Encounter for screening for diabetes mellitus
- Z13.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z13.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z13.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z13.1 may differ.
What is a diabetic retinal examination?
The purpose of a diabetes eye exam is to identify problems in the retina (a light-sensitive tissue in the back of the eye) or the optic nerve (a nerve that connects the brain to the eyes) before you notice any vision loss. Or, the exam can monitor the progression of eye problems that an eye doctor has already identified.
How to code diabetes correctly?
Diabetes Mellitus and the Use of Insulin and Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs If the documentation in a medical record does not indicate the type of diabetes but does indicate that the patient uses insulin: Assign code E11-, Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Assign code Z79.4, Long term (current) use of insulin, or Z79.84, Long-term (current) use of oral
What is ICD 10 for poorly controlled diabetes?
In ICD-10-CM, chapter 4, "Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases (E00-E89)," includes a separate subchapter (block), Diabetes mellitus E08-E13, with the categories:
- E08, Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition
- E09, Drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus
- E10, Type 1 diabetes mellitus
- E11, Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- E13, Other specified diabetes mellitus
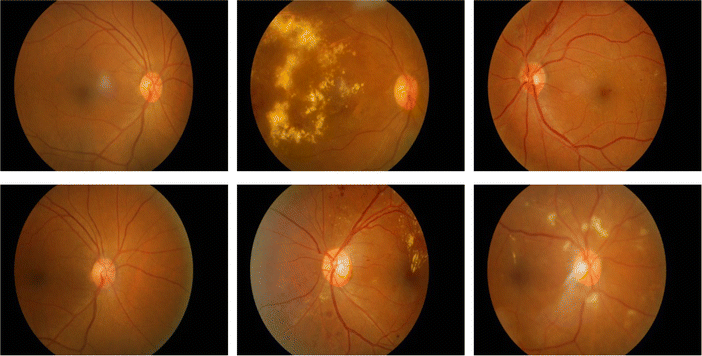
What are some symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
The symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include:
- Blurry vision
- Loss of central vision
- Inability to see colors
- Floaters
- Black areas in the vision
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic eye exam?
Encounter for screening for eye and ear disorders Z13. 5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z13. 5 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes with retinopathy?
ICD-10 code E11. 319 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with unspecified diabetic retinopathy without macular edema is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
How do you code diabetic retinopathy?
If a patient with diabetic retinopathy is experiencing macular edema, then code 362.07 is assigned along with the appropriate code for the retinopathy. If the severity of nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy is not specified, assign code 362.03. Diabetic retinopathy not further specified is classified to code 362.01.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for diabetic retinopathy?
E11. 31 - Type 2 diabetes mellitus with unspecified diabetic retinopathy. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for retinopathy?
Unspecified background retinopathy H35. 00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H35. 00 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is background diabetic retinopathy?
Background diabetic retinopathy, also known as non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR), is the early stage of diabetic retinopathy. This occurs when diabetes damages the small blood vessels and nerves in the retina. The retina acts like the film of the eye.
What is the ICD-9 code for diabetes retinopathy?
362.0ICD-9 code 362.0 for Diabetic retinopathy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -DISORDERS OF THE EYE AND ADNEXA (360-379).
What is the CPT code for Retinopathy?
CPT® 92229 allows coverage for Imaging of retina for detection or monitoring of disease; point-of-care automated analysis and report, unilateral or bilateral.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes?
E08. 3531 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition... E08. 3532 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition...
What ICD-10-CM code is reported for mild non proliferative diabetic retinopathy with macular edema?
ICD-10-CM Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with mild nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy with macular edema, bilateral E11. 3213.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 1 diabetes?
ICD-10 code E10. 9 for Type 1 diabetes mellitus without complications is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for hypertensive retinopathy?
033.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes?
For gestational diabetes (diabetes that occurs during pregnancy) women should be assigned a code under the 024.4 subheading and not any other codes under the 024 category.
What type of diabetes codes should be used?
If the type of diabetes that the patient has is not documented in the medical record, E11 codes for type 2 diabetes should be used as a default. If the medical record doesn’t say what type of diabetes the patient has but indicates that the patient uses insulin, the Type 2 diabetes codes should also be used.
When to use unspecified ICD-10?
The “unspecified” codes can be used when not enough information is known to give a more specific diagnosis; in that case, “unspecified” is technically more accurate than a more specific but as yet unconfirmed diagnosis. For more guidelines on using ICD-10 codes for diabetes mellitus, you can consult this document.
What is the ICd 10 code for diabetic retinopathy?
E11.311 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Type 2 diabetes w unsp diabetic retinopathy w macular edema This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.311 - other international versions of ICD-10 E11.311 may differ. A disease in which the body does not control the amount of glucose (a type of sugar) in the blood and the kidneys make a large amount of urine. This disease occurs when the body does not make enough insulin or does not use it the way it should. A heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance. A metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels due to diminished production of insulin or insulin resistance/desensitization. A subclass of diabetes mellitus that is not insulin-responsive or dependent (niddm). It is characterized initially by insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia; and eventually by glucose intolerance; hyperglycemia; and overt diabetes. Type ii diabetes mellitus is no longer considered a disease exclusively found in adults. Patients seldom develop ketosis but often exhibit obesity. A type of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by insulin resistance or desensitization and increased blood glucose levels. This is a chronic disease that can develop gradually over the life of a patient and can be linked to both environmental factors and heredity. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or sugar, levels are too high. Glucose comes from the foods you eat. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Without Continue reading >>
What is the ICd 10 code for macular edema?
E11.319 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Type 2 diabetes w unsp diabetic rtnop w/o macular edema This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.319 - other international versions of ICD-10 E11.319 may differ. Continue reading >>
What is the disease of diabetes mellitus?
A subtype of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by insulin deficiency. It is manifested by the sudden onset of severe hyperglycemia, rapid progression to diabetic ketoacidosis, and death unless treated with insulin. The disease may occur at any age, but is most common in childhood or adolescence. diabetes means your blood glucose, or blood sugar, is too high. With type 1 diabetes, your pancreas does not make insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood. Over time, high blood glucose can lead to serious problems with your heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and gums and teeth. Type 1 diabetes happens most often in children and young adults but can appear at any age. Symptoms may include being very thirsty urinating often feeling very hungry or tired losing weight without trying having sores that heal slowly having dry, itchy skin losing the feeling in your feet or having tingling in your feet having blurry eyesight a blood test can show if you have diabetes. If you do, you will need to take insulin for the rest of your life. Diabetes mellitus characterized by insulin deficiency, sudden onset, severe hyperglycemia, rapid progression to ketoacidosis, and death unless treated with insulin. The disease may occur at any age, but is most common in childhood or adolescence. Subtype of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by insulin deficiency; it is manifested by the sudden onset of severe hyperglycemia, rapid progression to diabetic ketoacidosis, and death unless treated with insulin; the disease may occur at any age, but is most common in childhood or adolescence. Continue reading >>
What is the ICd 10 code for diabetic retinopathy?
E11.311 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Type 2 diabetes w unsp diabetic retinopathy w macular edema This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.311 - other international versions of ICD-10 E11.311 may differ. A disease in which the body does not control the amount of glucose (a type of sugar) in the blood and the kidneys make a large amount of urine. This disease occurs when the body does not make enough insulin or does not use it the way it should. A heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance. A metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels due to diminished production of insulin or insulin resistance/desensitization. A subclass of diabetes mellitus that is not insulin-responsive or dependent (niddm). It is characterized initially by insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia; and eventually by glucose intolerance; hyperglycemia; and overt diabetes. Type ii diabetes mellitus is no longer considered a disease exclusively found in adults. Patients seldom develop ketosis but often exhibit obesity. A type of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by insulin resistance or desensitization and increased blood glucose levels. This is a chronic disease that can develop gradually over the life of a patient and can be linked to both environmental factors and heredity. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or sugar, levels are too high. Glucose comes from the foods you eat. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Without Continue reading >>
What is the ICd 10 code for macular edema?
E11.319 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Type 2 diabetes w unsp diabetic rtnop w/o macular edema This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.319 - other international versions of ICD-10 E11.319 may differ. Continue reading >>
What is the difference between ICd 10 and ICd 9?
The transition strategy, tools and resources ICD-10 simplifies coding of diabetic renal, ophthalmic & neurologic manifestations Just one combination code, E11.311 (Type 2 diabetes mellitus with unspecified diabetic retinopathy with macular edema), will sufficiently capture diabetic macular edema in ICD-10, whereas, in ICD-9, the condition requires three separate codes: 250.50 for the diabetes, 362.01 for background diabetic retinopathy and 362.07 for the diabetic macular edema. ICD-10 will simplify the coding of renal, ophthalmic and neurological diabetic manifestations, as most of these conditions, which require a minimum of two codes in ICD-9, are captured with single combination codes in the new code set. In fact, most of the time, the only additional code required when coding diabetic manifestations is that for insulin use (Z79.4, Long term (current) use of insulin) in patients with the type 2 form of the disease [I.C.4.a.3]. The ICD-10 codes that cover diabetes are found in Chapter 4 (Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases) and range from the E08 (Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition) to the E13 (Other specified diabetes mellitus) categories, depending on the type of the condition (1 or 2) and its cause (such as drug of chemical-induced diabetes, or diabetes resulting from another disease). Home health coding will make the most use of codes from the E11.- category (Type 2 diabetes mellitus), says Vonnie Blevins, HCS-D, coding and billing manager for Excellence Healthcare in Houston. Just like in ICD-9, when the type of diabetes is not specified, type 2 should be coded [I.C.4.a.2]. Renal, ophthalmic and neurological manifestations are indicated in ICD-10 with the use of the fourth character 2 for renal, 3 for ophthalmic and 4 for neurological. Continue reading >>
Why do optometrists do dilated eye exams?
Because doctors of optometry perform the majority of comprehensive, dilated eye examinations for people with diabetes in the United States and are well versed in the treatment and management of diabetic eye disease , it is critical that doctors of optometry are aware of these updated codes.
What is the ICD-10 code?
The new ICD-10 is five times larger than its 14,000-code predecessor ICD-9, ...
What is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance
A heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance. A metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels due to diminished production of insulin or insulin resistance/desensitization. A subclass of diabetes mellitus that is not insulin-responsive or dependent (niddm).

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2017 icd 10 code for history largengeal cancer
- 2. icd 10 code for presence of cardiac defibrillator
- 3. icd 10 code for cerebral degeneration
- 4. icd 10 code for mri wrist w/o right and right elbow
- 5. icd 9 code for degenerative arthritis lumbar spine
- 6. icd-9 code for neodymium yag laser peripheral iridotomy
- 7. icd 9 code for basilar atelectasis
- 8. icd-10-pcs code for percutaneous transmyocardial laser revascularization of left ventricle
- 9. icd 10 code for aki vs
- 10. icd 10 code for supracondylar humerus fracture with intercondylar extension