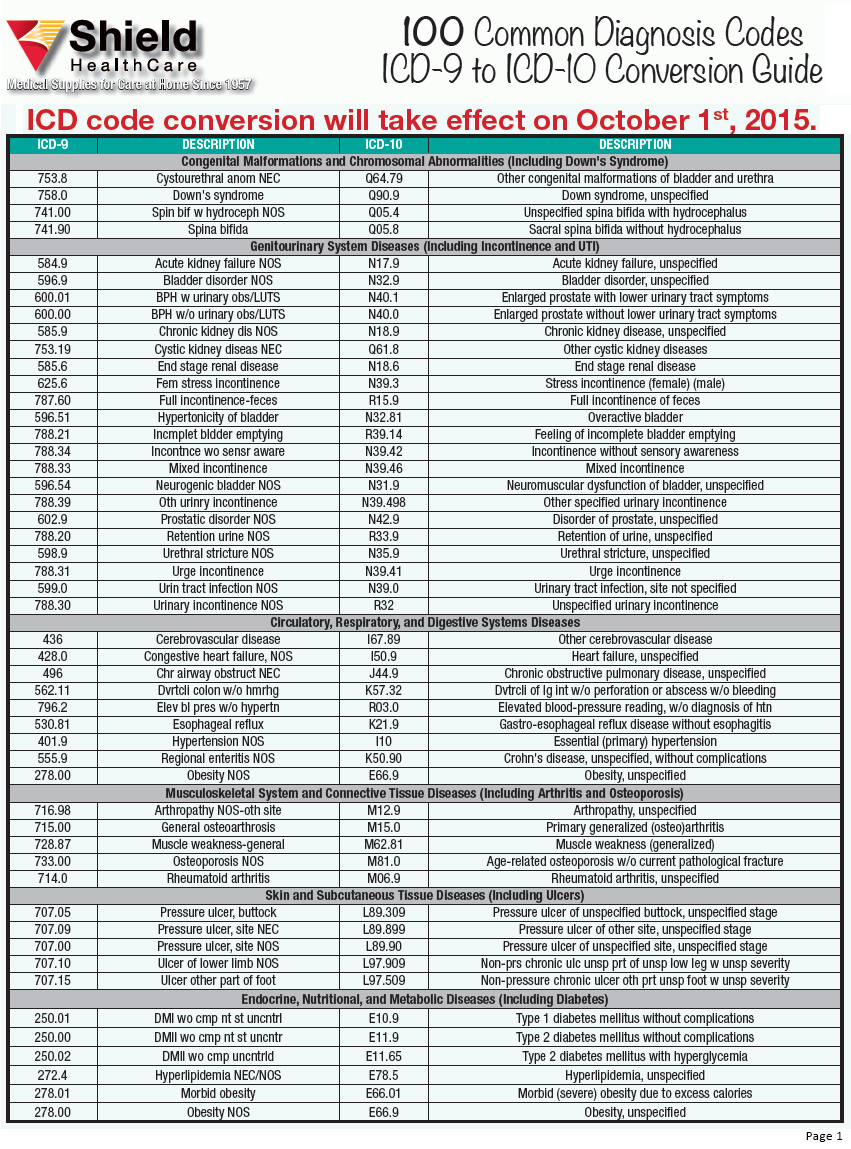
How many codes in ICD 10?
- ICD-10 codes were developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) External file_external .
- ICD-10-CM codes were developed and are maintained by CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics under authorization by the WHO.
- ICD-10-PCS codes External file_external were developed and are maintained by Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. ...
How to look up ICD 10 codes?
Search the full ICD-10 catalog by:
- Code
- Code Descriptions
- Clinical Terms or Synonyms
What is a valid ICD 10 code?
The following 72,752 ICD-10-CM codes are billable/specific and can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes as there are no codes with a greater level of specificity under each code. Displaying codes 1-100 of 72,752: A00.0 Cholera due to Vibrio cholerae 01, biovar cholerae. A00.1 Cholera due to Vibrio cholerae 01, biovar eltor. A00.9 Cholera, unspecified.
What are common ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10-CM Common Codes for Gynecology and Obstetrics ICD-10 Code Diagnoses Menstrual Abnormalities N91.2 Amenorrhea N91.5 Oligomenorrhea N92.0 Menorrhagia N92.1 Metrorrhagia N92.6 Irregular Menses N93.8 Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding N94.3 Premenstrual Syndrome N94.6 Dysmenorrhea Disorders Of Genital Area L29.3 Vaginal Itch N73.9 N75.0 Bartholin’s Cyst N76.0
What is the meaning of CML?
Listen to pronunciation. (KRAH-nik MY-eh-loyd loo-KEE-mee-uh) An indolent (slow-growing) cancer in which too many myeloblasts are found in the blood and bone marrow. Myeloblasts are a type of immature blood cell that makes white blood cells called myeloid cells.
Is CML a type of leukemia?
These are slow growing types of leukemia which result in overproduction of white blood cells by the bone marrow, causing high blood counts. Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) may also be referred to as chronic myelogenous leukemia, chronic myelocytic leukemia or chronic granulocytic leukemia.
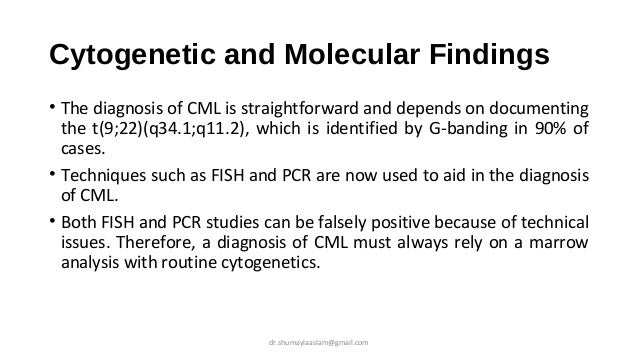
WHO CML diagnosis criteria?
The presence of the Ph chromosome in the bone marrow cells, along with a high white blood cell count and other characteristic blood and bone marrow test findings, confirm the diagnosis of CML. The bone marrow cells of about 95 percent of people with CML have a Ph chromosome that is detectable by cytogenetic analysis.
What is the difference between CML and CLL?
CML and CLL are caused by genetic mutations that affect the way your body produces blood cells. In CML the first changes occur in immature myeloid cells located in your bone marrow. Your myeloid cells are responsible for producing blood cells.
What is the main cause of CML?
CML is caused by a genetic change (mutation) in the stem cells produced by the bone marrow. The mutation causes the stem cells to produce too many underdeveloped white blood cells. It also leads to a reduction in the number of other blood cells, such as red blood cells.
What are the 3 stages of CML?
To help doctors plan treatment and predict prognosis, which is the chance of recovery, CML is divided into 3 different phases: chronic, accelerated, or blast.
What is the difference between AML and CML?
Summary. AML and CML are blood and bone marrow cancers that affect the same lines of white blood cells. AML comes on suddenly as very immature cells crowd out normal cells in the bone marrow. CML comes on more slowly, with the CML cells growing out of control.
What are the 4 main types of leukemia?
There are 4 main types of leukemia, based on whether they are acute or chronic, and myeloid or lymphocytic:Acute myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (AML)Chronic myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (CML)Acute lymphocytic (or lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL)Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
What are the 4 types of leukemia?
There are 4 main types of leukemia, based on whether they are acute or chronic, and myeloid or lymphocytic:Acute myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (AML)Chronic myeloid (or myelogenous) leukemia (CML)Acute lymphocytic (or lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL)Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
How long can you live with CML leukemia?
Historically, the median survival of patients with CML was 3-5 years from the time of diagnosis. Currently, patients with CML have a median survival of 5 or more years. The 5-year survival rate has more than doubled, from 31% in the early 1990s to 70.6% for patients diagnosed from 2011 to 2017.
What is the survival rate for CML leukemia?
Before the advent of targeted drug therapy, the five-year survival rate for people with CML was only 22%. Today, the overall five-year survival rate is 90%. (This means that 90% of people diagnosed with CML are still alive five years later.)
Can CML turn into other cancers?
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) can become resistant to treatment and progress to more advanced phases. But sometimes people with CML or develop a new, unrelated cancer later. This is called a second cancer. No matter what type of cancer you have or had, it's still possible to get another (new) cancer.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
Is morphology included in the category and codes?
In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What percentage of blasts are in the peripheral blood?
A chronic myelomonocytic leukemia characterized by the presence of less than 10 percent blasts in the bone marrow and less than 5 percent blasts in the peripheral blood.
What is a myelodysplastic disease?
A slowly progressing type of myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disease in which too many myelomonocytes (a type of white blood cell) are in the bone marrow, crowding out other normal blood cells, such as other white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. Code History.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
Is C93.1 a reimbursement code?
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. C93.1 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM C93.1 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is an acute myeloid leukemia?
An acute myeloid leukemia (aml) characterized by blasts with evidence of maturation to more mature neutrophils. Patients often present with anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia. Aml with the t (8;21) is usually aml with maturation.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
Is Raeb-T a subcategory of myelodysplastic syndrome?
Raeb-t used to be a subcategory of myelodysplastic syndromes in the past. Recently, the term has been eliminated from the who based classification of myelodysplastic syndromes. The reason is that the percentage of peripheral blood blasts required for the diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemia has been reduced to 20%.
What is a proliferative disease?
A progressive, proliferative disease of blood cells, originating from immature granulocytes. Form of leukemia characterized by an uncontrolled proliferation of the myeloid lineage and their precursors (myeloid progenitor cells) in the bone marrow and other sites.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
Malignant neoplasms of lymphoid, hematopoietic and related tissue. Clinical Information. A clonal proliferation of myeloid cells and their precursors in the bone marrow, peripheral blood, and spleen. When the proliferating cells are immature myeloid cells and myeloblasts, it is called acute myeloid leukemia.
What does "type 1 excludes" mean?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. personal history of leukemia (.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
What is CML in medical terms?
Chronic myelogenous (or myeloid or myelocytic) leukemia (CML), also known as chronic granulocytic leukemia (CGL), is a cancer of the white blood cells. It is a form of leukemia characterized by the increased and unregulated growth of predominantly myeloid cells in the bone marrow and the accumulation of these cells in the blood. CML is a clonal bone marrow stem cell disorder in which a proliferation of mature granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils) and their precursors is found. It is a type of myeloproliferative disease associated with a characteristic chromosomal translocation called the Philadelphia chromosome. CML is now largely treated with targeted drugs called tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) which have led to dramatically improved long-term survival rates since the introduction of the first such agent in 2001. These drugs have revolutionized treatment of this disease and allow most patients to have a good quality of life when compared to the former chemotherapy drugs. In Western countries it accounts for 15-20% of all adult leukemias and 14% of leukemias overall (including the pediatric population).
What is CML stem cell?
CML is a clonal bone marrow stem cell disorder in which a proliferation of mature granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils) and their precursors is found . It is a type of myeloproliferative disease associated with a characteristic chromosomal translocation called the Philadelphia chromosome.
What is acute myeloid leukemia?
A clonal expansion of myeloid blasts in the bone marrow, blood or other tissues. The classification of acute myeloid leukemias (amls) encompasses four major categories: 1) aml with recurrent genetic abnormalities 2) aml with multilineage dysplasia 3) therapy-related aml 4) aml not otherwise categorized.
What is the treatment for leukemia?
Treatments include chemotherapy, other drugs, radiation therapy, stem cell transplants, and targeted immune therapy. Once the leukemia is in remission, you need additional treatment to make sure that it does not come back. nih: national cancer institute.
What is the function of white blood cells in leukemia?
Your blood cells form in your bone marrow. In leukemia, however, the bone marrow produces abnormal white blood cells. These cells crowd out the healthy blood cells , making it hard for blood to do its work.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
Popular Posts:
- 1. 2017 icd 10 code for enteric tube placement
- 2. icd 10 code for mild splenomegaly
- 3. icd 10 dx code for refusual of blood jehovahs witness
- 4. icd 9 code for enterocutaneous fistula
- 5. icd 10 code for hemorrhoidectomy external
- 6. icd-10-cm code for suppurative pancreatitis
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for migraine
- 8. icd 10 code for laceration to foreskin
- 9. icd 10 code for gi bleedeed
- 10. icd-10-cm code for pneumonia with chicken pox