What are the top causes of conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss can be caused by problems in the external ear canal or in the middle ear. Possible causes include illnesses such as otosclerosis, cholesteatoma or inflammatory processes accompanied by middle ear effusion or scarring. Another frequent factor that causes conductive hearing loss is a buildup of earwax (cerumen), another ...
What is sensorineural and conductive hearing loss?
Conductive Hearing Loss: Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Any kind of blockage in the outer ear preventing the conduction of sound into the inner ear. Short-lived Hearing Loss. Rinne test is negative(-) i.e, BC(bone conduction) > AC(air conduction) for the bad ear. In this, the person hears better through nerve than that the ear.
What is a conductive hearing?
Your ear is made up of three parts— the outer, the middle, and the inner ear. A conductive hearing loss happens when sounds cannot get through the outer and middle ear. It may be hard to hear soft sounds. Louder sounds may be muffled. Medicine or surgery can often fix this type of hearing loss.
Can hearing aids help with unilateral hearing loss?
This way, it can increase hearing in a noisy environment and helps to localize the sounds. Hearing Aids like CROS and Bi-CROS assist the people and helps to reduce the problems of unilateral hearing loss. It routes the sound coming from the side of the deaf ear to the standard ear.
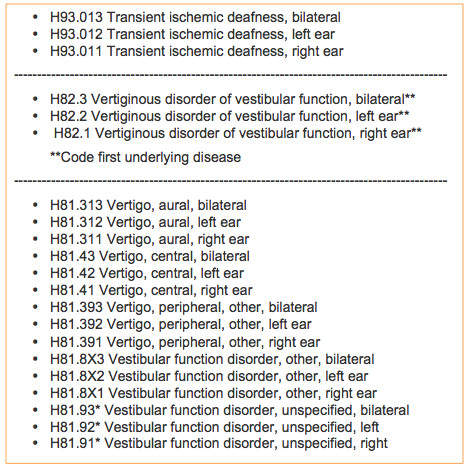
What is ICD-10 code for conductive hearing loss?
ICD-10-CM Code for Conductive hearing loss, bilateral H90. 0.
What is conductive hearing loss?
About Conductive Hearing Loss A conductive hearing loss happens when sounds cannot get through the outer and middle ear. It may be hard to hear soft sounds. Louder sounds may be muffled. Medicine or surgery can often fix this type of hearing loss.
What is the difference between a conductive and sensorineural hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound conduction is impeded through the external ear, the middle ear, or both. Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is a problem within the cochlea or the neural pathway to the auditory cortex.
What is another name for conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss (CHL) occurs when there is a problem transferring sound waves anywhere along the pathway through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear (ossicles). If a conductive hearing loss occurs in conjunction with a sensorineural hearing loss, it is referred to as a mixed hearing loss.
What characteristics of hearing loss are associated with conductive loss?
Conductive hearing loss causes range from earwax to ruptured eardrums....Conductive Hearing Loss SymptomsMuffled hearing.Inability to hear quiet sounds.Dizziness.Gradual loss of hearing.Ear pain.Fluid drainage from the ear.Feeling that your ears are full or stuffy.
What is a common cause of conductive hearing loss?
According to Rothholtz, the most common cause of conductive hearing loss is a buildup of earwax that muffles sound. Rothholtz adds that some other types of conductive hearing loss include: Otosclerosis: This causes bone from the cochlea to grow onto the stapes bone in the middle ear, making it more difficult to hear.
What are the 3 types of hearing loss?
Hearing loss affects people of all ages and can be caused by many different factors. The three basic categories of hearing loss are sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss and mixed hearing loss. Here is what patients should know about each type.
What are the 4 types of hearing loss?
The Four Types of Hearing LossSensorineural Hearing Loss.Conductive Hearing Loss.Mixed Hearing Loss.Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder.Talk to Your Audiologist.
What is the difference between sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss 1.3 1?
Sensorineural hearing loss is treated by the use of hearing aids or cochlear implants. Conductive hearing loss is hearing loss that stems from something, typically fluid, tissue, or bony growth, that blocks or reduces the incoming sound.
Who is most affected by conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss is prevalent and affects a wide demographic, from the very young to the elderly. [3] The causes can also range from the trivial otitis media with effusion in young children to potentially severe conditions such as an effusion caused by a nasopharyngeal tumor in adults.
What is unilateral conductive hearing loss?
What is a unilateral hearing loss? A unilateral hearing loss is a hearing loss in one ear, as opposed to a bilateral hearing loss, where the hearing loss occurs in both ears. A unilateral hearing loss can range from mild to severe or profound and often affects quality of life.
What is conductive hearing loss bilateral?
You can also have a bilateral hearing loss if both of your ears' ability to conduct sound into the inner ear are blocked or reduced. This is called a conductive hearing loss. When the bilateral hearing loss is both conductive and sensorineural, it is called a mixed hearing loss. Get your hearing checked.
What does conductive hearing loss feel like?
For example, if you are in a bad car accident and notice you're struggling to hear speech, and feel like your own voice sounds odd to you, you may have conductive hearing loss. Any pain, pressure, or strange odor in your ears are other clues you may have a condition that causes conductive hearing loss.
Can conductive hearing loss be corrected?
Yes, in most cases a conductive hearing loss can be either cured or treated. The main treatments for conductive hearing loss are: Medical treatment. Hearing instruments such as hearing aids or hearing implants such as e.g., bone conduction devices.
What are the 4 types of hearing loss?
The Four Types of Hearing LossSensorineural Hearing Loss.Conductive Hearing Loss.Mixed Hearing Loss.Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder.Talk to Your Audiologist.
Can conductive hearing loss be reversed?
Conductive hearing loss can usually be reversed by treating the cause of the blockage. If earwax build-up is the issue, a hearing healthcare specialist can safely remove the wax causing the blockage or give you eardrops to use at home to help break it down.
When will the ICD-10-CM H90.A1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H90.A1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can H90.A1 be used for reimbursement?
H90.A1 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2018 icd 10 code update for mental health
- 2. icd 10 code for back pain nos
- 3. icd 10 code for oa knees
- 4. icd 10 code for left conjunctival hemorrhage
- 5. icd 10 code for motorcycle driver hit by car
- 6. on icd-9 cm is for hansen's disease code
- 7. icd 10 code for severe vomiting
- 8. icd 10 code for ventricular enlargement
- 9. icd-10 code for sepsis due to aspiration pneumonia
- 10. icd 10 code for acute respiratory infection