Full Answer
What are the ICD 10 codes for stroke?
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
What is the ICD 10 code for history of cirrhosis?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J84.116. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. Type 1 Excludes. organizing pneumonia NOS, or due to known underlying cause ( J84.89) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z82.3 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Family history of stroke.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Oct 01, 2021 · J84.116 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J84.116 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J84.116 - other international versions of ICD-10 J84.116 may differ.
What is the ICD - 10 code for brain stem stroke?
• If the patient has late effects or residual deficits from the stroke, a code from category I69 (sequela of cerebrovascular disease) is appropriate as the principal diagnosis • If the patient has no residual deficits from the stroke, code Z86.73 (personal history of stroke or TIA without residual deficits) is appropriate as the principal diagnosis • Code Z86.73 can also be used as a …
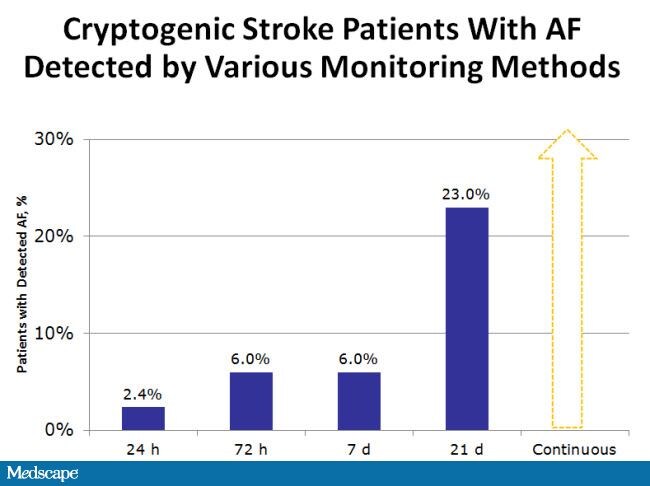
What is a cryptogenic stroke ICD-10?
Cerebral infarction due to embolism of unspecified cerebral artery. I63. 40 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is cryptogenic stroke?
By the TOAST classification (table 1), which is the one most commonly used in clinical practice, cryptogenic stroke (or stroke of undetermined origin in TOAST terminology) is defined as brain infarction that is not attributable to a source of definite cardioembolism, large artery atherosclerosis, or small artery ...
What is the ICD-10 code for cryptogenic cirrhosis?
K74. 69 - Other cirrhosis of liver | ICD-10-CM.
How many strokes are cryptogenic?
It's estimated that about 1 in 3 ischemic strokes are cryptogenic.
How is cryptogenic stroke diagnosed?
Diagnostic criteria for ESUS include brain CT or MRI to demonstrate non-lacunar stroke, extracranial and intracranial imaging to exclude ≥50% proximal stenosis, and electrocardiography, echocardiography, and cardiac rhythm monitoring for ≥24 hours to exclude cardioembolic sources 7.Feb 12, 2016
Is a TIA a cryptogenic stroke?
In contrast to myocardial infarction and peripheral vascular disease, up to one-third of TIA and ischemic strokes are cryptogenic despite detailed diagnostic workup, resulting in roughly 400,000 cases annually in Western Europe alone.
What is cryptogenic cirrhosis?
Cryptogenic cirrhosis is a condition that impairs liver function. People with this condition develop irreversible liver disease caused by scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), typically in mid- to late adulthood.
What is ICD 10 code for cirrhosis of liver?
Table 1ICD-10-AM coden with codeCirrhosisK70.3 Alcoholic cirrhosis of liver193K74.4 Secondary biliary cirrhosis*12K74.5 Biliary cirrhosis, unspecified617 more rows•Sep 17, 2020
How do you code decompensated cirrhosis of the liver?
K74.60 Unspecified cirrhosis of liver.K74.69 Other cirrhosis of liver.
What percentage of ischemic subtypes are cryptogenic?
In most cases, a stroke is caused by a blood clot that blocks the flow of blood to the brain. In some instances, despite testing, the cause of a stroke cannot be determined. In this case, the stroke of unknown cause is called a “cryptogenic stroke.” It's estimated that about 1 in 3 ischemic strokes are cryptogenic.
What happens during cryptogenic stroke?
These strokes happen when an artery to your brain becomes blocked, usually by a blood clot. About 25% of ischemic strokes are cryptogenic, meaning that tests do not show a definitive cause. The other 15% of strokes are considered hemorrhagic strokes, which happen when a weakened blood vessel ruptures in your brain.Jan 6, 2022
What are the broad classifications of ischemic stroke etiologies?
Results: The TOAST classification denotes five subtypes of ischemic stroke: 1) large-artery atherosclerosis, 2) cardioembolism, 3) small-vessel occlusion, 4) stroke of other determined etiology, and 5) stroke of undetermined etiology.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as J84.116. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is the T51-T65?
poisoning due to drug or toxin ( T51-T65 with fifth or sixth character to indicate intent), for toxic pneumonopathy. underlying cause of pneumonopathy, if known. Type 1 Excludes. cryptogenic organizing pneumonia ( J84.116) idiopathic non-specific interstitial pneumonitis ( J84.113)
What is bronchiolitis obliterans?
Idiopathic bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Clinical Information. A disease formerly considered a form of interstitial pneumonia. Its etiology is obscure but it may be associated with toxic fumes, infection, and connective tissue disease.
How is a stroke classified?
Stroke is classified by the type of tissue necrosis, such as the anatomic location, vasculature involved, etiology, age of the affected individual, and hemorrhagic vs. Non-hemorrhagic nature. (from Adams et al., Principles of Neurology, 6th ed, pp777-810) A stroke is a medical emergency.
What is the term for a loss of blood flow to the brain?
An ischemic condition of the brain, producing a persistent focal neurological deficit in the area of distribution of the cerebral arteries. In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. Strokes are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain.
How long does it take for a patient to have a hemorrhage?
Infarction or hemorrhage may be demonstrated either directly by imaging, laboratory, or pathologic examination in patients with symptom duration less than 24 hours, or inferred by symptoms lasting greater than or equal to 24 hours (or fatal within 24 hours) that cannot be attributed to another cause.
What is the ICD-10 code for stroke?
Explicitly document findings to support diagnoses of › Stroke sequela codes (ICD-10 category I69.-) should acute stroke, stroke and subsequent sequela of be used at the time of an ambulatory care visit stroke, and personal history of stroke without sequela, oce, which is considered subsequent to any acute
What is the term for a stroke that occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue?
stroke occurs when there is disruption of blood flow to brain tissue, this leads to ischemia (deprivation of oxygen) and potentially infarction (dysfunctional scar tissue). Strokes can be either hemorrhagic, or embolic/thrombotic. Hemorrhagic strokes occur as a result of a ruptured cerebral blood vessel. Embolic/thrombic strokes occur as a result of an obstructed cerebral vessel.
What is the code for cerebral infarction?
While the majority of stroke diagnoses outside of the diagnostic radiology setting will not include enough supplementary information to code beyond I63.9 Cerebral infarction, unspecified, you should be prepared if, and when, the clinical encounter presents itself.
When is a stroke alert included in a diagnosis?
A stroke alert may be included as a supplementary diagnosis when the patient’s signs and symptoms are indicative of a possible stroke. However, the impression of the dictation report will have final say as to whether a stroke is revealed in the imaging scan.
What is a TIA in coding?
While there’s a clear-cut diagnosis (G45.9 Transient cerebral ischemic attack, unspecified) for a TIA, it’s often the surrounding speculative documentation that leads you to question the original diagnosis. While a TIA is often referred to as a “mini stroke,” from an ICD-10-CM coding perspective, it’s important to keep the two diagnoses entirely separate.
How long does a stroke last?
As defined by the NCHS, a disease is to be considered chronic if its symptoms last more than three months. Formulating the series of steps from which a hyperacute stroke becomes chronic is not as straightforward — in part because no universal set of guidelines exists to help elaborate on those distinctions.
What is the purpose of a CT scan for a stroke?
A traditional computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan evaluates the parenchyma of the brain. These scans will show the result of an occluded artery (i.e., stroke), but not the occlusion itself.
Can you code TIA without a diagnosis?
If not, there’s a possibility that the patient’s symptoms are the result of a TIA, but without a definitive TIA diagnosis, you should code only the signs and symptoms. Coder’s note: A TIA diagnosis, unlike a stroke diagnosis, can be coded from the indication.
Who is Brett Rosenberg?
Brett Rosenberg, MA, CPC , COC, CCS-P , serves as the editor of The Coding Institute’s (TCI’s) Radiology, Otolaryngology, and Outpatient Facility Coding Alerts. He earned his bachelor’s degree in psychology from the University of Vermont in 2011 and his master’s degree in psychology from Medaille College in 2016. Rosenberg is affiliated with the Flower City Professional Coders local chapter in Rochester, N.Y.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for falling on floor
- 2. icd 10 code for septicemia with sirs acute respiratory and hepatic failure
- 3. icd-10 code for parkinson's disease
- 4. icd 10 code for cerebral cavernoma
- 5. icd 10 code for vernal conjunctivitis
- 6. icd 10 cm code for cardiomegaly
- 7. icd 10 code for malignant carcinoid of appendix
- 8. icd 10 code for hepatitis a exposure
- 9. icd 10 code for speech apraxia
- 10. icd 9 code for bk amputation