What is the ICD 10 code for cryptogenic organizing pneumonia?
Oct 01, 2021 · Pulmonary cryptococcosis. B45.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B45.0 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B45.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 B45.0 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for pulmonary cryptococcosis?
Oct 01, 2021 · Cryptococcosis, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code B45.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B45.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for fungal pneumonia?
Oct 01, 2021 · J16.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J16.8 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J16.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 J16.8 may differ.
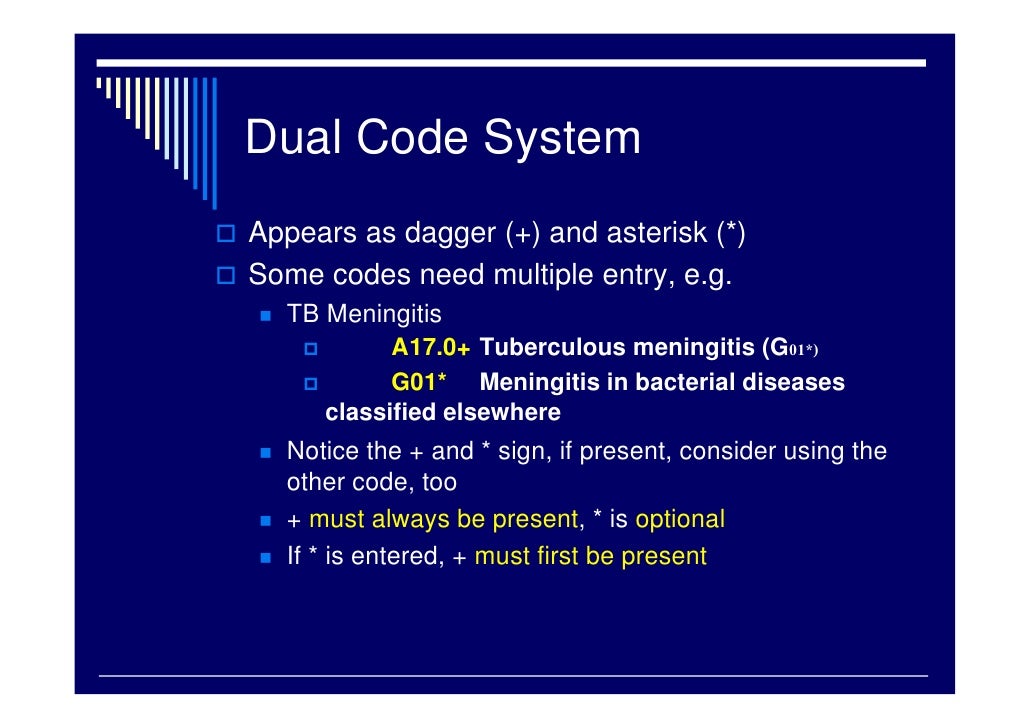
What is the ICD 10 code for excluded note?
Oct 01, 2021 · Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. J84.116 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J84.116 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is cryptococcal pneumonia?
What is disseminated cryptococcosis?
What is the ICD-10 code for cryptococcal meningitis?
What is the ICD-10 code for community acquired pneumonia?
What causes cryptococcal disease?
How many types of cryptococcosis are there?
How do you get cryptococcal meningitis?
What are the symptoms of cryptococcal meningitis?
...
The symptoms of cryptococcal meningitis include:
- Headache.
- Fever.
- Neck pain.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Sensitivity to light.
- Confusion or changes in behavior.
What is Crypto caucus?
What is the most common cause of community acquired pneumonia?
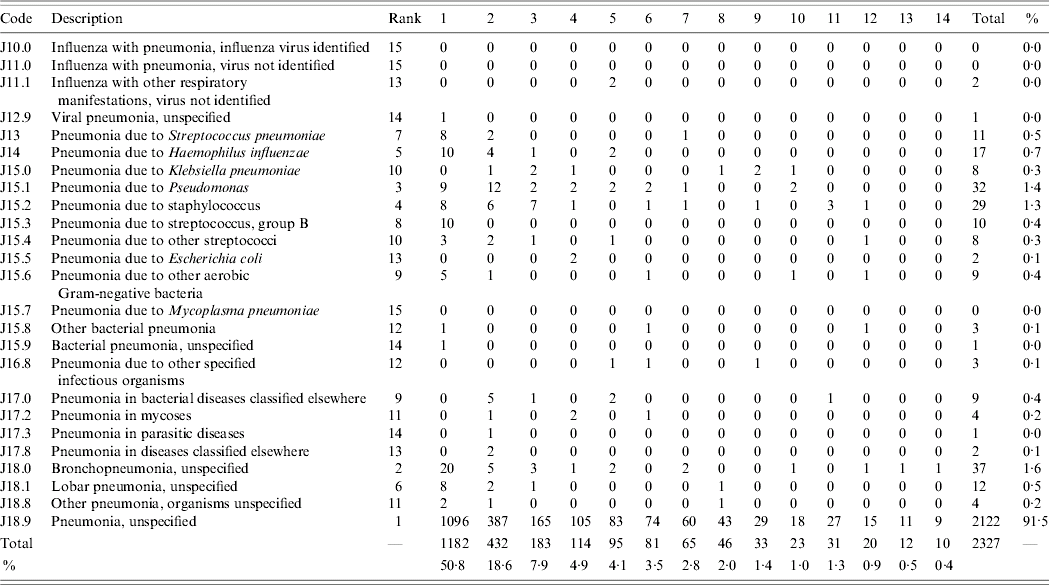
What is the ICD-10 code J18 9?
What is the ICD-10 code for atypical pneumonia?
| ICD-10 code | ICD-10 term | Read term |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumonia – PPLO | ||
| Atypical pneumonia | ||
| J158 | Other bacterial pneumonia | Other bacterial pneumonia |
| Pneumonia – other specif.bact. |
What is a Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia?
it is characterized by a dramatic onset of a "pneumonia like" illness with cough fever malaise fatigue and weight loss. pathological features include prominent interstitial inflammation without collagen fibrosis diffuse fibroblastic foci and no microscopic honeycomb change. there is excessive proliferation of granulation tissue within small airways and alveolar ducts.
What is pneumonia in the lungs?
Pneumonia is an infection in one or both of the lungs. Many germs, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, can cause pneumonia. You can also get pneumonia by inhaling a liquid or chemical. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age, or already have health problems.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
Type 1 Excludes. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes note. It means "NOT CODED HERE!". An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note.
What does "excludes" mean in a note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes note. It means "NOT CODED HERE!" . An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. ...
What is interstitial lung disease?
Information for Patients. Interstitial Lung Diseases. Interstitial lung disease is the name for a large group of diseases that inflame or scar the lungs. The inflammation and scarring make it hard to get enough oxygen. The scarring is called pulmonary fibrosis.
What is the name of the disease that scars the lungs?
Interstitial lung disease is the name for a large group of diseases that inflame or scar the lungs. The inflammation and scarring make it hard to get enough oxygen. The scarring is called pulmonary fibrosis. Breathing in dust or other particles in the air is responsible for some types of interstitial lung diseases .
What causes silica dust?
Silicosis, from inhaling silica dust. Other causes include autoimmune diseases or occupational exposures to molds, gases, or fumes. Some types of interstitial lung disease have no known cause. Treatment depends on the type of exposure and the stage of the disease.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, fevers, chills, chest pain, headache, sweating, and weakness. Inflammation of any part, segment or lobe, of the lung parenchyma. Inflammation of the lungs with consolidation and exudation. Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung, usually caused by an infection.
How old do you have to be to get pneumonia?
People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age , or already have health problems. If you have pneumonia, you may have difficulty breathing and have a cough and a fever. A physical exam and history can help determine if you have pneumonia.
What causes pneumonia in the lung?
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung, usually caused by an infection. Three common causes are bacteria, viruses and fungi. You can also get pneumonia by accidentally inhaling a liquid or chemical. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age, or already have health problems.
What causes pneumonia in older people?
Three common causes are bacteria, viruses and fungi. You can also get pneumonia by accidentally inhaling a liquid or chemical. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age, or already have health problems. If you have pneumonia, you may have difficulty breathing and have a cough and a fever.
What is lung parenchyma?
An acute, acute and chronic, or chronic inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma, due to infections (viruses, fungi, mycoplasma, or bacteria), treatment (e.g. Radiation), or exposure (inhalation) to chemicals.
What is pneumonia in the lungs?
Pneumonia is an infection in one or both of the lungs. Many germs, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, can cause pneumonia. You can also get pneumonia by inhaling a liquid or chemical. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age, or already have health problems.
How old do you have to be to get pneumonia?
You can also get pneumonia by inhaling a liquid or chemical. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age, or already have health problems. Symptoms of pneumonia vary from mild to severe. See your doctor promptly if you.
Can antibiotics help with pneumonia?
If bacteria are the cause, antibiotics should help. If you have viral pneumonia, your doctor may prescribe an antiviral medicine to treat it. Preventing pneumonia is always better than treating it. Vaccines are available to prevent pneumococcal pneumonia and the flu.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for abnormal finding chest imaging.
- 2. icd code for serve neck pain
- 3. icd 10 code for cystic fibrosis in pregnancy
- 4. icd 10 code for anal fissures
- 5. icd 10 code for sickle-cell crisis with acute chest syndrome
- 6. icd 10 code for stage 3 sacral decubitus
- 7. icd 10 code for deficient homocysteine
- 8. icd 10 cm code for nonspecific plump lymph nodes
- 9. icd 10 code for abn mammo
- 10. icd 10 code for colitis due to clostridium difficile