What are the complications of colon resection?
The side effects of colon resection may include:
- Anesthetic side effects such as Headache Nausea Confusion
- Abdominal pain from the surgery Fatigue Constipation and/or diarrhea
- Inconvenience of the attached ostomy bag
What is the ICD 10 code for small bowel obstruction?
Unspecified intestinal obstruction, unspecified as to partial versus complete obstruction
- K56.609 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- Short description: Unsp intestnl obst, unsp as to partial versus complete obst
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K56.609 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for colon polyp?
Polyp of colon
- K63.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K63.5 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K63.5 - other international versions of ICD-10 K63.5 may differ.
What is the diagnosis code for rectal bleeding?
- Bleeding (see also Hemorrhage) 459.0 anal 569.3 rectum, rectal 569.3
- BRBPR (bright red blood per rectum) 569.3
- Bright red blood per rectum (BRBPR) 569.3
- Hemorrhage, hemorrhagic (nontraumatic) 459.0 anus (sphincter) 569.3 rectum (sphincter) 569.3
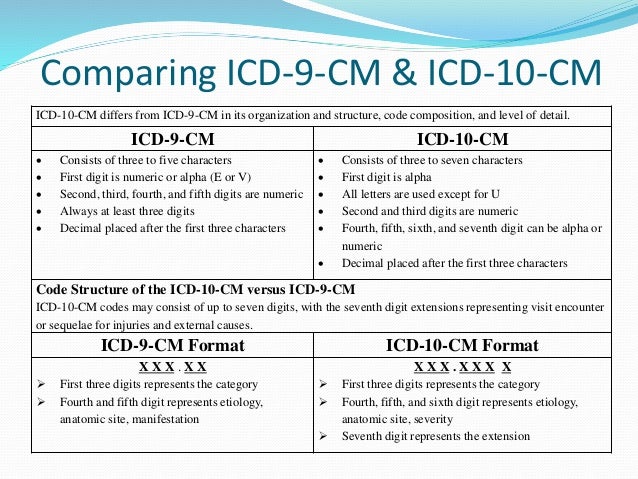
What is the ICD-10-CM code for perforated viscus?
H72. 829 Total perforations of tympanic membrane, unsp...
What is the ICD-10 code for duodenal perforation?
Acute duodenal ulcer with perforation K26. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K26. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is colonic perforation?
A colon perforation is a puncture, cut, or tear in the wall of the colon (large intestine). This can cause air and intestinal material to leak into the abdomen. Normal Colon. Copyright © Nucleus Medical Media, Inc.
What is the ICD-10 code k52 9?
Noninfective gastroenteritis and colitis, unspecified9 Noninfective gastroenteritis and colitis, unspecified. colitis, diarrhoea, enteritis, gastroenteritis: infectious (A09.
What is the ICD 10 code for intestinal perforation?
ICD-10 code K63. 1 for Perforation of intestine (nontraumatic) is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is a duodenal perforation?
Perforation of the duodenum is defined as a transmural injury to the duodenal wall. A partial thickness laceration may over time develop into a transmural injury. Duodenal perforation can cause acute pain associated with free perforation, or less acute symptoms associated with abscess or fistula formation.
What happens if the colon is perforated during colonoscopy?
Your doctor then watches the perforation to make sure it heals. However, more serious tears will require surgery. If waste material has leaked into the abdomen, it should be cleaned out as well, otherwise, a patient could suffer peritonitis, which is a potentially fatal infection.
What is perforation in medical term?
Perforation is a hole that develops through the wall of a body organ. This problem may occur in the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, or gallbladder.
What happens when you have a perforated colon?
The contents in your colon can leak out through the hole caused by a perforated bowel. This can cause bleeding, as well as a painful and serious infection. A bowel perforation usually can be treated with surgery. If left untreated, though, the infection it causes can lead to death and disability.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for R11 0?
ICD-10 code R11. 0 for Nausea is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is Illitus?
What is ileitis? Ileitis is a condition characterized by irritation or inflammation of the ileum, the last part of the small intestine that joins the large intestine. Symptoms of ileitis include the following: Weight loss. Diarrhea.
What does a perforated colon feel like?
The primary symptoms of gastrointestinal perforation are severe abdominal pain and tenderness. The abdomen may also protrude or feel hard to the touch. If the hole is in a person's stomach or small intestine, the onset of pain is usually sudden, but if the hole is in the large bowel, the pain may come on gradually.
Can a perforated colon heal itself?
Small gastrointestinal or bowel perforations can sometimes heal without surgery. However, you can't know this until you have a diagnosis, so seek medical care right away.
How long can you live with a perforated colon?
Patients who underwent surgery for treatment of their bowel perforation had a longer median survival time compared to patients who were treated conservatively, including observation (13.7 months compared to 0.50 months, p=0.007). Survival from the time of perforation differed when compared by BMI groups (p-0.013).
How does someone get a perforated bowel?
The most common trauma that causes a perforated bowel occurs during abdominal surgery, when the surgeon may accidentally nick or cut the bowel and not notice it. Occasionally, a rupture or perforation may happen following bowel surgery, because the stitches or staples used to close the bowel come undone.
When will the ICD-10-CM K22.3 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K22.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What causes a hole in the esophagus?
The most common cause of esophageal perforation is injury during a medical procedure such as esophagoscopy or placement of a naso-gastric tube; and pathologic process such as neoplasm or gastric reflux with ulceration. Less common causes include injuries from penetrating or blunt trauma or injury to the esophagus during an operation on another organ, mechanical problem such as violent retching or vomiting; ingestion of a foreign body or caustic agents. The condition often results in infection of the mediastinum and mediastinitis.
What is the ICd 10 code for appendicitis with perforation?
K35.33 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Acute appendicitis with perforation and localized peritonitis, with abscess . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also:
What are the risks of colonoscopy?
What You Need to Know#N#Background#N#Screening colonoscopies are associated with a low risk of severe local adverse events: colonic perforations, gastrointestinal bleeding, and splenic injuries. These complications can be associated with patient, procedure, endoscopist, and facility characteristics.#N#Findings#N#Perforations and bleeding related to screening and diagnostic colonoscopies were more frequent in older patients, patients with cancer and cardiovascular disease and with less experienced endoscopists. Splenic injury rate was 0.20 per 10,000 procedures.#N#Implications for patient care#N#Patients at risk of severe adverse events should be identified and colonoscopies in these patients should be performed or supervised by experienced endoscopists.
What are the different types of colonoscopy?
Three types of colonoscopy were distinguished according to the information available in the French classification of clinical procedures: colonoscopies without resection or destruction of polyps, colonoscopies with resection or destruction of 1–3 polyps <1 cm in diameter, and colonoscopies with resection of 1 polyp larger than 1 cm in diameter or 4 or more polyps. The databases do not contain information about polyp location. Bowel preparation was identified in the SNIIRAM by reimbursement of a polyethylene glycol, phosphate, or magnesium preparation during the 6 months preceding the colonoscopy.
What is the ICd 9 code for colonoscopic perforation?
Perforations were identified using the ICD-9 codes for perforation of intestine and accidental puncture or laceration during a procedure (ICD-9 codes 569.83 and 998.2).
What is the role of colonoscopy in inflammatory bowel disease?
Ileocolonoscopy plays a critical role for diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and treatment. 1, 2 In addition to surveillance colonoscopy in outpatient setting, colonoscopy is a key modality for diagnosis, prediction of prognosis (such as mucosal healing), and in therapy for IBD related strictures. Inpatient colonoscopy in IBD patients is often performed to assess disease activity, disease extent, to identify superimposed infection (such as cytomegalovirus infection and Clostridium difficile infection), and to execute endoscopic therapy (such as stricture dilation). 3

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for cauda equina syndrome with neurogenic bladder
- 2. icd 10 code for feeling faint
- 3. icd 10 code for asyptomatic hiv infection
- 4. what is the icd-10 code for full-term complicatedvaginal delivery
- 5. icd 10 code for laceration to ankle
- 6. icd 9 code for episodic vomiting
- 7. icd-10-cm code for migraine classical
- 8. icd 10 code for trouble focusing
- 9. icd 10 cm code for varicose veins of lower extremities
- 10. icd 10 cm code for acute eustachian dysfunction.