What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Can S20.224 be used for reimbursement?
About this website
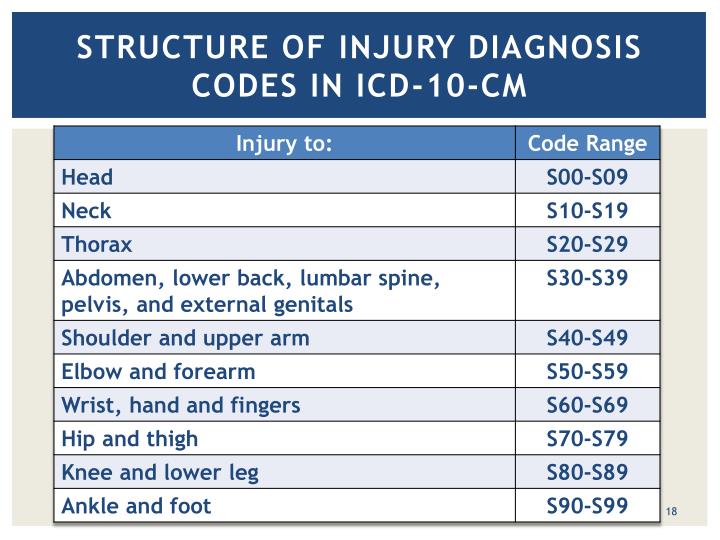
What is the ICD 10 code for Contusion of back?
Contusion of lower back and pelvis, initial encounter S30. 0XXA is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S30. 0XXA became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-9 code for back Contusion?
ICD-9 code 922.3 for Contusion of back is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -CONTUSION WITH INTACT SKIN SURFACE (920-924).
What is the ICD 10 code for chest Contusion?
922.1 - Contusion of chest wall | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD 10 code for Contusion left buttock?
922.32 - Contusion of buttock. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for M54 50?
M54. 50, Low back pain, unspecified.
What is ICD-10 code R05?
1 (Acute cough) R05.
What is the ICD 10 code for contusion?
Contusion of thorax, unspecified, initial encounter S20. 20XA is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S20. 20XA became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for multiple contusions?
922.8 - Contusion of multiple sites of trunk | ICD-10-CM.
What do you do for a contusion?
Initial treatment for contusion should include rest, icing the affected area for 20 minutes, and applying a compression wrap to help minimize swelling. If there is an accompanying open wound, keep the area clean and bandaged.
What is the ICD 10 code for buttock pain?
Although there isn't a specific ICD-10-CM code for pain in the buttock, you can use M79. 1 Myalgia. In the clinical description for M79.
What is the ICD 10 code for lumbar Strain?
ICD-10-CM Code for Strain of muscle, fascia and tendon of lower back, initial encounter S39. 012A.
What is the ICD 10 code for left shoulder pain?
M25. 512 Pain in left shoulder - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What is chest contusion?
A chest contusion, or bruise, is caused by a fall or direct blow to the chest. Car crashes, falls, getting punched, and injury from bicycle handlebars are common causes of chest contusions.
What is lung contusion?
Pulmonary contusion is another name for a bruised lung. A blow to your chest, such as from hitting a car steering wheel or air bag, can bruise your lung.
What is mediastinal hematoma?
A mediastinal hematoma is defined as presence of blood within the mediastinum as it dissects fascial planes. Traumatic etiologies that can contribute to a widened mediastinum, either in isolation or associated with an aortic injury, include vertebral or sternal fractures or a ruptured esophagus.
What is the ICD 10 code for chest wall hematoma?
219A: Contusion of unspecified front wall of thorax, initial encounter.
What is a bruise?
A bruise, or contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue in which capillaries and sometimes venules are damaged by trauma, allowing blood to seep, hemorr hage, or extravasate into the surrounding interstitial tissues . Bruises, which do not blanch under pressure, can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle, or bone. Bruises are not to be confused with other similar-looking lesions primarily distinguished by their by their diameter or causation. These lesions include petechia (< 3 mm result from numerous and diverse etiologies such as adverse reactions from medications such as warfarin, straining, asphyxiation, platelet disorders and diseases such as cytomegalovirus), purpura (3 mm to 1 cm, classified as palpable purpura or non-palpable purpura and indicates various pathologic conditions such as thrombocytopenia), and ecchymosis (>1 cm caused blood dissecting through tissue planes and settled in an area remote from the site of trauma or pathology such as periorbital ecchymosis, i.e.,"raccoon eyes" , arising from a basilar skull fracture or from a neuroblastoma).
What is DRG 604-605?
DRG Group #604-605 - Trauma to the skin, subcut tissue and breast without MCC.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes. birth trauma ( P10-P15)
Can S20.224 be used for reimbursement?
S20.224 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for annual psa screening
- 2. icd-10-cm code for infectional erythema
- 3. icd 10 code for foot contusion
- 4. icd 10 code for diabetes 2 insulin dependent
- 5. icd 10 code for round ligament pain in pregnancy
- 6. icd 10 code for status bronchoscopy
- 7. icd 10 code for dysarthria
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for removal of gastric balloon
- 9. icd 10 code for closed nondisplaced fracture of triquetrum
- 10. icd 10 code for foley catheter pulled out