How many codes in ICD 10?
Aug 22, 2020 · Just so, what is the ICD 10 code for positive D dimer? R79. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM R79. 1 became effective on October 1, 2019. What is a D dimer blood test? This test measures the amount of D-dimer, a type of protein the body produces to break down …
How do you code elevated D dimer?
Feb 28, 2020 · Likewise, what is the ICD 10 code for positive D dimer? R79. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM R79. 1 became effective on October 1, 2019. Likewise, what does an elevated D dimer mean? A positive D-dimer result may indicate the presence of an abnormally …
What is a valid ICD 10 code?
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated D dimer? R79. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. What is the ICD-10 code for Perinephric fluid collection? N15.1 Renal and perinephric abscess The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N15. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
Feb 08, 2022 · How do you code an elevated d dimer in icd 10? Code: R79.89.Code Name: ICD-10 Code for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry.Block: Abnormal findings on examination of blood, without diagnosis (R70-R79)Excludes 1:abnormalities (of) (on):abnormal findings on antenatal screening of mother (O28.-)
What ICD-10 code covers D-dimer?
R79. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R79. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How do you code D-dimer?
115188: D-Dimer | Labcorp.
What is the diagnosis code for PT INR?
1.
What is R79 89 diagnosis?
Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistryICD-10 code R79. 89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What tube is D-dimer?
D-DIMERORDERING INFORMATION:Geisinger Epic Procedure Code: LAB2173 Geisinger Epic ID: 18327Specimen type:Platelet-free plasmaPreferred collection container:2.7 mL blue-top (3.2% sodium citrate) tubeAlternate Collection Container:Other size blue-top (3.2% sodium citrate) tubes (e.g., 1.8 mL, 4.5 mL)19 more rows•Apr 29, 2019
What ICD 10 code covers PT PTT?
NCD - Partial ThromboplastinTime (PTT) (190.16)
What is the correct ICD-10 code for leukocytosis?
288.60 - Leukocytosis, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for PE?
ICD-10 code I26. 9 for Pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated fibrinogen?
1 - Abnormal coagulation profile is a sample topic from the ICD-10-CM. To view other topics, please log in or purchase a subscription. ICD-10-CM 2022 Coding Guide™ from Unbound Medicine.
What is the ICD-10 code for ferritin?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R97 R97.
What is the ICD-10 code for lethargic?
R53.83Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What is diagnosis code R53 83?
ICD-10 | Other fatigue (R53. 83)
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated D dimer?
R79. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for iron deficiency anemia?
Iron deficiency anemia, unspecified 9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D50. 9 – other international versions of ICD-10 D50.
What diagnosis covers PTT?
A PTT may be used to assess patients with signs or symptoms of hemorrhage or thrombosis. For example: abnormal bleeding, hemorrhage or hematoma petechiae or other signs of thrombocytopenia that could be due to disseminated intravascular coagulation; swollen extremity with or without prior trauma.
When is D-dimer elevated?
An elevated D-dimer level is not normal. It’s usually found after a clot has formed and is in the process of breaking down. If you are having significant formation and breakdown of blood clot in your body, your D-dimer may be elevated. A negative D-dimer test means that a blood clot is highly unlikely.
What is diagnosis code N28 89?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N28. 89: Other specified disorders of kidney and ureter.
What is Perinephric fluid collection?
Perinephric fluid is a critical finding of ultrasonography in daily clinical practice. The condition includes a broad spectrum of diseases and the fluid may arise from the kidney or adjacent retroperitoneal structures. We present a case series of patients with perinephric fluid collection with ultrasound images.
What is ICD 10 code for vitamin B12 deficiency?
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, unspecified D51. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
How do you code an elevated d dimer in icd 10?
Code: R79.89.Code Name: ICD-10 Code for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry.Block: Abnormal findings on examination of blood, without diagnosis (R70-R79)Excludes 1:abnormalities (of) (on):abnormal findings on antenatal screening of mother (O28.-)
What does diagnosis code R79 89 mean?
89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range – Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What can cause a raised D-dimer?
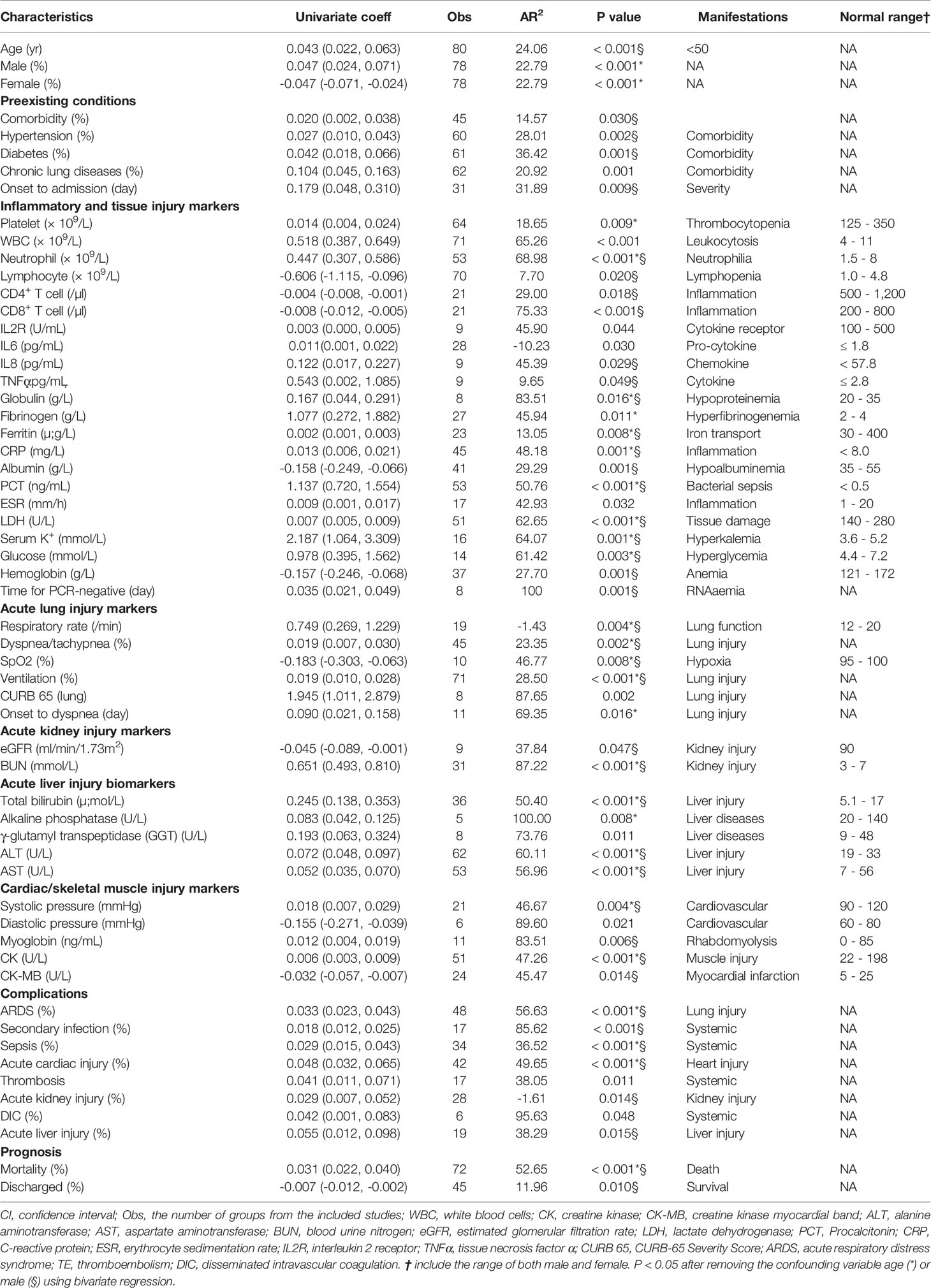
An elevated D-dimer may be due to a VTE or DIC but it may also be due to a recent surgery, or trauma, infection, liver or kidney disease, cancers, in normal pregnancy but also some diseases of pregnancy such as eclampsia.
What ICD-10 code covers a CMP?
Encounter for screening for other metabolic disorders The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z13. 228 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is D-dimer elevated in Covid?
Since then, however, elevated D-dimer and thrombotic complications have been widely reported in COVID-19 patients. Guan et al. reported that D-dimer more than 0.5 μg/ml was found in 260 out of 560 patients (46%) [3].
What is considered extremely elevated D-dimer?
Very high D-dimer level was defined as 100 times above the cutoff point, i.e. equal to or greater than 50 mg/L FEU. We analyzed the results of the 1,053 samples, reviewed the history of the patients with very high D-dimer through the hospital computer system, and found out the causes producing very high D-dimer.
Can inflammation cause elevated D-dimer?
Elevated levels of d-dimer are associated with inflammation and disease activity rather than risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis in long term observation. Adv Med Sci.
What is the diagnosis code for elevated D dimer?
For elevated D-dimer, look to ICD-10-CM R79. 1 Abnormal coagulation profile.
What is the ICD 10 code for an elevated D-dimer?
R79. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What ICD 10 code will cover CMP?
Encounter for screening for other metabolic disorders The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z13. 228 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is R79 89 diagnosis?
89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range – Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What can cause a raised D-dimer?
An elevated D-dimer may be due to a VTE or DIC but it may also be due to a recent surgery, or trauma, infection, liver or kidney disease, cancers, in normal pregnancy but also some diseases of pregnancy such as eclampsia.
What diagnosis covers CPT 85610?
A: When physicians use a prothrombin time test (reported with CPT code 85610) to monitor patients on anticoagulant drugs, Medicare pays the entity that performed the test. Its payment for the test is based on the geographically specific laboratory test fee schedule.
What diagnosis covers PTT?
A PTT may be used to assess patients with signs or symptoms of hemorrhage or thrombosis. For example: abnormal bleeding, hemorrhage or hematoma petechiae or other signs of thrombocytopenia that could be due to disseminated intravascular coagulation; swollen extremity with or without prior trauma.
Special Instructions
If the patient's hematocrit exceeds 55%, the volume of citrate in the collection tube must be adjusted. Refer to Coagulation Collection Procedures for directions.
Expected Turnaround Time
Turnaround time is defined as the usual number of days from the date of pickup of a specimen for testing to when the result is released to the ordering provider. In some cases, additional time should be allowed for additional confirmatory or additional reflex tests. Testing schedules may vary.
Collection
Blood should be collected in a blue-top tube containing 3.2% buffered sodium citrate. 1 Evacuated collection tubes must be filled to completion to ensure a proper blood to anticoagulant ratio. 2,3 The sample should be mixed immediately by gentle inversion at least six times to ensure adequate mixing of the anticoagulant with the blood.
Causes for Rejection
Gross hemolysis; clotted specimen; specimen thawed in transit; improper labeling
Limitations
Results of this test should always be interpreted in conjunction with the patient's medical history, clinical presentation, and other findings. DVT clinical diagnosis should not be based on the result of Innovance® D-dimer alone.
Additional Information
Coagulation activation results in the cleavage of fibrinogen to fibrin monomer. 7,8 The fibrin monomers spontaneously aggregate to fibrin and are cross-linked by factor XIII; this produces a fibrin clot.
Popular Posts:
- 1. 2015 icd 10 code for degenerative bilateralhips
- 2. icd 10 code for liveborn single infant delivered by lower segment cesarean section
- 3. icd 10 code for otitis media
- 4. icd 10 code for myopia bilateral
- 5. icd 10 code for night sweat
- 6. icd 10 code for ibuprofen
- 7. icd 10 code for bilateral shoulder tenderness
- 8. icd 10 code for other elevated white blood cell count
- 9. icd-10 code for beta blocker use
- 10. icd 10 code for long term use of finasteride