Are all colon polyps precancerous or worse?
These types of polyps are not cancer, but they are pre-cancerous (meaning that they can turn into cancers). Someone who has had one of these types of polyps has an increased risk of later developing cancer of the colon. Most patients with these polyps, however, never develop colon cancer.
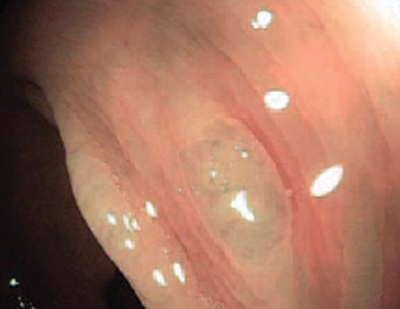
What are the chances of a sessile polyp being cancerous?
What are the chances of a sessile polyp being cancerous? There’s a 10% chance a colon polyp that size contains cancerous cells. Which types of colon polyps are most likely to turn into cancer? Villous adenomas, also called tubulovillous adenomas, and large serrated sessile polyps are either precancerous or carry a high risk of becoming cancerous.
What percentage of large polyps are cancerous?
What percentage of large polyps are cancerous? Approximately 1% of polyps with a diameter less than 1 centimeter (cm) are cancerous. If you have more than one polyp or the polyp is 1 cm or bigger, you’re considered at higher risk for colon cancer.
What to know about sessile polyps?
What a polyp’s shape suggests
- About 85 percent of polyps are “sessile”: dome-shaped, without a stalk.
- About 13 percent of polyps are “pedunculated,” hanging from the colon wall on a stalk like a cherry on a stem.
- About 2 percent of precancerous lesions are flat.

What is an adenomatous colon polyp?
Adenomatous colon polyps are considered to be precursor lesions of colon cancer. An extra piece of tissue that grows in the large intestine, or colon. Discrete tissue masses that protrude into the lumen of the colon. These polyps are connected to the wall of the colon either by a stalk, pedunculus, or by a broad base.
What is a polypoid lesion?
A polypoid lesion that arises from the colon and protrudes into the lumen. This group includes adenomatous polyps, serrated polyps, and hamartomatous polyps. Abnormal growths of tissue in the lining of the bowel. Polyps are a risk factor for colon cancer.
What is a mass of tissue that bulges or projects into the lumen of the colon?
This is a descriptive term referring of a mass of tissue that bulges or projects into the lumen of the colon. The mass is macroscopically visible and may either have a broad base attachment to the colon wall, or be on a pedunculated stalk. These may be benign or malignant.
Is a polyp of the intestine dangerous?
Polyp colon, hyperplastic. Polyp of intestine. Clinical Information. A polyp is an extra piece of tissue that grows inside your body. Colonic polyps grow in the large intestine, or colon. Most polyps are not dangerous . However, some polyps may turn into cancer or already be cancer.
Can colon polyps cause diarrhea?
most colon polyps do not cause symptoms. If you have symptoms, they may include blood on your underwear or on toilet paper after a bowel movement, blood in your stool, or constipation or diarrhea lasting more than a week. nih: national institute of diabetes and digestive diseases.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as D12.6. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is invisible dysplasia?
Invisible dysplasia. Visible lesions are endoscopically resected or biopsied. Biopsies adjacent to endoscopically resected lesion may also be taken to ensure complete removal. Random biopsies may be taken to detect endoscopically invisible dysplasia.
What is colonic epithelium?
Definition / general. Dysplasia of colonic epithelium identified in setting of colonic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), usually in colonic biopsies from surveillance colonoscopies. Precursor of invasive carcinoma. Can be endoscopically visible or invisible.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for aftercare kidney transplant
- 2. icd 10 code for oliguric aki
- 3. icd 10 code for infected left hip prosthesis
- 4. icd 10 code for contusion sacral
- 5. icd 10 code for confusion and disorientation
- 6. icd-10 code for leg pain right
- 7. main term and icd 10 cm code for cochlear otosclerosis, bilateral
- 8. icd 10 code for medical letters
- 9. icd 9 code for femoral hematoma
- 10. icd-10 code for borderline personality disorder