Perforated corneal ulcer, unspecified eye
- H16.079 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H16.079 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H16.079 - other international versions of ICD-10 H16.079 may differ.
What are the less common causes of corneal ulcer?
Less common causes of corneal ulcers include bacterial infections, viral infections, and other diseases. These may originate in the eye or may develop secondary to a disease elsewhere in the body. Examples of other diseases that may predispose a pet to corneal ulcers include:
Can I work with a corneal ulcer?
Treating a corneal ulcer starts with correctly identifying the causative organism, and that involves a combination of approaches. Here, experts share diagnostic tips, and explain how and when to culture and which treatments you should reach for.
What does a corneal ulcer feel like?
A corneal ulcer is an open sore on the cornea of the eye. It's usually due to an infection affecting the clear front surface of the eye, resulting in inflammation of the cornea ( keratitis ). A corneal ulcer typically causes a painful red eye, with mild to severe eye discharge and reduced vision. Medical treatment is required.
What are the differential diagnoses for corneal ulcer?
•The most important, and at times the most difficult, differential diagnosis is determining whether one is dealing with an infection of the cornea or purely inflammation of the cornea Infection - Hallmarks •Epithelial defect(s) •Underlying stromal infiltrate (immune ring)
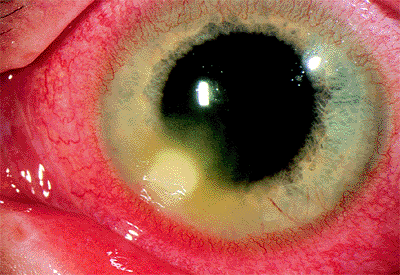
Are corneal ulcer and keratitis the same?
Keratitis, also known as a corneal ulcer, is an inflammation or irritation of the cornea. Although treatable, this condition is the most common cause of corneal blindness through an infection in the United States.
Does corneal ulcer affect both eyes?
There may be scarring from prior corneal ulcers. There may be a single (or multiple ulcers) in the eye, and ulcers may be present in one or both eyes. Some more severe corneal ulcers are associated with iritis, which is an inflammatory response within the anterior chamber.
What are the types of corneal ulcer?
The main cause of corneal ulcers is infection.Acanthamoeba keratitis. This infection most often occurs in contact lens wearers. ... Herpes simplex keratitis. Herpes simplex keratitis is a viral infection that causes repeated flare-ups of lesions or sores in the eye. ... Fungal keratitis. ... Other causes.
What is a marginal corneal ulcer?
Disease. Marginal keratitis is an inflammatory disease of the peripheral cornea, characterized by peripheral stromal infiltrates which are often associated with epithelium break down and ulceration.
What is corneal ulcer of the eye?
Definition. The cornea is the clear tissue at the front of the eye. A corneal ulcer is an open sore in the outer layer of the cornea. It is often caused by infection. At first, a corneal ulcer may seem like conjunctivitis, or pink eye.
What is the difference between a corneal ulcer and an abrasion?
A corneal abrasion is a scrape of the top layer, the epithelium, but does not go through Bowman's layer underneath this. A corneal ulcer is an open sore/erosion (from inflammation or infection) that goes through Bowman's layer into the deeper layers of the cornea.
How is a corneal ulcer diagnosed?
How is a corneal ulcer diagnosed?Perform an examination with a slit lamp microscope. The slit lamp focuses a narrow “slit” of light onto the eye. ... Your provider may apply a fluorescein dye to your eye. This yellow dye highlights any damage to your cornea.Take a sample of the infected tissue.
What is the white part of the eye called?
Listen to pronunciation. (SKLAYR-uh) The white layer of the eye that covers most of the outside of the eyeball.
What is non healing corneal ulcer?
Non-healing corneal ulcers (often called Indolent Ulcers) are superficial abrasions on the surface of the eye that fail to heal after 7-10 days. Non-healing ulcers are due to an abnormality of the corneal epithelium of the eye. This abnormal epithelium cannot stick to the surface of the eye following a minor injury.
Is bacterial keratitis unilateral or bilateral?
The disease is usually unilateral, but rarely may be bilateral in contact lens wearers.
What is superficial keratitis?
Superficial punctate keratitis is an eye disorder caused by death of small groups of cells on the surface of the cornea (the clear layer in front of the iris and pupil). The eyes become red, watery, and sensitive to light, and vision may decrease somewhat.
What is interstitial keratitis?
ICD-9. 370.50. Defined narrowly, interstitial keratitis is any non-ulcerating inflammation of the corneal stroma without the involvement of either the epithelium or endothelium.
The ICD code H160 is used to code Corneal ulcer
Corneal ulcer, or ulcerative keratitis, is an inflammatory or more seriously, infective condition of the cornea involving disruption of its epithelial layer with involvement of the corneal stroma. It is a common condition in humans particularly in the tropics and the agrarian societies.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code H16.011 and a single ICD9 code, 370.03 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
.jpg)
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for fracture from 5 years ago
- 2. icd 10 code for unknown cause of injury
- 3. icd 10 cm code for uveitic glaucoma
- 4. icd 10 code for back pain due to mva
- 5. icd 10 code for aftercare wound debridement
- 6. icd 10 code for status post g tube
- 7. icd 10 code for trembling of hands
- 8. icd 10 code for pain in the lung
- 9. icd 10 code for active pulmonary tuberculosis
- 10. icd 10 code for laceration left elbow