What is the ICD 10 code for overactivity?
Oct 01, 2021 · N32.81 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N32.81 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N32.81 - other international versions of ICD-10 N32.81 may differ. Applicable To Detrusor muscle hyperactivity
What is the ICD 10 code for overactive bladder?
Oct 01, 2021 · N31.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N31.9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N31.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 N31.9 may differ. Applicable To Neurogenic bladder dysfunction NOS
What is the ICD 10 code for excluded note?
N32.81 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of overactive bladder. The code N32.81 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through September 30, 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The ICD-10-CM code N32.81 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like autonomic hyperreflexia of bladder, bladder …
What is the ICD 10 code for urinalysis?
Dec 25, 2021 · According to the code set, N32.81 is the billable ICD 10 code for overactive bladder, which is also applicable to detrusor muscle hyperactivity. Cases which have been diagnosed with frequent urination due to a specified bladder condition should be …

What is overactive detrusor?
Detrusor overactivity is defined as a urodynamic observation characterized by involuntary detrusor contractions during the filling phase that may be spontaneous or provoked.
What is the ICD-10 code for detrusor instability?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N32. 81: Overactive bladder.
How do you code an overactive bladder?
ICD-10-CM Code for Overactive bladder N32. 81.
What does neurogenic detrusor overactivity mean?
Neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) is a bladder dysfunction frequently observed in patients with conditions such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and spinal cord injury (SCI). Increased storage pressure can put the upper urinary tract at risk of deterioration and reducing this risk is a primary aim of therapy.
What is ICD-10 code R32?
Unspecified urinary incontinenceICD-10 code: R32 Unspecified urinary incontinence.
What N39 41?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N39. 41: Urge incontinence.
What is the ICD-10 code for urinary urgency?
R39. 15 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for urine retention?
ICD-10 | Retention of urine, unspecified (R33. 9)
What is the ICD-10 code for irritable bladder?
N32. 81 - Overactive bladder | ICD-10-CM.
What causes overactivity of the detrusor muscles?
Neurogenic detrusor overactivity, previously known as hyperreflexia, is increased or involuntary muscle contractions of the detrusor muscle in the bladder. It is a neurological condition causing urinary incontinence and is due to damage or disruption of the nerves supplying the detrusor muscle.
What is terminal detrusor overactivity?
The term, terminal detrusor overactivity (TDO), is defined as a single involuntary detrusor contraction that cannot be suppressed and that occurs when the maximum bladder capacity is reached, resulting in urinary incontinence and often complete bladder emptying (Figure 2) (1).Dec 10, 2020
Is overactive bladder the same as neurogenic bladder?
Neurogenic bladder is a nervous system condition that keeps you from having normal bladder control. It happens when the nerves that control your bladder get damaged, often due to illness or injury. There are two types of neurogenic bladder. Overactive bladder causes you to have little or no control over your urination.
What is the code for bladder overactiveness?
N32.81 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of overactive bladder. The code N32.81 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is an overactive bladder?
URINARY BLADDER OVERACTIVE-. symptom of overactive detrusor muscle of the urinary bladder that contracts with abnormally high frequency and urgency. overactive bladder is characterized by the frequent feeling of needing to urinate during the day during the night or both. urinary incontinence may or may not be present.
Overview
Overactive bladder, or OAB, is a condition that is characterized by sudden and frequent urge to urinate that is often difficult to control. It is common to observe an unintentional loss of urine, or urinary incontinence and the patient may pass urine several times in a day.
Causes
In normal conditions, the brain sends signals to the bladder when it identifies that the bladder is full of urine. The bladder muscles then squeeze to allow the urine to pass through the urethra and reach the sphincter muscles that open to allow the urine to flow out.
Diagnosis
When a patient shares their symptoms with a healthcare provider, the provider would perform an exam to determine the cause. In some cases, the provider may refer to a urologist who specializes in diagnosing and treatment of overactive bladder.
Healthcare Providers Who Treat Overactive Bladder
There are several healthcare providers that provide varying treatment for overactive bladder, and it is important for all of them to be familiar and well versed with the coding for ICD 10 overactive bladder, including:
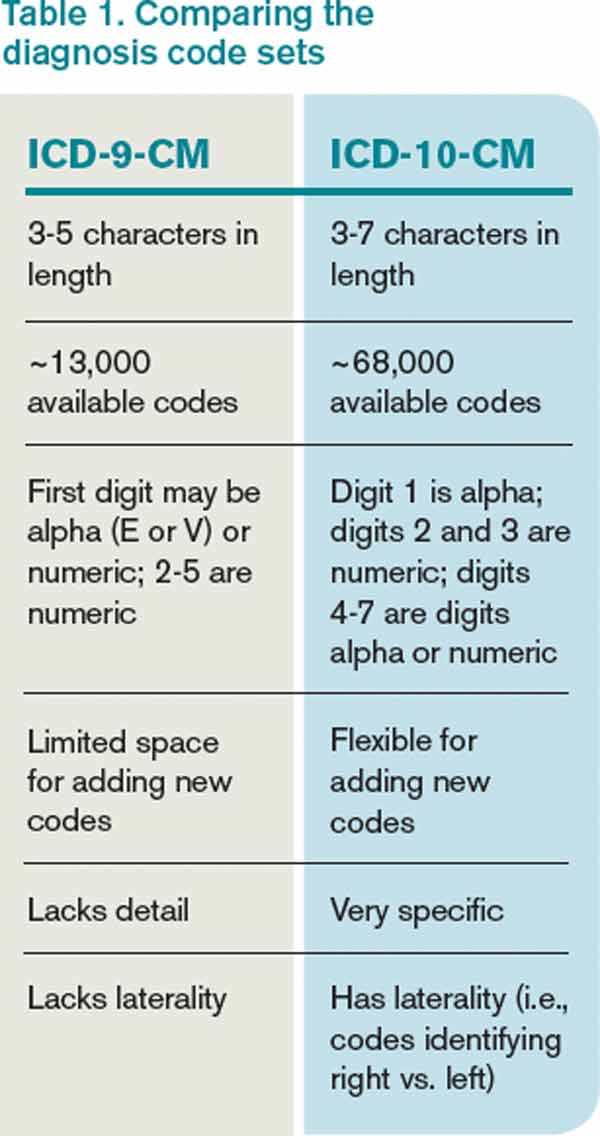
About the ICD 10
The International Classification of Diseases, tenth revision is a clinical system applied by healthcare providers and physicians to code and classify the diseases, diagnoses, symptoms and procedures that are recorded during health care provided. The ICD 10 is important to compile diagnostic specificity and morbidity data in the US.
Coding for Overactive Bladder ICD 10
When coding for OAB, the first thing to specify is what is the ICD 10 for active bladder. According to the code set, N32.81 is the billable ICD 10 code for overactive bladder, which is also applicable to detrusor muscle hyperactivity.
Determining the Correct Overactive Bladder ICD 10 code
Since overactive bladder is oftentimes confused with other types of urinary incontinence, it is important to have a clear understanding of the differences between them and the specific ICD 10 codes they are assigned to avoid any coding errors. Here are some of the most common types of incontinence and their corresponding ICD 10 codes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for relapsed multiple myeloma
- 2. what is the icd-10 code for ct-scan
- 3. icd 10 cm code for ear lobe pain
- 4. icd 10 code for elevated co2 level
- 5. icd 10 code for depression with anxeity
- 6. icd 10 code for cytology
- 7. icd 10 code for ulcerative pancolitis with rectal bleeding
- 8. icd 10 cm code for inflamed right index finger
- 9. icd 10 code for papilledema
- 10. icd 10 code for abdominal cramps