What is Class 3 severe obesity?
The following are levels of obesity based on BMI:
- Overweight: BMI 25.0-29.9 kg/m²
- Class I Obesity: BMI 30.0-34.9 kg/m²
- Class II Obesity: BMI 35.0-39.9 kg/m²
- Class III Obesity: BMI ≥ 40.0 kg/m²*
What is obesity class 3?
These ranges of BMI are used to describe levels of risk:
- Overweight (not obese), if BMI is 25.0 to 29.9
- Class 1 (low-risk) obesity, if BMI is 30.0 to 34.9
- Class 2 (moderate-risk) obesity, if BMI is 35.0 to 39.9
- Class 3 (high-risk) obesity, if BMI is equal to or greater than 40.0
What are the 3 classes of obesity?
Types of Obesity and its Complications
- Peripheral: Accumulation of excess fat in the hips, buttocks and thighs.
- Central: Accumulation of excess fat in the abdominal area.
- Combination of both peripheral and central obesity.
What BMI is considered obesity?
obesity is a BMI greater than or equal to 30. BMI provides the most useful population-level measure of overweight and obesity as it is the same for both sexes and for all ages of adults. However, it should be considered a rough guide because it may not correspond to the same degree of fatness in different individuals.
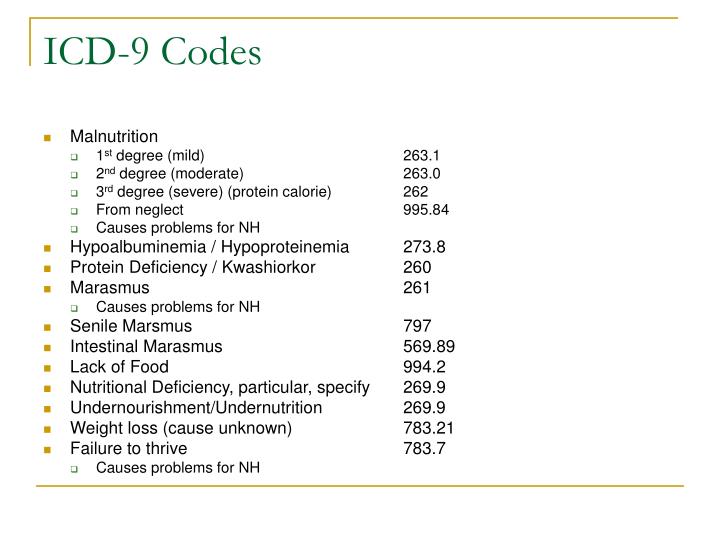
What is class 3 obesity?
These ranges of BMI are used to describe levels of risk: Overweight (not obese), if BMI is 25.0 to 29.9. Class 1 (low-risk) obesity, if BMI is 30.0 to 34.9. Class 2 (moderate-risk) obesity, if BMI is 35.0 to 39.9. Class 3 (high-risk) obesity, if BMI is equal to or greater than 40.0.
What is class 3 obesity weight?
Class 3: BMI of 40 or higher. Class 3 obesity is sometimes categorized as “severe” obesity.
Is Class 3 obesity considered morbid obesity?
What is morbid obesity (now known as class III obesity)? Class III obesity, formerly known as morbid obesity, is a complex chronic disease in which a person has a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher or a BMI of 35 or higher and is experiencing obesity-related health conditions.
What is the ICD 10 code for class 2 obesity?
Overweight and obesity ICD-10-CM E66.
What is class II obesity?
Additionally, you can divide obesity into three separate categories of severity: Obesity class 1: BMI between 30 and less than 35. Obesity class 2: BMI between 35 and less than 40 Obesity class 3: BMI of 40 or higher
What are the stages of obesity?
BMI Categories:Underweight = 18.5 or less.Normal weight = 18.5 – 24.9.Overweight = 25 – 29.9.Obese (class I) = 30 – 34.9.Obese (class II) = 35 – 39.9.Obese (class III) = 40 or more.
Are there 4 categories of obesity?
Four phenotypes of obesity have been described, based on body fat composition and distribution: (1) normal weight obese; (2) metabolically obese normal weight; (3) metabolically healthy obese; and (4) metabolically unhealthy obese. Sarcopenic obesity has been characterized, related to all the described phenotypes.
What qualifies as morbid obesity?
A BMI above 40 indicates that a person is morbidly obese and therefore a candidate for bariatric surgery. Bariatric surgery may also be an option for people with a BMI between 35 and 40 who suffer from life-threatening cardiopulmonary problems, diabetes, or other medical problems listed below.
What is the difference between obese and morbidly obese?
Obesity, having too much body fat, is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of greater than 30. BMI is a measure of your weight relative to your height. Morbid obesity, which is also termed “clinically severe obesity,” is typically defined as being more than 100 pounds overweight or having a BMI of 40 or higher.
When do you use Z71 89?
ICD-10 code Z71. 89 for Other specified counseling is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What diagnosis Z71 89?
Other specified counseling89: Other specified counseling.
Is Class 2 obesity Morbid?
Clinically severe obesity, which people sometimes call morbid obesity, can increase the risk of a range of other health issues....What is morbid obesity?BMIDescription25 to less than 30Overweight30 to less than 35Class 1 obesity35 to less than 40Class 2 obesityAbove 40Class 3 obesity2 more rows•Apr 28, 2021
What is the BMI of a severe obesity?
Severe adult obesity with bmi between 50 to 59.9
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as E66.01. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
When will the ICd 10 E66.01 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E66.01 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for obesity complicating pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium?
Category E66 contains two instructional notes: Code first obesity complicating pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium, if applicable (O99.21) 2. Use an additional code to identify body mass index (BMI) if known (Z68). Body mass index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight that applies to adult men and women.
What is the code for morbid obesity?
Based on this documentation, the patient is diagnosed with morbid obesity due to excess calories, which would be coded E66.01 Morbid (severe) obesity due to excess calories.
What is the BMI code for adults?
BMI adult codes (Z68.1- thru Z68.4-) are for use for persons 21 years of age or older.
What is BMI code assignment?
For the Body Mass Index (BMI), code assignment may be based on medical record documentation from clinicians who are not the patient’s provider (i.e., physician or other qualified healthcare practitioner legally accountable for establishing the patient’s diagnosis), since this information is typically documented by other clinicians involved in the care of the patient (e.g., a dietitian often documents the BMI ). However, the associated diagnosis (such as overweight, obesity) must be documented by the patient’s provider. If there is conflicting medical record documentation, either from the same clinician or different clinicians, the patient’s attending provider should be queried for clarification.
How to calculate body mass index?
Body mass index is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms (kg) by height in meters (m) squared. Category. BMI.
What does it mean to be obese?
Obesity means having too much body fat. Obesity increases the risk of diabetes, heart disease, stroke, arthritis, and some cancers. If you are obese, losing even 5-10 percent of your weight can delay or prevent some of these diseases. Obesity is a substantial public health crisis in the United States, and internationally, ...
Can E66 be used as primary diagnosis?
Not sure about the others here, but we get denials all the time for coding the E66 as primary diagnosis (primarily from Medicaid). We’ve found that using the BMI as primary tends to work, but it causes some problems for our pediatricians who see over-weight patients under the age of 2.
What is the BMI of obesity?
Adult obesity with bmi between 38 to 38.9
What is the average BMI for obesity?
Adult obesity with bmi between 33 to 33.9
Why does obesity occur over time?
Obesity occurs over time when you eat more calories than you use. The balance between calories-in and calories-out differs for each person. Factors that might tip the balance include your genetic makeup, overeating, eating high-fat foods and not being physically active.
What does it mean to be obese?
A person is considered obese if they have a body mass index (bmi) of 30 or more. Obesity means having too much body fat. It is different from being overweight, which means weighing too much. The weight may come from muscle, bone, fat and/or body water.
What is excessive fat?
Excessively high accumulation of body fat or adipose tissue in relation to lean body mass; the amount of body fat (or adiposity) includes concern for both the distribution of fat throughout the body and the size of the adipose tissue deposits; individuals are usually at high clinical risk because of excess amount of body fat (bmi greater than 30).
What is postpartum obesity?
Postpartum obesity. Clinical Information. A condition marked by an abnormally high, unhealthy amount of body fat. A disorder characterized by having a high amount of body fat. A status with body weight that is grossly above the acceptable or desirable weight, usually due to accumulation of excess fats in the body.
When will the ICd 10 E66.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E66.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the BMI of overweight?
In the scale of body mass index, overweight is defined as having a bmi of 25.0-29.9 kg/m2. Overweight may or may not be due to increases in body fat (adipose tissue), hence overweight does not equal "over fat".
When will the ICD-10-CM E66.3 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E66.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the fourth quarter of the Coding Clinic?
The Coding Clinic published in the fourth quarter of specifically states that the provider must provide documentation of a clinical condition such as obesity or overweight to justify the reporting of a code for BMI. Are one or more of your physicians under-coding?
When should BMI code Z68 be coded?
BMI codes Z68 should only be coded when there is a diagnosis such as obesity, overweight, underweight etc. What is your most frequent nonmaternal, non-neonatal principal diagnosis? Refer to Coding Clinic, Third Quarterpagesfor additional information on coding chronic conditions.
Is BMI a reportable diagnosis?
It is also a topic that is brought up in conversations about inpatient DRG coding denials. BMI codes need to be supported as medically relevant by an associated diagnosis that is considered a reportable diagnosis.
Is BMI a standalone code?
Rose T. The icd 10 coding guidelines for morbid obesity is required to follow the classification based on the Official Coding and Reporting Guidelines. Keep in mind that that BMI codes were never intended to be used as standalone codes; they were always meant to be accompanied by a corresponding diagnosis code. While not much has changed in the way we code for this condition, with all the buzz around Hierarchical Condition Categories HCCsobesity and body mass index BMI have become a popular topic. June 12, at am 6.
Is BMI reported when obese?
This issue of Coding Clinic supports that the BMI can only be reported whenever a weight diagnosis is documented by the provider.
Can BMI be reported?
This issue of Coding Clinic supports that the BMI can only be reported whenever a weight diagnosis is documented by the provider .
Is it appropriate to assign a diagnosis code based on BMI?
It is not appropriate to assign the diagnosis code based on BMI. Her vitals are normal. Log in. When coding for obesity it is important to know how a person is considered as obese. The following code s above E I know this can be an issue since the various types of reimbursement methodologies, such as risk adjustment, include the BMI codes, but these codes were always meant to be accompanied by a corresponding diagnosis code. Comment on this article.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for .right middle lobe carcinoma
- 2. icd-10 code for postherpetic trigeminal neuralgia
- 3. icd 10 code for generalized joint pain.
- 4. icd 10 code for subendocardial myocardial infarction
- 5. 2016 icd 10 code for lumbar laminectomy
- 6. icd 10 code for hepatospermia
- 7. icd 10 code for rt ankle ap and lat
- 8. icd 10 code for dizziness and headache
- 9. icd-10 code for symptoms of the spleen
- 10. icd 10 code for sfood disorder