What is the ICD 10 code for coagulation disorders?
Oct 01, 2021 · The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D68.4 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D68.4 - other international versions of ICD-10 D68.4 may differ. Applicable To. Deficiency of coagulation factor due to liver disease. Deficiency of coagulation factor due to vitamin K deficiency.
What is the ICD 10 code for liver disease?
Oct 01, 2021 · Liver disease, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code K76.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM …
What is the CPT code for coagulopathy?
Oct 01, 2021 · Coagulation defect, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. D68.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D68.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the CPT code for coagulation factor deficiency?
- coagulation NOS - D68.9 - acquired (any) - D68.4 - due to - hyperprothrombinemia - D68.4 - liver disease - D68.4 - vitamin K deficiency - D68.4 - factor - See Also: Deficiency, coagulation; - multiple (congenital) - D68.8 - acquired - D68.4 - fibrin-stabilizing factor (congenital) (hereditary) - D68.2 - acquired - D68.4
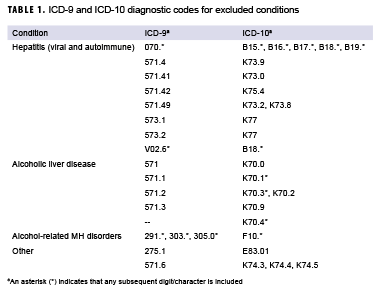
What is the ICD 10 code for coagulopathy?
9.
What is coagulation defect unspecified?
Coagulation defects — also known as bleeding disorders and blood clotting disorders — are problems with your blood's ability to form clots. The defects can involve your blood vessels and the cells and proteins in your blood.Nov 23, 2021
What is the ICD 10 code for Warfarin induced coagulopathy?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D68. 32: Hemorrhagic disorder due to extrinsic circulating anticoagulants.
What is acquired coagulation deficiency?
Acquired factor VIII deficiency is a bleeding disorder that requires prompt diagnosis and management to avert severe, life-threatening bleeding and death. Despite knowledge of this disorder of coagulation for several decades, relatively little is still known about this disease because of its rare incidence.Mar 24, 2017
What is coagulopathy?
Coagulopathy is often broadly defined as any derangement of hemostasis resulting in either excessive bleeding or clotting, although most typically it is defined as impaired clot formation.
What is another word for coagulation?
What is another word for coagulation?cakingclottingcoalescencecongealinggellingjellingsettingagglomerationconcentrationconcretion7 more rows
What is warfarin induced coagulopathy?
Warfarin-induced coagulopathy Warfarin and related VKAs, whether ingested accidentally, factitiously, or as an overdose of oral anticoagulant therapy, lead to a deficiency of vitamin K–dependent proteins, prolongation of the prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time, and clinical bleeding manifestations.
How do you code coagulopathy with Coumadin?
Anticoagulant therapy includes drugs such as Coumadin, warfarin, heparin, and other anticoagulants and the adverse effect code is T45. 515-, Adverse effect of anticoagulant.Jan 16, 2017
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated D dimer?
For elevated D-dimer, look to ICD-10-CM R79. 1 Abnormal coagulation profile.Jul 28, 2017
What is the most common acquired coagulopathy?
The most common causes of acquired coagulation disorders are liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). More rarely, inhibitors, external factors such as drugs or extracorporeal circulation, or other diseases such as amyloidosis are present.
What is the most common cause of coagulopathy?
Coagulopathy may be caused by reduced levels or absence of blood-clotting proteins, known as clotting factors or coagulation factors. Genetic disorders, such as hemophilia and Von Willebrand disease, can cause a reduction in clotting factors.
What is acquired VIII deficiency?
Acquired factor VIII deficiency is a bleeding disorder that requires prompt diagnosis and management to avert severe, life-threatening bleeding and death. Despite knowledge of this disorder of coagulation for several decades, relatively little is still known about this disease because of its rare incidence.Mar 24, 2017
What is a type 1 exclude note?
Type 1 Excludes. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes note. It means "NOT CODED HERE!". An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code D68.4 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What happens when you get hurt?
For blood to clot, your body needs cells called platelets and proteins known as clotting factors. If you have a bleeding disorder, you either do not have enough platelets or clotting factors or they don't work the way they should.
What is the term for a condition in which the blood’s ability to coagulate (form clot
Coagulopathy (also called a bleeding disorder) is a condition in which the blood’s ability to coagulate (form clots) is impaired. This condition can cause a tendency toward prolonged or excessive bleeding (bleeding diathesis or bleeding disorder), which may occur spontaneously or following an injury or medical and dental procedures.
What is the condition called when the blood clots?
Coagulopathy (also called a bleeding disorder) is a condition in which the blood’s ability to coagulate (form clots) is impaired. This condition can cause a tendency toward prolonged or excessive bleeding (bleeding diathesis or bleeding disorder), which may occur spontaneously or following an injury or medical and dental procedures. Specialty:

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for end stage respiratory failure
- 2. icd 9 code for diabetic ulcer of foot
- 3. 2015 icd 10 code for status post cervical fusion
- 4. icd 10 cm code for s/p tah\
- 5. icd 9 code for severe canal stenosis
- 6. icd 9 code for blood work
- 7. icd 10 code for pustule foot
- 8. icd-10 code for visual deterioration
- 9. icd 9 code for elongated metatarsal
- 10. icd 10 code for t12 vertebral fracture