What are the new ICD 10 codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I31.1 Chronic constrictive pericarditis 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code I31.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I31.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How ICD 10 is different from ICD 9 codes?
500 results found. Showing 1-25: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I31.1 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Chronic constrictive pericarditis. Calcification of pericardium; Constrictive pericarditis; Concretio cordis; Pericardial calcification. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I31.1. Chronic constrictive pericarditis.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Oct 01, 2021 · I31.1 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Chronic constrictive pericarditis. It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
What ICD 10 cm code(s) are reported?
The ICD-10-CM code I31.1 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like calcification of pericardium, chronic constrictive pericarditis, chronic pericarditis, constrictive pericarditis, constrictive pericarditis , constrictive pericarditis due to …
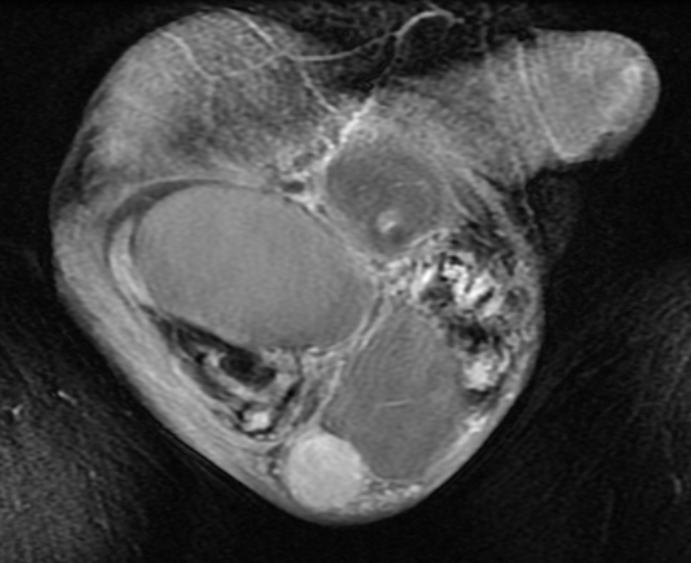
What is constrictive pericarditis?
Constrictive pericarditis – Constrictive pericarditis is the result of scarring and consequent loss of the normal elasticity of the pericardial sac. Pericardial constriction is typically chronic, but variants include subacute, transient, and occult constrictive pericarditis.Dec 2, 2021
Is constrictive pericarditis acute or chronic?
Constrictive pericarditis is long-term, or chronic, inflammation of the pericardium. The pericardium is the sac-like membrane that surrounds the heart. Inflammation in this part of the heart causes scarring, thickening, and muscle tightening, or contracture.
Is constrictive pericarditis the same as cardiac tamponade?
Constrictive pericarditis (CP) and pericardial tamponade are two different entities with different pathophysiology and treatment modalities. However, infrequently patients can present with comparable clinical features, equivocal electrocardiogram (ECG), and analogous echocardiogram and MRI findings.Jul 6, 2020
What is the ICD-10 code for small pericardial effusion?
I31.3ICD-10 code I31. 3 for Pericardial effusion (noninflammatory) is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is the management of constrictive pericarditis?
Pericardiectomy remains the only definitive treatment for constrictive pericarditis. Pericardiectomy, particularly complete pericardiectomy, is indicated once the diagnosis of CP has been confirmed.Dec 6, 2017
What is the difference between acute and constrictive pericarditis?
Acute pericarditis: inflammation of the pericardium that either occurs as an isolated process or with concurrent myocarditis (myopericarditis). Constrictive pericarditis is characterized by compromised cardiac function caused by a thickened, rigid, and fibrous pericardium secondary to acute pericarditis.Mar 18, 2022
What is effusive constrictive pericarditis?
Effusive–constrictive pericarditis is a clinical hemodynamic syndrome in which constriction of the heart by the visceral pericardium occurs in the presence of tense effusion in a free pericardial space.Jan 29, 2004
What is regional cardiac tamponade?
Cardiac tamponade usually results from a general increase in intrapericardial pressure that is applied to the surfaces of the atria, the ventricles and the intrapericardial surfaces of the venae cavae and pulmonary veins, as well as the aorta and the pulmonary arteries.
How does constrictive pericarditis cause pleural effusion?
Pleural effusion occurs in about 50% of patients with constrictive pericarditis [6], and several mechanisms have been proposed for its occurrence. The diastolic dysfunction of the left ventricle might cause elevations in the intravascular hydrostatic pressure, leading to a transudative pleural effusion.Apr 9, 2018
What is the correct ICD-10 code for thrombocytopenia?
ICD-10 | Thrombocytopenia, unspecified (D69. 6)
What is the ICD-10 code for pericardial tamponade?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cardiac tamponade I31. 4.
Which is the correct code for unspecified acute pericarditis?
ICD-10 code I30. 9 for Acute pericarditis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What are the problems with the pericardium?
Problems with the pericardium include. Pericarditis - an inflammation of the sac. It can be from a virus or other infection, a heart attack, heart surgery, other medical conditions, injuries, and certain medicines. Pericardial effusion - the buildup of fluid in the sac.
What is the I31.1 code?
I31.1 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of chronic constrictive pericarditis. The code I31.1 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
Is fever a symptom of pericarditis?
Fever is a common symptom of acute pericarditis. Your doctor may use a physical exam, imaging tests, and heart tests to make a diagnosis. Treatment depends on the cause. NIH: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Cardiac tamponade (Medical Encyclopedia) Pericardiocentesis (Medical Encyclopedia)
What is the cause of pericarditis?
When the cause is established, it is most often due to a viral infection. Bacterial infections and fungal organisms are less common causes.
What does pericarditis look like?
Since most patients will experience vague chest pain, the diagnosis may look like a heart attack, pleurisy, or angina. Patients with suspected acute pericarditis should have an ECG, echocardiogram, and chest X-ray done.
What is the most common disease process involving the pericardium?
What is Pericarditis ? Pericarditis is the most common disease process involving the pericardium and is defined as inflammation of the pericardium, otherwise referred to as the pericardial sac, according to the the National Center for Biotechnology Information.
How long does pericarditis last?
Acute pericarditis, lasting less than 3 weeks. Incessant pericarditis, lasting approximately 4-6 weeks but less than 3 months. Chronic pericarditis, lasting more than 3 months. Recurrent pericarditis, an episode that occurs after being symptom free for 4-6 weeks.
Where does pericardial irritability occur?
It occurs when the irritated layers of the pericardium rub against each other. It often comes on quickly and occurs in the middle or left side of the chest. It may spread to the left shoulder and neck. It often gets worse when coughing, taking deep breaths, or lying down. It lessens when sitting up and leaning forward.
Why is the pericardium important?
The pericardium, although not critical for human survival, does serve some important functions: It keeps the heart fixed in place within the thoracic (chest) cavity. It forms as a barrier to the heart to prevent infection and malignancy that might spread from nearby organs like the lungs.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for instrasubstance tear
- 2. icd 9 code for abnormal stress test
- 3. icd 9 code for rectal cancer
- 4. icd 10 code for pressure ulcer left ankle unspecifed
- 5. icd-10-cm external cause of morbidity code for contact with hot drink, initial encounter, is
- 6. icd 10 code for screening for hepatitis b immunity
- 7. icd 10 code for bilateral lower quad pain
- 8. icd 10 code for pregnancy, twins, undelivered
- 9. icd 10 code for accudebtak striking another person
- 10. icd 10 code for ethrimoral