What is the ICD 10 code for allergy to milk products?
Allergy to milk products 1 Z91.011 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Z91.011 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z91.011 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z91.011 may differ. More ...
What is the ICD 10 code for allergic rhinitis?
This code includes colitis, gastroenteritis, and milk protein. Allergic rhinitis is classified to code 477.1. An atopic food allergy is classified to code 691.8. If the dermatitis was due to food in contact with the skin, assign code 692.5. Code 693.1 is assigned for dermatitis due to food taken internally.
What is the ICD 10 code for potential health hazards?
Z77-Z99 Persons with potential health hazards related to family and personal history and certain conditions influencing health status Z91.011 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z91.011 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the CPT code for gastroenteritis and Colitis?
A gastrointestinal manifestation is classified to code 558.3, Allergic gastroenteritis and colitis. This code includes colitis, gastroenteritis, and milk protein. Allergic rhinitis is classified to code 477.1. An atopic food allergy is classified to code 691.8.
What is the ICD-10 code for cow's milk protein sensitivity?
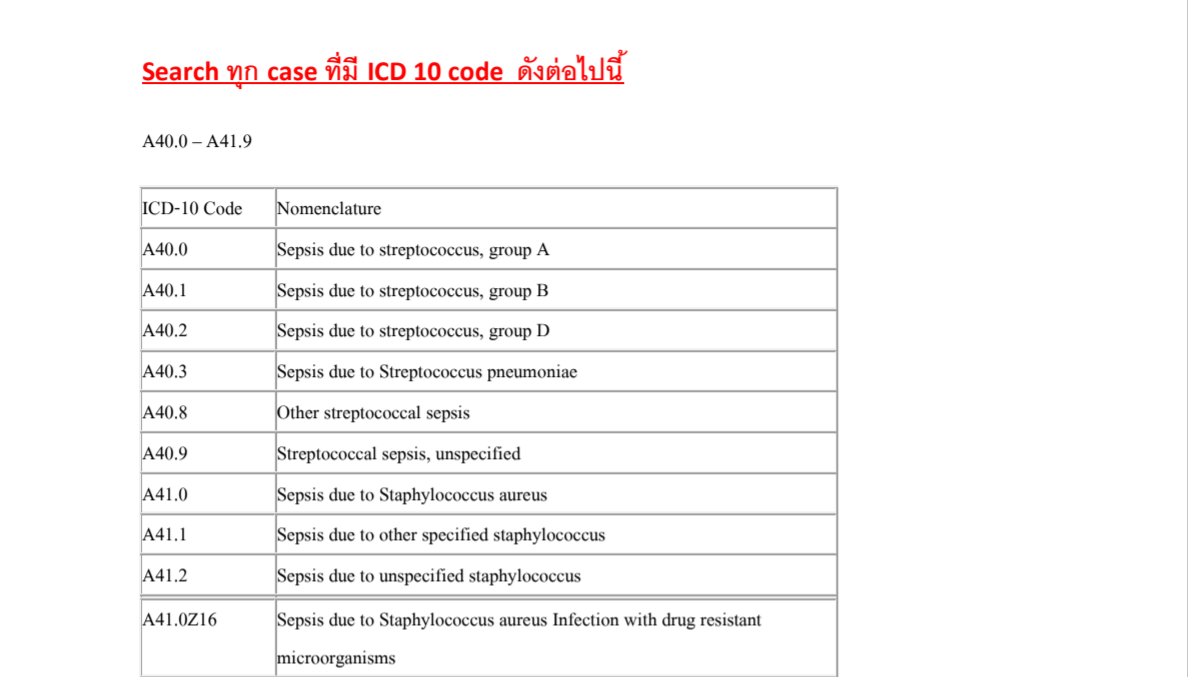
ICD-10 Code for Allergy to milk products- Z91. 011- Codify by AAPC.
What is cow protein Allergy?
Cow's milk protein allergy (CMPA) is the most common food allergy in babies. CMPA occurs when the body's immune system abnormally reacts to a protein in the milk of cows and some other animals. It usually occurs in babies younger than 1 year of age.
Which protein is CMPA?
CMPA is an immunological reaction to one or more milk proteins: α-lactalbumin, ß-lactoglobulin, casein, IgE or non-IgE associated, responsible of immediate or late onset symptoms.
How do you test for cow protein Allergy?
If cow's milk protein allergy (CMPA), also known as cow's milk allergy (CMA), is suspected, your doctor may then perform specific allergy tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include a blood test, skin prick test, patch test, or elimination diet followed by food challenge.
Is cow's milk protein allergy the same as lactose intolerant?
It can be tricky to distinguish between the two but they're actually completely different conditions. A food allergy, such as cow's milk allergy, is an immune reaction to the protein in milk. A lactose intolerance is caused by the inability to break down lactose, which is the sugar in milk.
What causes cow milk protein allergy?
CMPA is a food allergy caused by a baby's immune system reacting to proteins in cow's milk. Some babies may develop CMPA after eating or drinking products containing cow's milk protein, which can cause an immune reaction resulting in allergic symptoms.
What is cow milk allergy?
Cows' milk allergy can cause a wide range of symptoms, including: skin reactions – such as a red itchy rash or swelling of the lips, face and around the eyes. digestive problems – such as stomach ache, vomiting, colic, diarrhoea or constipation. hay fever-like symptoms – such as a runny or blocked nose.
How long does cow's milk protein allergy last?
Studies show that most children with non-IgE-mediated reactions will outgrow cows' milk allergy by the time they are 3 years old. For children with IgE-mediated reactions, studies show that about half of these children will outgrow cows' milk allergy by the time they are 5 years old.
When does cow's milk protein allergy start?
Typically the presence of cow's milk allergy appears within the first few months of life and usually before six months. Symptoms can present a few days or weeks after the ingestion of cow's milk protein. The symptoms can vary from diarrhea and emesis to life-threatening anaphylaxis.
Can you be allergic to protein?
Excessive intestinal gas, bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea are common presenting symptoms. Whereas, in immunological food protein allergies, even trace amounts of the sensitized food protein can trigger an explosive reaction and may involve the skin and blood vessels.
What are the symptoms of protein intolerance?
Table 5.1GastrointestinalSymptomsSyndromesVomitingQuick onset syndromesDiarrhoeaLate onset syndromesAbdominal painCows' milk sensitive enteropathy15 more rows
How do you get a CMPA diagnosis?
In addition to your child's history and a physical examination, the two best tests for CMPA are a stool test and an elimination diet. A stool test, which checks for blood in the stool, can be done at most pediatricians' offices. This is a very common test.
What are the symptoms of protein intolerance?
Table 5.1GastrointestinalSymptomsSyndromesVomitingQuick onset syndromesDiarrhoeaLate onset syndromesAbdominal painCows' milk sensitive enteropathy15 more rows
What are the symptoms of cow milk allergy?
Cows' milk allergy can cause a wide range of symptoms, including: skin reactions – such as a red itchy rash or swelling of the lips, face and around the eyes. digestive problems – such as stomach ache, vomiting, colic, diarrhoea or constipation. hay fever-like symptoms – such as a runny or blocked nose.
What foods to avoid if you have a milk protein allergy?
Meats, fish, poultry and cheeseAll cheese, cottage cheese, cream cheese.Some sausage products, bologna, frankfurters.Breaded meats, meatloaf, croquettes, casseroles, hamburgers (unless made without milk)Commercial entrees made with milk or milk solids.
When does cows milk protein allergy present?
Typically the presence of cow's milk allergy appears within the first few months of life and usually before six months. Symptoms can present a few days or weeks after the ingestion of cow's milk protein. The symptoms can vary from diarrhea and emesis to life-threatening anaphylaxis.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code.
When will the ICD-10 T78.40XA be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM T78.40XA became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a Z code?
Note: Z codes represent reasons for encounters. A corresponding procedure code must accompany a Z code if a procedure is performed. Categories Z00-Z99 are provided for occasions when circumstances other than a disease, injury or external cause classifiable to categories A00-Y89 are recorded as 'diagnoses' or 'problems'. This can arise in two main ways:
What does K90.4 mean in milk NEC?
If you go into the index under "intolerance, milk NEC" it leads you to K90.4 - Malabsorption due to intolerance, not elsewhere classified#N#Under K90.4 in the tabular it also says "Malabsorption due to intolerance to protein"
What is the code for atopic food allergy?
An atopic food allergy is classified to code 691.8. If the dermatitis was due to food in contact with the skin, assign code 692.5. Code 693.1 is assigned for dermatitis due to food taken internally. This code is also used if the food allergy is unspecified. Code 995.7 is assigned for other adverse food reactions, not elsewhere classified. Also assign additional codes to identify the type of reaction such as hives (708.0) and wheezing (786.07).
What is the ICD-9 code for colitis?
The appropriate ICD-9-CM code assignment will depend on the patient’s response to the food allergy. A gastrointestinal manifestation is classified to code 558.3, Allergic gastroenteritis and colitis. This code includes colitis, gastroenteritis, and milk protein. Allergic rhinitis is classified to code 477.1.
What is it called when you are allergic to food?
A severe allergic reaction to food is called anaphylaxis. Signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis include the following: • quick swelling of the throat and tongue; • airway constriction causing breathing trouble; • shock; • rapid pulse; and/or. • dizziness, lightheadedness, or loss of consciousness.
What is the ICd 10 code for milk allergy?
Z91.011 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of allergy to milk products. The code Z91.011 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code Z91.011 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like allergy to casein, allergy to cheese, allergy to cow's milk protein, allergy to dairy food, milk-induced pulmonary disease in infant , secondary hemosiderosis, etc. The code is exempt from present on admission (POA) reporting for inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals.#N#The code Z91.011 describes a circumstance which influences the patient's health status but not a current illness or injury. The code is unacceptable as a principal diagnosis.
How to prevent food allergies?
Wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace, and carry an auto-injector device containing epinephrine (adrenaline). You can only prevent the symptoms of food allergy by avoiding the food. After you and your health care provider have identified the foods to which you are sensitive, you must remove them from your diet.
What does "undetermined" mean in medical terms?
Clinically undetermined - unable to clinically determine whether the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission.
Is Z91.011 a POA?
Z91.011 is exempt from POA reporting - The Present on Admission (POA) indicator is used for diagnosis codes included in claims involving inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals. POA indicators must be reported to CMS on each claim to facilitate the grouping of diagnoses codes into the proper Diagnostic Related Groups (DRG). CMS publishes a listing of specific diagnosis codes that are exempt from the POA reporting requirement. Review other POA exempt codes here.
What is Cow's milk protein intolerance?
Cow’s milk protein intolerance (CMPI) is an abnormal response by the body's immune system to a protein found in cow's milk, which causes injury to the stomach and intestines. Cow's milk protein intolerance is not lactose intolerance .
Signs and Symptoms
CMPI symptoms will usually develop within the first week of starting cow’s milk in their diet. The signs might manifest as a skin rash or eczema, or involve the GI tract, such as vomiting, abdominal pain, blood in the stool, mucousy stool, and diarrhea.
Diagnosis
History and physical examination are the most helpful investigations in diagnosing CMPI. Timing of the symptoms, age of the patient, and symptoms related to feeds are key to diagnosis. There may be microscopic blood in the stool due to damage to the intestines.
Treatment
The main treatment of CMPI is to remove cow's milk protein from the diet Typically, the diet starts with an extensively hydrolyzed formula which is a formula of broken down proteins Soy milk / goat's milk / sheep's milk are not appropriate alternatives in most children.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for metal grinding
- 2. icd-10 code for v iral uri
- 3. icd 10 pcs code for stenting of the lad with drug eluting stent
- 4. icd code for tinea
- 5. icd 9 code for toothache
- 6. icd 10 code for aphasia following traumatic brain injury
- 7. icd 10 pcs code for epidural during labor
- 8. icd 10 code for fibrous cyst right post auricular
- 9. icd 10 code for less friction with intercourse
- 10. icd 10 code for cast complication