mean?
What is diagnosis code Z13 220?
What is the ICD 10 code for elevated creatinine?
What is the ICD-10 code for fatty liver disease?
What ICD-10 code covers PT PTT?
What is R53 83?
What diagnosis will cover 80061?
What is the ICD-10 code for annual physical exam?
What ICD-10 codes cover BMP?
Z13. 228 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z13. 228 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is elevated creatinine?
What should your creatinine level be?
Expected Turnaround Time
Turnaround time is defined as the usual number of days from the date of pickup of a specimen for testing to when the result is released to the ordering provider. In some cases, additional time should be allowed for additional confirmatory or additional reflex tests. Testing schedules may vary.
Container
Red-top tube, gel-barrier tube, or green-top (lithium heparin) tube. Do not use oxalate, EDTA, or citrate plasma.
Collection
Separate serum or plasma from cells. Avoid prolonged contact of serum or plasma with red cells.
Patient Preparation
Avoid exercise before venipuncture. Increases may be anticipated in the immediate postoperative period following surgical procedures involving incision through muscle.
Use
Test for acute myocardial infarct and for skeletal muscular damage; elevated in some patients with myxedema (hypothyroidism), malignant hyperthermia syndrome, and muscular dystrophy. CK is a marker for Duchenne muscular dystrophy, with elevations of 20 to 200 times normal.
Limitations
Intramuscular injections increase serum CK activity. Elevated following exercise. Normal at onset of acute MI unless the subject has been exercising or doing physical work. Elevation of CK following acute MI may not be observed until six or more hours after onset. CK returns to normal in approximately 48 to 72 hours after acute MI.
Additional Information
High CK is found after trauma, surgery, and exercise; these entities may not be accompanied by elevation of CK-MB. To distinguish myoglobinuria from hemoglobinuria, serum CK and LD may be helpful. CK is normal with uncomplicated hemolysis but LD and LD 1 usually are increased.
Is CK-MB elevated in exercise?
Additional Information. CK-MB is usually not eleva ted in exercise (total CK elevated); myxedema (total CK elevated in about half of cases); injections into muscle (total CK elevated); strokes, CVA, and other brain disorders in which total CK may be increased; pericarditis; pneumonias or other lung diseases; pulmonary embolus;
How long does it take for CK-MB to peak?
Another at 48 hours may be needed. CK-MB usually peaks between 15 and 20 hours after the onset of a myocardial infarction.
What is MB in a heart?
MB is the myocardial fraction associated with MI and occurs in certain other states. MB can be used in estimation of infarct size. MB increases have been reported with entities which cause damage to the myocardium, such as myocarditis, some instances of cardiomyopathy, and with extensive rhabdomyolysis, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, malignant hyperthermia, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, mixed connective tissue disease, myoglobinemia, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Reye syndrome, and rarely in rheumatoid arthritis with high titer RF. 2 CK-MB does not generally abruptly rise and fall in such nonacute MI settings, as it does in acute myocardial infarct (AMI).
What is a blood typing test?
Blood typing is a screening test to determine blood groups and Rh antigen for blood transfusion and pregnancy. The four blood groups A, B, O, and AB are determined by the presence of antigens A and B or their absence (O) on a patient's red blood cells. In addition to ABO grouping, most immunohematology testing includes evaluation of Rh typing tests for Rh (D) antigen. Blood cells that express Rh (D) antigen are Rh positive. Red blood cells found lacking Rh (D) are considered Rh negative. Rh typing is also important during pregnancy because of the potential for mother and fetus Rh incompatiblity. If the mother is Rh negative but the father is Rh positive, the fetus may be positive for the Rh antigen. As a result, the mother’s body could develop antibodies against the Rh antigen. These antibodies may cross the placenta and cause destruction of the baby’s red blood cells, resulting in a condition known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn.
Why is it important to have blood transfusions?
Transfusion of blood components of the correct blood type is necessary in order to prevent an adverse immunologic reaction. These reactions can range from very mild and sub-clinical to very severe or fatal, depending upon the components involved and condition of the recipient.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for traumatic left hip fracture
- 2. icd-10-cm do you code for hiv in a patient with retroperineal tuberculosis
- 3. icd 10 code for history of cantholoplasty
- 4. icd 10 code for history of primary neoplasm of ovary
- 5. icd 10 cm code for cholecystectomy
- 6. icd-10 code for pes planus
- 7. icd 10 code for urinary bladder screening
- 8. icd 10 code for type ii diabetes uncontrolled
- 9. icd 10 code for academic underachievement
- 10. 2020 icd 10 code for post nasal drip