2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z13.40 Encounter for screening for unspecified developmental delays 2019 - New Code Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt Present On Admission Z13.40 is considered exempt from POA reporting.
What are the ICD-10 delays?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F84.9 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Pervasive developmental disorder, unspecified. Developmental disorder, pervasive; Developmental disorder, pervasive, residual state; Pervasive developmental disorder; Pervasive developmental disorder of residual state; Atypical autism. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F84.9.
What is ICD 10 code for DVT?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. R62.50 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Unsp lack of expected normal physiol dev in childhood. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R62.50 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is Procedure Code 10e0xzz?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F80.9 Developmental disorder of speech and language, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code F80.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F80.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for DJD?
Z13.41 ICD-10-CM Code for Encounter for screening for unspecified developmental delays Z13.40 ICD-10 code Z13.40 for Encounter for screening for unspecified developmental delays is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .

What is the ICD-10 code for developmental delay?
Encounter for screening for global developmental delays (milestones) Z13. 42 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
How do you code developmental delays?
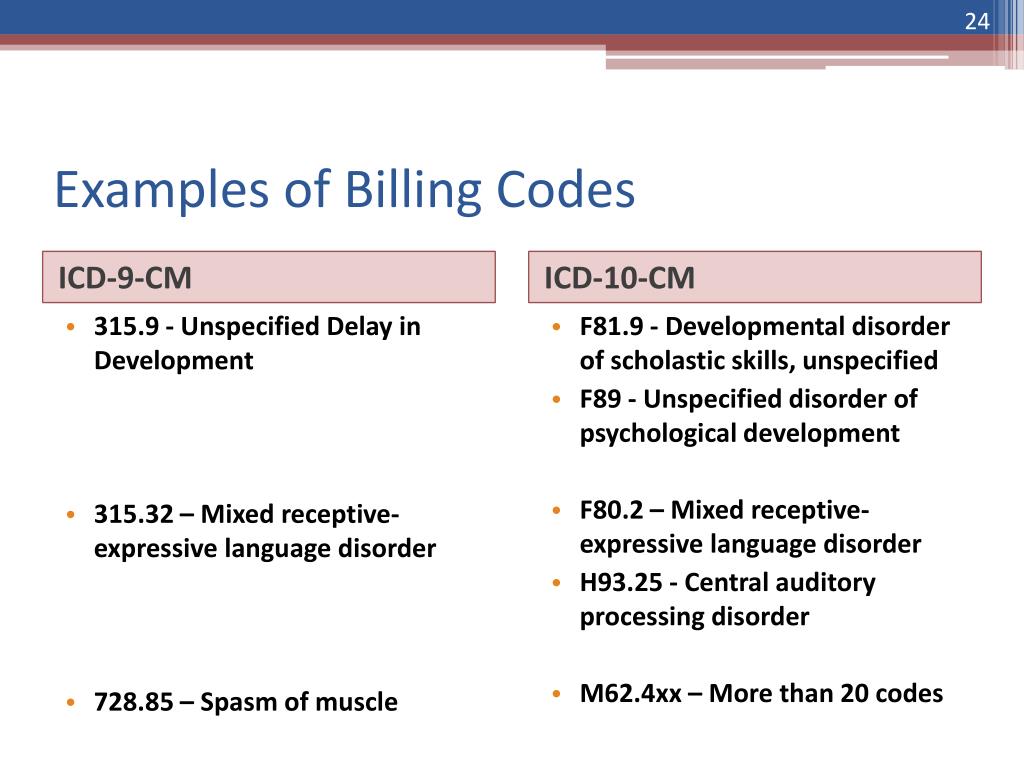
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 315.9 : Unspecified delay in development.
Is R62 50 a developmental delay?
50 - Unspecified lack of expected normal physiological development in childhood.
What is the ICD-10 code for cognitive developmental delay?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R41 R41. 89 Other symptoms and signs involving cognitive ...
What is the difference between 96127 and 96160?
Note: Because confusion about these codes is common, you should verify your payers' policies. For instance, some plans require reporting of code 96160 for depression screening other than post- partum depression even though code 96127 is intended for reporting this service.
What is developmental delay?
• When a child's progression through predictable developmental phases slows, stops, or reverses. •Symptoms include slower-than-normal development of motor, cognitive, social, and emotional skills. •Treatment includes occupational therapy, speech therapy and/or physical therapy services.
What is R46 89?
R46. 89 - Other Symptoms and Signs Involving Appearance and Behavior [Internet]. In: ICD-10-CM.
What is F80 89?
Other developmental disorders of speech and language89 for Other developmental disorders of speech and language is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders .
What is diagnosis code F84?
Home State Health denying Autism Spectrum Disorder (F84. 0) without additional Intellectual Disability diagnosis code.
Is global developmental delay a diagnosis?
A diagnosis of global developmental delay (GDD) means that a child has not reached two or more milestones in all of the five areas of development: Cognitive – relating to a child's ability to learn and solve problems.
What is the difference between global developmental delay and autism?
To put it simply, a developmental delay is when your child does not reach their developmental milestones at the expected times, whilst Autism refers to a group of complex neurodevelopmental disorders, present from early childhood which is characterised by the difficulty in communicating and forming relationships with ...
What is cognitive developmental delay?
A cognitive developmental delay refers to the condition of children whose intellectual function and adaptive behavior are significantly below the expected average for their age. Other names for cognitive developmental delays include intellectual disabilities, cognitive impairment, or cognitive/intellectual disorder.
What is a disorder characterized by an impairment in the development of an individual's language capabilities?
A disorder characterized by an individual's inability to comprehend or share ideas or feelings because of an impairment in language, speech, or hearing.
What is diminished ability?
Diminished ability to exchange thoughts, opinions, or information.
What are developmental disabilities?
Developmental disabilities are birth defects that cause lifelong problems with how a body part or system works. They include. nervous system disabilities affecting how the brain, spinal cord and nervous system function. They cause mental retardation, including down syndrome and fragile x syndrome.
What age do impairments occur?
These impairments or disabilities originate before age 18, may be expected to continue indefinitely, and constitute a substantial impairment.
What are the best ways to treat developmental disabilities?
most developmental disabilities have no cure, but you can often treat the symptoms. Physical, speech and occupational therapy might help. Special education classes and psychological counseling can also help. nih: national institute of child health and human development.
What is the ICd 9 code for a syringe?
ICD-9-CM 315.9 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 315.9 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes).
What are learning disabilities?
According to United States Federal legislation, learning problems that are due to visual, hearing, or motor handicaps, mental retardation, emotional disturbance or environmental, cultural, or economic disadvantage. Compare learning disabilities.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for pulmonary fibrosis
- 2. icd 10 code for multiple fractures unspecified
- 3. icd 10 code for uninsured
- 4. icd 10 code for iletis
- 5. icd-10 code for aspiration
- 6. icd 10 code for lupus antiphospholipid syndrome
- 7. icd 10 code for insect bite on head
- 8. icd 10 code for opioid dependence in remission
- 9. icd 10 code for basic metabolic panel
- 10. icd 10 code for pre eclampsia