What is the CPT code for coagulopathy due to Coumadin?
Apr 12, 2016 · In the 1st Q coding clinic we were given an unexpected clarification to report ICD 10 code D68.32 for certain patients experiencing adverse effects from Coumadin administration. D68.32: Hemorrhagic...
What is the new ICD 10 for coagulopathy?
Oct 01, 2021 · D68.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D68.9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D68.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 D68.9 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for anticoagulant hemorrhagic disorder?
Oct 01, 2021 · T45.515A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM T45.515A became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of T45.515A - other international versions of ICD-10 T45.515A may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for coagulation factor deficiency?
Oct 01, 2021 · D68.32 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Hemorrhagic disord d/t extrinsic circulating anticoagulants. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D68.32 became effective on October 1, …
How do you code coagulopathy with Coumadin?
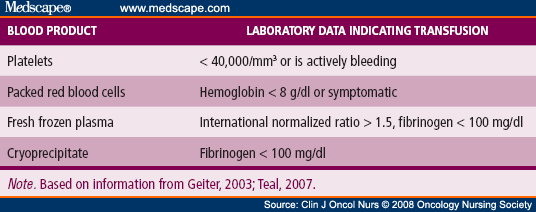
The physician attributed the bleeding to long term Coumadin therapy and adjusts the Coumadin dosage. Assign D68. 32, Hemorrhagic disorder due to extrinsic circulating anticoagulants, followed by K26.16 Jan 2017
What is Coumadin coagulopathy?
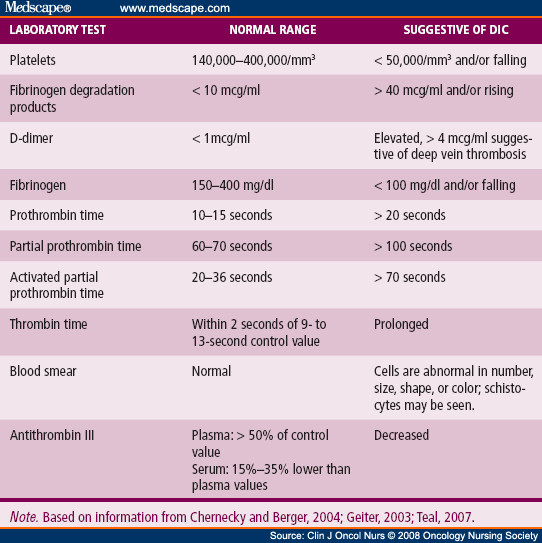
Warfarin-induced coagulopathy Warfarin and related VKAs, whether ingested accidentally, factitiously, or as an overdose of oral anticoagulant therapy, lead to a deficiency of vitamin K–dependent proteins, prolongation of the prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time, and clinical bleeding manifestations.
What is the ICD 10 code for coagulopathy?
ICD-10-CM Code for Coagulation defect, unspecified D68. 9.
What is drug induced coagulopathy?
DRUG-INDUCED COAGULOPATHY: DIRECT ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) are oral anticoagulants that directly inhibit thrombin (dabigatran) or factor Xa (rivaroxaban, apixaban, endoxaban, betrixaban).
Does Coumadin cause coagulopathy?
Abstract. Warfarin is the most common form of oral anticoagulant therapy. Although it has indisputable benefit in the management of thromboembolic disease, warfarin-associated coagulopathy (WAC) is a well-documented complication of its use.
What does coagulopathy mean?
Coagulopathy is often broadly defined as any derangement of hemostasis resulting in either excessive bleeding or clotting, although most typically it is defined as impaired clot formation.
What is the ICD 10 code for ASHD?
ICD-10-CM Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris I25. 10.
How is coagulopathy treated?
Treatment for a coagulopathyMedications that prevent the formation of blood clots.Contraceptive pills to counteract the excessive bleeding during menstruation.Medication that substitutes protein in the blood to ensure you do not excessively bleed.
What is the correct ICD 10 code for leukocytosis?
288.60 - Leukocytosis, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is the code for hemorrhagic disorder?
For bleeding in a patient who is being treated with warfarin (Coumadin), heparin, anticoagulants, or other antithrombotics as a part of anticoagulation therapy, assign code D68.32, Hemorrhagic disorder due to extrinsic circulating anticoagulants.
What is hypercoagulable state?
Hypercoagulable states refer to a group of acquired and inherited disorders caused by increased thrombin generation. There is an increased tendency for blood clotting, and there may be fibrin deposition in the small blood vessels. These disorders are divided into primary and secondary hypercoagulable states.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for acute left arm embolus
- 2. icd 10 code for servalience of contraception
- 3. icd 10 code for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
- 4. icd 10 code for cholelithiosis
- 5. icd 10 code for right shoulder dislocation
- 6. icd 10 code for air distended loop bowel
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for mavyret
- 8. icd-10 code for repetitive motion
- 9. icd 10 code for ct scan of mandibe
- 10. icd 10 code for absent septum pellucidum