What is the DX code for dermatitis?
The ICD-10 code range for Dermatitis and eczema L20-L30 is medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO).
What is the ICD-10 code for eczematous dermatitis?
9: Atopic dermatitis, unspecified.
Is atopic dermatitis the same as eczema?
Eczema is a general term for rash-like skin conditions. The most common type of eczema is called atopic dermatitis. Eczema is often very itchy. When you scratch it, your skin becomes red and inflamed (puffy).
What is the ICD-10 code for Dyshidrotic eczema?
ICD-10 code: L30. 1 Dyshidrosis [pompholyx] | gesund.bund.de.
What is non specific dermatitis?
Background. Irritant contact dermatitis (ICD) is a nonspecific, nonallergic response of the skin to direct chemical damage from a corrosive agent that releases mediators of inflammation predominantly from epidermal cells. Irritant contact dermatitis can be acute or chronic.
What does dermatitis unspecified mean?
Dermatitis is a general term that describes a common skin irritation. It has many causes and forms and usually involves itchy, dry skin or a rash. Or it might cause the skin to blister, ooze, crust or flake off.
What is dermatitis on hands?
Hand eczema, also called hand dermatitis, is an inflammatory skin condition. It forms swollen, itchy, scaly, discolored rashes on the hands and fingers. The skin may blister and crack, and this can be painful. Hand eczema is fairly common.
What is the ICD 10 code for atopic dermatitis?
ICD-10 code L20. 9 for Atopic dermatitis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What causes atopic dermatitis on hands?
Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is caused by a combination of immune system activation, genetics, environmental triggers and stress. Your immune system. If you have eczema, your immune system overreacts to small irritants or allergens. This overreaction can inflame your skin.
How do you describe Dyshidrotic eczema?
Dyshidrotic eczema is a type of eczema (dermatitis) that is characterized by a pruritic vesicular eruption (bullae, or blisters) on the fingers, palms, and soles; typically these intensely itchy blisters develop on the edges of the fingers, toes, palms, and soles of the feet.
How do you treat Dyshidrotic eczema?
How is dyshidrotic eczema treated?Moisturizing lotion or cream. This helps treat dry skin.Steroid ointment. This can reduce inflammation.Calcineurin creams. ... Steroid medicines taken by mouth (oral). ... Draining of very large blisters. ... Treatment with psoralen and ultraviolet light (PUVA). ... Other medicines.
What is the ICD 10 code for folliculitis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Folliculitis decalvans L66. 2.
What is the best treatment for atopic dermatitis?
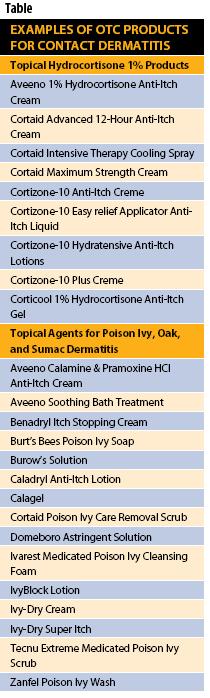
A nonprescription hydrocortisone cream, containing at least 1 percent hydrocortisone, can temporarily relieve the itch. Apply it no more than twice a day to the affected area, after moisturizing. Using the moisturizer first helps the medicated cream penetrate the skin better.
Does atopic dermatitis go away?
Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema, a skin condition that makes you itch and leaves red blotches, usually on your face, arms, and legs. While it happens most often in children, it also affects an estimated 18 million adults. The rashes tend to flare and go away, but then come back again.
What does atopic dermatitis look like?
Red to brownish-gray patches, especially on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, inside the bend of the elbows and knees, and in infants, the face and scalp. Small, raised bumps, which may leak fluid and crust over when scratched. Thickened, cracked, scaly skin.
Can atopic dermatitis be cured?
There's no cure, but many children find their symptoms naturally improve as they get older. The main treatments for atopic eczema are: emollients (moisturisers) – used every day to stop the skin becoming dry. topical corticosteroids – creams and ointments used to reduce swelling and redness during flare-ups.
What is stasis dermatitis?
Clinical Information. A chronic inflammatory genetically determined disease of the skin marked by increased ability to form reagin (ige), with increased susceptibility to allergic rhinitis and asthma, and hereditary disposition to a lowered threshold for pruritus.
Is dermatitis a genetic disease?
In this block the terms dermatitis and eczema are used synonymously and interchangeably. A chronic inflammatory genetically determined disease of the skin marked by increased ability to form reagin (ige), with increased susceptibility to allergic rhinitis and asthma, and hereditary disposition to a lowered threshold for pruritus.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for spondylosis with radiculopathy cervical region
- 2. icd 10 cm code for flu exposure
- 3. icd-10 code for nasal congestion
- 4. icd 10 code for mdd recurrent severe
- 5. icd 10 code for stoke
- 6. icd 10 code for chest wall tightness pressure discomfort
- 7. icd code for covid-19 positive
- 8. icd code for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- 9. icd-10 code for unknown immunodeficiency
- 10. icd 10 code for neurofibromatosis