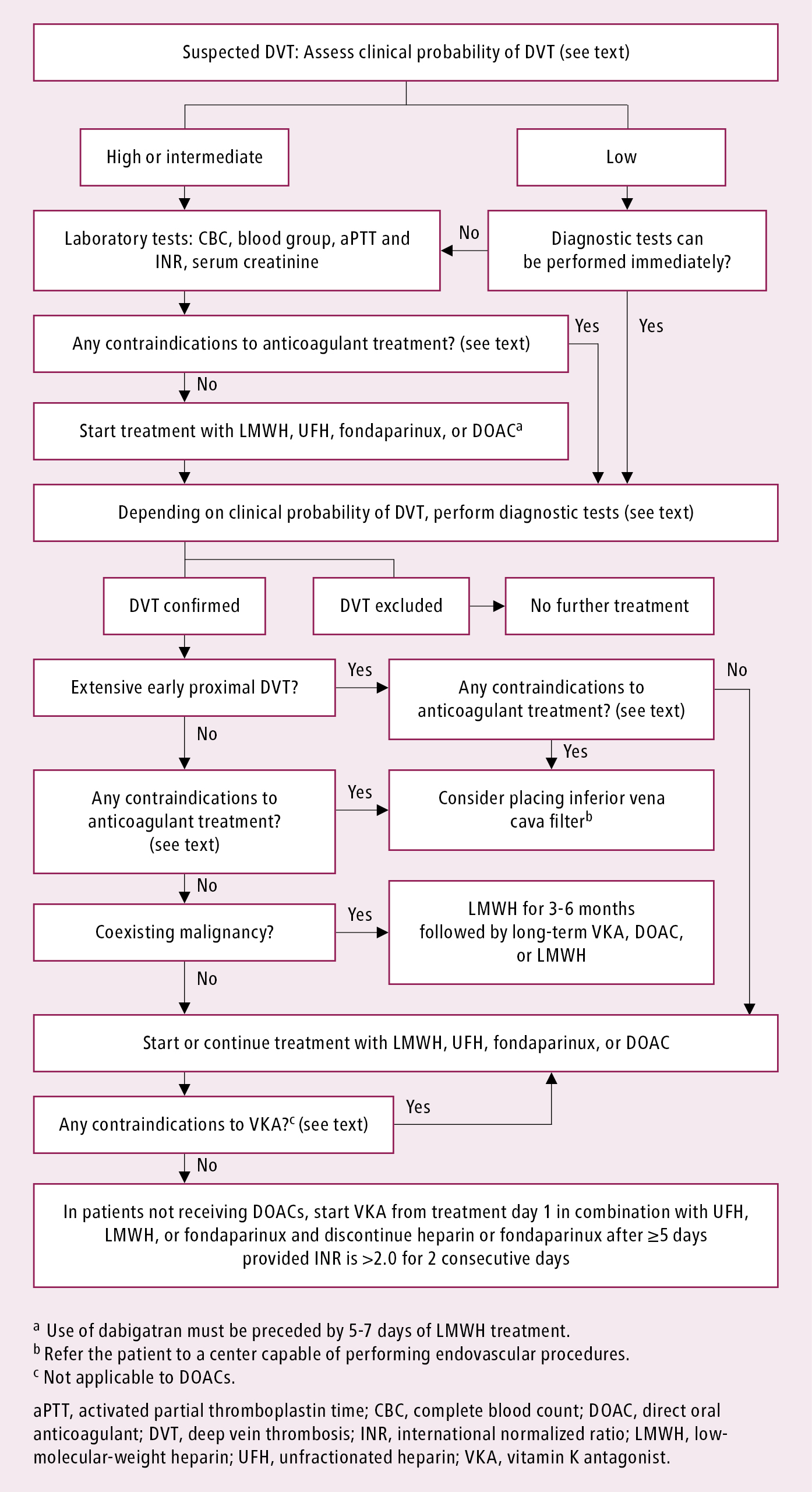
How do we diagnose and treat deep vein thrombosis?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I82.40 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I82.40 Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of lower extremity 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code I82.40 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of …
How to deal with deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute postprocedural deep venous thrombosis (dvt) of left leg ICD-10-CM I82.402 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 299 Peripheral vascular disorders with mcc 300 Peripheral vascular disorders with cc 301 Peripheral vascular disorders without cc/mcc Convert I82.402 to ICD-9-CM Code History
What are the causes of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Feb 03, 2021 · I82.90 2021 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I82. 90: Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified vein. What is DVT in right leg? Blood clot in leg vein Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or …
Can deep vein thrombosis be prevented?
Mar 22, 2021 · ICD 10 Codes for DVT of Lower Extremities and Upper Extremities – Acute and Chronic. Acute embolism and thrombosis of lower extremity. I82.41 femoral vein 182.42 Iliac vein I82.43 Popliteal vein I82.44 Tibial vein I82.45 Peroneal vein I82.46 Calf muscular vein I82.49 Other specified deep vein of lower extremity

What is the ICD-10 code for DVT lower extremity?
I82.403Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of lower extremity, bilateral. I82. 403 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code I82 409?
ICD-10 | Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of unspecified lower extremity (I82. 409)
What is the ICD-10 code for I82 402?
ICD-10 | Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of left lower extremity (I82. 402)
What is the ICD-10 code for left DVT?
I82.4022022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I82. 402: Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of left lower extremity.
What is the diagnosis code for deep vein thrombosis?
I82. 401 – Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of right lower extremity.May 15, 2020
What is a thrombosis?
Thrombosis occurs when blood clots block your blood vessels. There are 2 main types of thrombosis: Venous thrombosis is when the blood clot blocks a vein. Veins carry blood from the body back into the heart. Arterial thrombosis is when the blood clot blocks an artery.
What is Phlegmasia Cerulea Dolens?
Phlegmasia cerulea dolens is an uncommon, severe form of deep venous thrombosis (blood clots in the vein). It most often occurs in the upper leg.Feb 6, 2020
What is acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of left lower extremity?
402 for Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of left lower extremity is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated D dimer?
For elevated D-dimer, look to ICD-10-CM R79. 1 Abnormal coagulation profile.Jul 28, 2017
Is Soleal vein thrombosis DVT?
During the past two decades, diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) or calf vein thrombosis has made considerable progress. Distal DVT is located along the lower leg and includes the infrapopliteal veins, such as the posterior tibial, peroneal, anterior tibial and muscular calf veins (soleal or gemellar).
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA?
I63.99.
Where is the Gastroc vein?
Characterised by veins emerging from the lateral and medial heads of gastrocnemius muscle, converging directly toward the main gastrocnemius trunk.
What is a DVT?
DVT occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more veins located deep inside the body. This serious condition occurs when the blood moves too slowly through the veins due to long periods of immobility or reduced mobility or other factors.
What are the symptoms of a DVT?
Symptoms of DVT can include. Swelling in the foot, ankle, or leg. Cramping and pain. swollen veins. Tenderness. Discoloration. Unusually hot skin in the affected area. If DVT occurs with no identifiable risk factor, the condition is called unprovoked DVT. There are many risk factors for DVT.
What is the most common cause of PE?
DVT, deep vein thrombophlebitis, or central vein thrombosis are the the most common causes of PE. Documenting to the Highest Level of Specificity: Providers should clearly document whether DVT is acute, chronic or historical. A diagnosis of acute thrombosis is assigned when a new, symptomatic thrombosis is detected and anticoagulation therapy is ...
How to check for blood clots?
Methods use to diagnose DVT or check for a blood clot include: Venous Ultrasound: This standard test for DVT involves using sound waves to display how blood flows through the veins. Venography: This x-ray test involves injecting a dye into a large vein in the foot or ankle to detect clots.
What is DVT awareness month?
March is national Deep-Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Awareness Month. This public health initiative aims to raise awareness about this widely prevalent medical condition and its potentially life-threatening complication, pulmonary embolism (PE). The American Medical Association estimates that about 2 million people are affected by DVT each year, more than the numbers affected by heart attack or stroke annually. Billing and coding for these conditions is complex. An experienced medical billing and coding service provider would have proper knowledge of important diagnostic norms and documentation requirements to help physicians assign appropriate diagnoses and procedure codes on claims.
What is the treatment for a blood clot?
Therapies include: Anticoagulant Medications: Usually, heparin is prescribed first to prevent further clotting, which may be followed by warfarin to prevent another blood clot forming. Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter: This small, cone-shaped filter is inserted into the inferior vena cava, the largest vein in your body.
What veins should be documented in a physician's diagnosis?
The specific vein such as femoral, iliac or tibial. The physician should also document the diagnostic method used, the anticoagulants administered and duration of treatment. The treatment and its goals should be linked to the diagnosis.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hx of cdiff
- 2. icd 10 code for contact hot curling iron
- 3. icd 9 code for aftercare following hysterectomy
- 4. icd 10 code for nocturnal foot pain
- 5. icd-1- code for lll penumonia
- 6. medicare icd 10 code for total knee replacement
- 7. icd 10 code for fracture of left hand
- 8. icd 10 code for m25.569
- 9. icd 10 cm code for s
- 10. icd 10 code for wounds to both legs