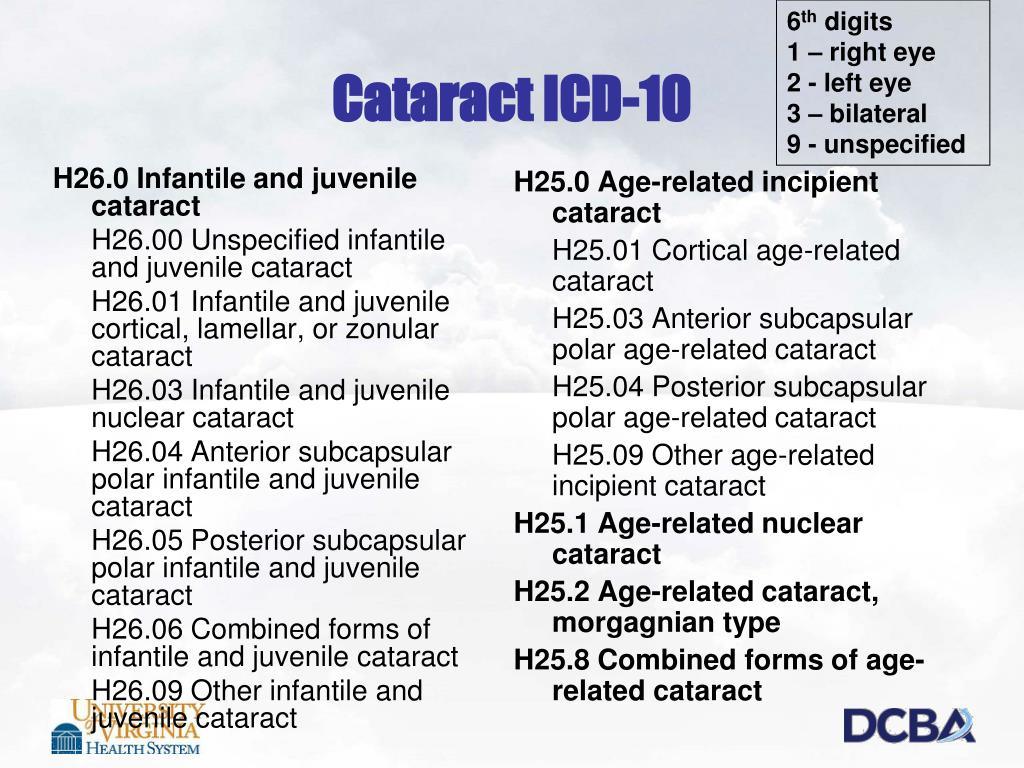
What is a cortical cataract and how is it treated?
· Cortical age-related cataract, right eye. H25.011 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H25.011 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for cataract?
· H25.011. H25.011 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Cortical age-related cataract, right eye . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
What is the diagnosis code for cataract surgery?
Consider using any of the following ICD-10 codes with a higher level of specificity when coding for cortical age-related cataract: BILLABLE CODE - Use H25.011 for Cortical age-related cataract, right eye BILLABLE CODE - Use H25.012 for Cortical age-related cataract, left eye BILLABLE CODE - Use H25.013 for Cortical age-related cataract, bilateral
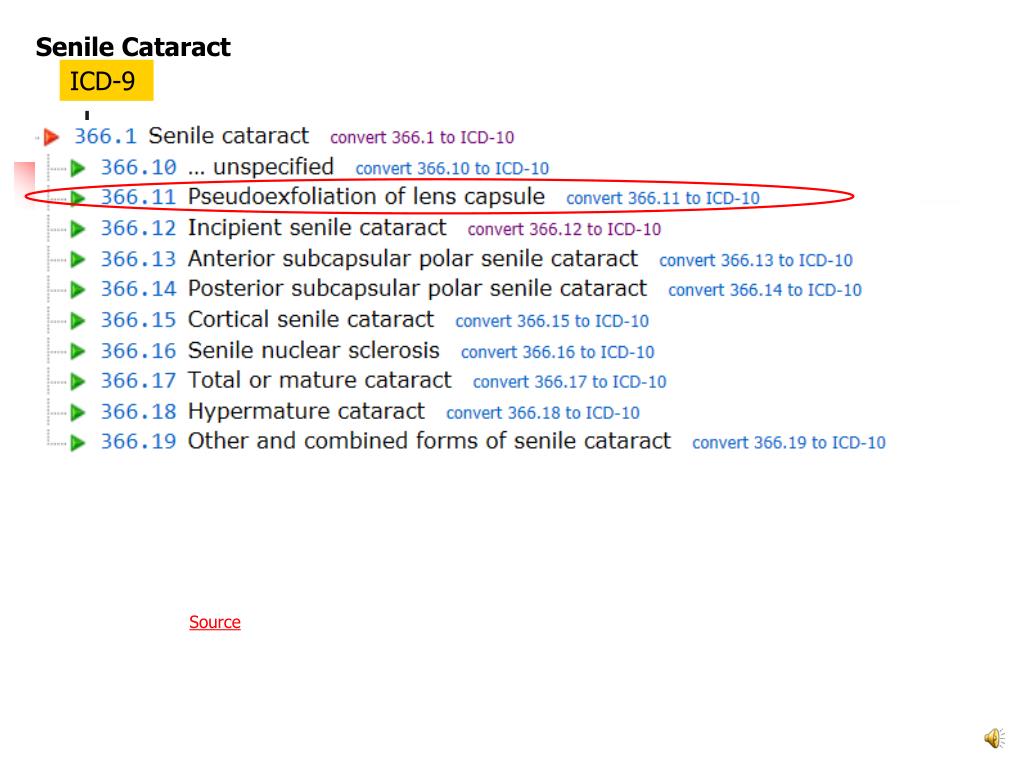
What is incipient senile cataract?
· Unspecified cataract. H26.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H26.9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H26.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 H26.9 may differ.
What is cortical cataract?
Cataracts that affect the edges of the lens (cortical cataracts). A cortical cataract begins as whitish, wedge-shaped opacities or streaks on the outer edge of the lens cortex. As it slowly progresses, the streaks extend to the center and interfere with light passing through the center of the lens.
What is DX code H25 812?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H25. 812: Combined forms of age-related cataract, left eye.
What is the ICD-10 code for cataract surgery?
Z98. 4 - Cataract extraction status. ICD-10-CM.
What is H25 13 code?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H25. 13: Age-related nuclear cataract, bilateral.
What is diagnosis code Z51 11?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z51. 11: Encounter for antineoplastic chemotherapy.
How do you code left eye cataract?
ICD-10 Code for Combined forms of age-related cataract, left eye- H25. 812- Codify by AAPC.
What is the extraction of cataract?
Cataract extraction is a surgical procedure to remove a lens in the eye that has become cloudy over time, affecting vision in that eye. It is part of a cataract operation, in which the removed lens is replaced with an artificial, manmade lens.
How do you bill Goniotomy for cataract surgery?
A. Use CPT 65820 (Goniotomy).
What is the CPT code 66984?
66984—Extracapsular cataract removal with insertion of intraocular lens prosthesis (1-stage procedure), manual or mechanical technique (e.g., irrigation and aspiration or phacoemulsification); without endoscopic cyclophotocoagulation.
What is diagnosis code H52 13?
13.
What is diagnosis code H43 393?
ICD-10 code H43. 393 for Other vitreous opacities, bilateral is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the eye and adnexa .
What is H52 03 code?
03.
How many different types of cataracts are there?
How many different types of cataracts are there? According to ICD-10-CM, there are close to 70 — ranging from age-related to zonular cataracts.
What is the sixth character of a code?
For most codes that require laterality, you report this number as the sixth character (e.g., H21.22- Degeneration of ciliary body ), but there are some codes where it appears as the fifth character (e.g., H26.3-, Drug-induced cataract ). And for other codes, you don’t report laterality at all.
How to treat cataracts?
Cataracts usually develop slowly. New glasses, brighter lighting, anti-glare sunglasses or magnifying lenses can help at first. Surgery is also an option. It involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial lens. Wearing sunglasses and a hat with a brim to block ultraviolet sunlight may help to delay cataracts.
What is H25.01 code?
H25.01 is a "header" nonspecific and non-billable diagnosis code code , consider using a code with a higher level of specificity for a diagnosis of cortical age-related cataract. The code is NOT valid for the year 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. Category or Header define the heading of a category of codes that may be further subdivided by the use of 4th, 5th, 6th or 7th characters.
Can cataracts spread to both eyes?
A cataract can occur in either or both eyes. It cannot spread from one eye to the other. Common symptoms are
What is the cause of cataracts?
They may occur in people of all ages, but are most common in the elderly. A disorder characterized by partial or complete opacity of the crystalline lens of one or both eyes. This results in a decrease in visual acuity and eventual blindness if untreated.
When will the ICd 10-CM H26.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H26.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the condition where the lens of the eye becomes cloudy?
A condition in which the lens of the eye becomes cloudy. Symptoms include blurred, cloudy, or double vision; sensitivity to light; and difficulty seeing at night. Without treatment, cataracts can cause blindness. There are many different types and causes of cataracts.
What is the ICD code for cataracts?
The ICD code H25 is used to code Cataract. A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye leading to a decrease in vision. It can affect one or both eyes. Often it develops slowly. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, ...
What is the ICD code for age related cataract?
ICD Code H25.01 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the four child codes of H25.01 that describes the diagnosis 'cortical age-related cataract' in more detail.
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code H25.01 is a non-billable code.
What is the ICd 10 code for cataract?
H25.013 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of cortical age-related cataract, bilateral. The code H25.013 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code H25.013 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like bilateral cortical age-related cataract eyes, cortical age-related cataract of left eye, cortical age-related cataract of right eye or cortical senile cataract.#N#The code H25.013 is applicable to adult patients aged 15 through 124 years inclusive. It is clinically and virtually impossible to use this code on a patient outside the stated age range.
How to treat cataracts?
Cataracts usually develop slowly. New glasses, brighter lighting, anti-glare sunglasses or magnifying lenses can help at first. Surgery is also an option. It involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial lens. Wearing sunglasses and a hat with a brim to block ultraviolet sunlight may help to delay cataracts.
Can cataracts spread to both eyes?
A cataract can occur in either or both eyes. It cannot spread from one eye to the other. Common symptoms are
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for noncompliant with medications
- 2. icd 10 code for cerebral metastases
- 3. icd 10 code for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
- 4. icd 10 code for uti with e coli
- 5. icd 10 cm code for uterine fibroid tumor in pregnancy week 14
- 6. icd 9 code for paracentesis
- 7. icd 10 code for abnormal skin lesion on face
- 8. icd 10 code for bruising of skin
- 9. icd 10 code for neuro
- 10. icd 10 code for raised intraocular pressure