What are the genetic causes of muscular dystrophy?
What causes muscular dystrophy (MD)? Most cases of MD are caused by gene mutations (changes in the DNA sequence) that affect muscle proteins. The mutations are usually inherited, but in some cases they occur spontaneously. These spontaneous mutations can then be inherited by an affected person’s offspring. 1
What is the diagnosis of muscular dystrophy?
The diagnosis of muscular dystrophy is made with a physical examination and diagnostic testing by your child's physician. During the examination, your child's doctor obtains a complete prenatal and birth history of the child and asks if other family members are known to have muscular dystrophy. Blood tests.
Why is muscular dystrophy a genetic disorder?
- Having muscular dystrophy
- Being healthy but carry the mother’s faulty gene
- Being healthy but carry the father’s faulty gene
- Being healthy and won’t inherit any mutated genes
Can congenital muscular dystrophy be prevented?
Currently, Merosin-Positive Congenital Muscular Dystrophy may not be preventable, since it is a genetic disorder. If there is a family history of the condition, then genetic counseling will help assess risks, before planning for a child.
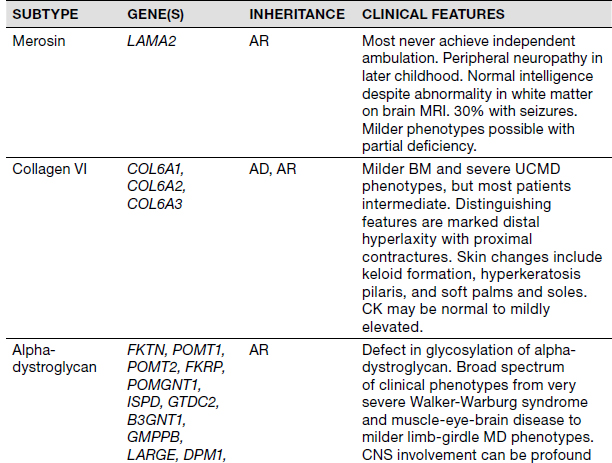
What is congenital muscular dystrophy?
Congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) refers to a group of muscular dystrophies that become apparent at or near birth. Muscular dystrophies in general are genetic, degenerative diseases primarily affecting voluntary muscles.
What is the ICD-10 code for muscular dystrophy?
The ICD-10 Code for muscular dystrophy is G71. 0.
Which code describes congenital myopathy?
ICD-10 code G71. 2 for Congenital myopathies is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
What is the code for congenital?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Q89. 9: Congenital malformation, unspecified.
Which of the following conditions would be reported with Code Q65 81?
Which of the following conditions would be reported with code Q65. 81? Imaging of the renal area reveals congenital left renal agenesis and right renal hypoplasia.
Is muscular dystrophy progressive?
Muscular dystrophy is a group of diseases that cause progressive weakness and loss of muscle mass. In muscular dystrophy, abnormal genes (mutations) interfere with the production of proteins needed to form healthy muscle.
Is congenital myopathy a form of muscular dystrophy?
Congenital myopathies are conditions where changes in the muscle cells make them less able to contract. All these forms of congenital muscular dystrophy lead to muscle weakness and a decrease of muscle tone in early childhood.
What are the different types of congenital myopathy?
The six main types of congenital myopathy are:Central core disease. Central core disease is a type of core myopathy. ... Minicore (multicore) disease. Minicore (multicore) disease is another type of core myopathy. ... Nemaline myopathy. ... Centronuclear myopathy. ... Myotubular myopathy. ... Congenital fiber-type disproportion myopathy.
What is Nemaline myopathy?
Nemaline myopathy is defined by muscle weakness and the presence of fine, thread-like or rod-like structures called “nemaline bodies”, when muscle biopsies are viewed under the microscope.
What is the ICD-10 code for congenital anomalies?
If coded, the ICD-10 code is Q89. 9 (Congenital malformation, unspecified).
What is the ICD-10 code for congenital heart disease?
Q24. 9 - Congenital malformation of heart, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What does the ICD convention NEC indicate?
CPT Coding Mid Term College America Kate PlucasQuestionAnswerWhat does the ICD convention NEC indicate?This designation is used to indicate there is no separate specific code available to represent the condition documented.19 more rows
The ICD code G710 is used to code Distal muscular dystrophy
Distal muscular dystrophy (or distal myopathy) is a group of disorders characterized by onset in the hands or feet. Many types involve dysferlin, but it has been suggested that not all cases do.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'G71.0 - Muscular dystrophy'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code G71.0. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 359.1 was previously used, G71.0 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for upper lip laceration
- 2. what's the icd 10 code for scoliosis
- 3. icd-10 code for heart surgery
- 4. icd 10 code for cirrhosis unspecified
- 5. icd 10 code for heart stents
- 6. icd 10 code for history of panic attacks
- 7. icd 9 code for elevated amonia levels
- 8. icd 10 code for place of occurrence tennis court
- 9. icd 10 code for malignant neoplasm left ovary
- 10. icd 10 code for severe dysmenorrhea