What is the best treatment for a diabetic foot ulcer?
Treatment
- Debridement. Debridement should be carried out in all chronic wounds to remove surface debris and necrotic tissues.
- Off-loading. Off-loading of the ulcer area is extremely important for the healing of plantar ulcers. ...
- Dressings. ...
- Growth Factors. ...
- Bioengineered Skin Substitutes. ...
- Extracellular Matrix Proteins. ...
- Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy. ...
How to get rid of diabetic foot ulcers?
Get Rid Of The Ulcer With Rhubarb Root. 3. Honey Is A Proven Remedy For Diabetic Foot Ulcers. 4. Build Your Immunity With Astragalus Herb. 5. Gotu Kola Herbal Paste Benefits Diabetic Ulcers. 6. Minimize Inflammation With Aloe Vera Gel. 7. Heal The Diabetic Foot Ulcer With Apple Cider Vinegar. Diabetes is a chronic ailment that can be fatal if ...
What are the symptoms of diabetic foot ulcers?
What increases my risk for a diabetic foot ulcer?
- Blood sugar levels that are not controlled
- Nerve damage and numbness in your feet
- Poor blood flow
- A foot deformity, such as a bunion or hammertoe
- Calluses or corns on your feet or toes
- A decrease in vision that keeps you from seeing your feet clearly
- Being overweight
- Cigarette smoking or alcohol use
Are diabetic foot ulcers contagious?
Prevent hand-foot-and-mouth disease. It’s contagious, but you can reduce your child’s risk of catching it. Find out what helps. ... Diabetes: 12 warning signs that appear on your skin ... These open wounds are called diabetic ulcers. Diabetes and feet. If you have diabetes, you should check your feet every day for sores and open wounds.
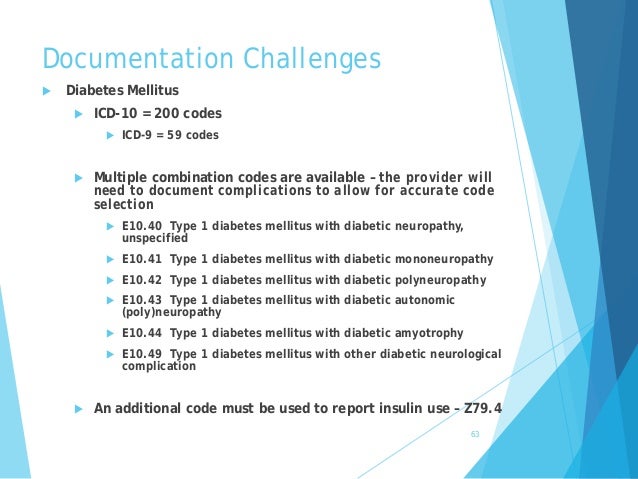
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic right foot ulcer?
Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of right foot with unspecified severity. L97. 519 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L97.
How do you code a diabetic with an ulcer?
Of these options, the most commonly used codes for diabetic foot ulcers are E10. 621 (Type 1 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer) and E11. 621 (Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer). “Code first” indicates that an additional code is required, and it must be listed first.
What is the ICD-10 code for ulcer of right foot?
519 for Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of right foot with unspecified severity is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic foot?
The ICD-10 codes are too extensive. For example, diabetic foot syndrome can be coded as 'diabetes mellitus with neurological complications' (E11. 4) and 'with impaired peripheral circulation' (E11. 5).
Is a diabetic foot ulcer a pressure ulcer?
Skin necrosis and gangrene are also included in the current system as ulcers.” This definition is similar to that of the EPUAP, all-inclusive and, as such, any pressure ulcer on the foot of a person with diabetes is a diabetic foot ulcer — as is any traumatic wound, including a thermal or chemical injury.
What is diabetic foot ulcer?
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that occurs in approximately 15 percent of patients with diabetes, and is commonly located on the bottom of the foot. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, six percent will be hospitalized due to infection or other ulcer-related complication.
Whats the difference between a pressure ulcer and a diabetic ulcer?
While diabetic patients can get pressure ulcers due to abuse or neglect in a nursing home, diabetic ulcers may appear in areas that are not typically subject to extended pressure—such as the bottoms of the feet when a resident has been lying down. In these cases, a diagnosis of a diabetic ulcer is more apt.
How do you code a diabetic foot infection?
71 a diabetic, it is considered a diabetic foot ulcer, and therefore should be coded using an L97- code. This is true even if arterial disease and/or pressure played a role in the develop- ment of this ulcer. patients, we must be thorough and accurate with our coding, compliance, and documen- tation.
What's the code for a non pressure chronic ulcer of the right foot with a breakdown of the skin?
ICD-10-CM Code for Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of right foot limited to breakdown of skin L97. 511.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of diabetic foot ulcer?
ICD-10 code Z86. 31 for Personal history of diabetic foot ulcer is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
When do you code E11 9?
ICD-10 Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications- E11. 9- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic foot ulcer left foot?
529: Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of left foot with unspecified severity.
Is a diabetic ulcer considered a stasis ulcer?
There are four (4) common types of skin ulcers: venous stasis ulcers, arterial ulcers, diabetic neuropathic ulcers and pressure ulcers. Three (3) of these ulcer types are exclusively lower-extremity wounds located on the foot, ankle and lower leg: venous stasis ulcers, arterial ulcers, and diabetic neuropathic ulcers.
What is the ICD 10 code for left diabetic foot ulcer?
Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of left foot with unspecified severity. L97. 529 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L97.
What is the difference between a pressure ulcer and a non-pressure ulcer?
The term “non-pressure ulcer” was coined to designate a primary mechanism other than shear or pressure. If there is poor circulation, such as that caused by venous or arterial insufficiency or excessive moisture or trauma, a patient may develop a non-pressure ulcer.
What is a full thickness ulcer?
Full-Thickness – A full-Thickness wound indicates that damage extends below the epidermis and dermis (all layers of the skin) into the subcutaneous tissue or beyond (into muscle, bone, tendons, etc.).
What causes diabetic foot ulcers?
A “diabetic foot ulcer,” which is caused exclusively by hyperglycemia, in the absence of neuropathy or ischemia, is a rarity. That term almost always refers to an ulcer on the foot of a diabetic that derives from neuro/ischemic etiology, as opposed to being strictly and principally due to pressure injury.
Why do diabetics get ulcers on their feet?
The American Podiatric Medical Association adds that “ (diabetic foot) ulcers form due to a combination of factors, such as lack of feeling in the foot, poor circulation, foot deformities, irritation (such as friction or pressure), and trauma, as well as duration of diabetes.” They go on to note that “vascular disease can complicate a foot ulcer, reducing the body’s ability to heal and increasing the risk for an infection.”
Why do diabetics have neuropathy?
Neuropathy occurs due to damage to the nerves and causes impaired sensation. After 10 years, ~90 percent of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics have some degree of neuropathy, most commonly affecting the feet and legs, and 90 percent of diabetic foot ulcers have diabetic neuropathy as a contributing factor. If the diabetic doesn’t recognize discomfort due to nerve impairment, they may not adjust their shoes and socks or seek medical attention for minor cuts or blisters.
What is a malum perforans pedis ulcer?
Neuropathy results in malum perforans pedis (a.k.a. bad perforating foot) ulcers. These are painless, non-necrotic, circular lesions circumscribed by hyperkeratosis. They often overlie a metatarsal head. Ischemic wounds manifest local signs of ischemia such as thin, shiny, hairless skin with pallor and coldness. These are often found at areas of friction and may be painful.
Why are pressure ulcers considered a patient safety indicator?
Pressure ulcers are deemed patient safety indicators and hospital acquired conditions because a concerted program for prevention and treatment can prevent them and protect our patients from iatrogenic harm. The diagnosis of a “pressure ulcer” may trigger prevalence and incident reporting.
Why should we specifically carve out pressure ulcers?
Why should we specifically carve out pressure ulcers? Pressure ulcers are deemed patient safety indicators and hospital acquired conditions because a concerted program for prevention and treatment can prevent them and protect our patients from iatrogenic harm. The diagnosis of a “pressure ulcer” may trigger prevalence and incident reporting.
What is non pressure ulcer?
The term “non-pressure ulcer” was coined to designate a primary mechanism other than shear or pressure. If there is poor circulation, such as that caused by venous or arterial insufficiency or excessive moisture or trauma, a patient may develop a non-pressure ulcer.
What is the ICd 10 code for osteomyelitis?
Other acute osteomyelitis, right ankle and foot M86.171 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.171 became effective on October 1, 2017. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M86.171 - other international versions of ICD-10 M86.171 may differ. The following code (s) above M86.171 contain annotation back-references In this context, annotation back-references refer to codes that contain: Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue Use an external cause code following the code for the musculoskeletal condition, if applicable, to identify the cause of the musculoskeletal condition certain conditions originating in the perinatal period ( P04 - P96 ) certain infectious and parasitic diseases ( A00-B99 ) compartment syndrome (traumatic) ( T79.A- ) complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium ( O00-O9A ) congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities ( Q00-Q99 ) endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases ( E00 - E88 ) injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes ( S00-T88 ) symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified ( R00 - R94 ) Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue 2016 2017 2018 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code code ( B95-B97 ) to identify infectious agent ICD-10-CM M86.171 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v35.0): : New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM) M86.149 Other acute osteomyelitis, unspecified hand M86.151 Other acute osteomyelitis, right femur M86.152 Other acute osteomyelitis, left femur M86.159 Other acute osteomyelitis, unspecified femur M86.16 Other acute osteomyelitis, tibia and fibula M86. Continue reading >>
What is the ICd 10 code for Legionella?
M86.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M86.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 M86.9 may differ. Legionella Testing Lab - High Quality Lab Results CDC ELITE & NYSDOH ELAP Certified - Fast Results North America Lab Locations legionellatesting.com Approximate Synonyms Aseptic necrosis with osteomyelitis Avascular necrosis of bone as late effect of osteomyelitis Bone infection of ankle Bone infection of femur Bone infection of foot Bone infection of pelvis Diabetes, type 1 with osteomyelitis Diabetes, type 2 with osteomyelitis Infection bone hand Infection bone in multiple sites Infection bone shoulder region Infection bone upper arm Infection of bone Infection of bone of ankle Infection of bone of finger Infection of bone of foot Infection of bone of forearm Infection of bone of hand Infection of bone of lower leg Infection of bone of multiple sites Infection of bone of shoulder girdle Infection of bone of the forearm Infection of bone of the lower leg Infection of bone of upper arm Infection of femur Infection of pelvis Infection of phalanx of finger or thumb Osteitis of bilateral femurs Osteitis of bilateral humeri Osteitis of bilateral pelvis Osteitis of bilateral pelvises Osteitis of left femur Osteitis of left humerus Osteitis of left pelvis Osteitis of multiple sites Osteitis of pelvic region Osteitis of right femur Osteitis of right humerus Osteitis of right pelvis Osteitis of thigh Osteitis of upper arm Osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis (bone infection) Osteomyelitis due to staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis due to type 1 diabetes mellitus Osteomyelitis due to type 2 diabetes mellitus Osteomyelitis of bilateral ankles Osteomyelitis of bilateral fee Continue reading >>
What is the code for diabetic foot ulcer?
Example: Diabetes with heel ulcer of the right foot, fat layer exposed, would be coded E11.621 and L97.412. Note the additional code for the ulcer and the increase in specificity with this diagnosis.
What are the ICD-10 codes for ulcers?
Codes for pressure ulcers and non-pressure chronic ulcers are located in ICD-10-CM chapter 12, Disease of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. The concept of laterality (e.g., left or right) is introduced, and should be included in the clinical documentation for skin ulcers. ICD-10-CM codes for Pressure ulcers, located in Category L89, are combination codes that identify the site, stage, and (in most cases) the laterality of the ulcer. Possible stages are 1-4, and unstageable. Stage 1: Skin changes limited to persistent focal edema Stage 2: An abrasion, blister, and partial thickness skin loss involving the dermis and epidermis Stage 3: Full thickness skin loss involving damage and necrosis of subcutaneous tissue Stage 4: Necrosis of soft tissues through the underlying muscle, tendon, or bone Unstageable: Based on clinical documentation the stage cannot be determined clinically (e.g., the wound is covered with eschar) or for ulcers documented as deep tissue injury without evidence of trauma. An instructional note in ICD-10 instructs us to code also any associated gangrene (I96). Non-pressure chronic ulcers are similar to pressure ulcers in that they require documentation of the site, severity, and laterality. Category L97 and L98 are for Non-pressure ulcers, and have an instructional note to code first any associated underlying condition, such as: The severity of the ulcers is described as: Example: A type 1 diabetic patient is seen in the clinic. Upon examination of her feet, she is noted to have a left heel ulcer with the breakdown of skin into the dermis, but not full thickness. The physician documents a diagnosis of diabetic heel ulcer. E10.621 Type 1 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer L97.421 Non-pressure chronic ulcer of left heel and midfoot limited to breakdown of Continue reading >>
What is the ICd 10 code for diabetic gangrene?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic peripheral angiopathy with gangrene E11.52 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Type 2 diabetes w diabetic peripheral angiopathy w gangrene The 2018 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.52 became effective on October 1, 2017. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.52 - other international versions of ICD-10 E11.52 may differ. Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic gangrene The following code (s) above E11.52 contain annotation back-references In this context, annotation back-references refer to codes that contain: Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases All neoplasms, whether functionally active or not, are classified in Chapter 2. Appropriate codes in this chapter (i.e. E05.8 , E07.0 , E16 - E31 , E34.- ) may be used as additional codes to indicate either functional activity by neoplasms and ectopic endocrine tissue or hyperfunction and hypofunction of endocrine glands associated with neoplasms and other conditions classified elsewhere. transitory endocrine and metabolic disorders specific to newborn ( P70-P74 ) Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases 2016 2017 2018 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code diabetes (mellitus) due to insulin secretory defect diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition ( E08.- ) drug or chemical induced diabetes mellitus ( E09.- ) secondary diabetes mellitus NEC ( E13.- ) Gangrene associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus Gangrene associated with type ii diabetes mellitus ICD-10-CM E11.52 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v35.0): 008 Simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplant 299 Peripheral vascular disorders with mcc 300 Peripheral vascular disorders with cc 301 Peripheral vascular disorders Continue reading >>
What is the ICd 9 code for diabetes?
Diabetes with peripheral circulatory disorders, type II or unspecified type, not stated as uncontrolled Short description: DMII circ nt st uncntrld. ICD-9-CM 250.70 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however, 250.70 should only be used for claims with a date of service on or before September 30, 2015. For claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015, use an equivalent ICD-10-CM code (or codes). You are viewing the 2014 version of ICD-9-CM 250.70. More recent version (s) of ICD-9-CM 250.70: 2015 . Convert to ICD-10-CM : 250.70 converts approximately to: 2015/16 ICD-10-CM E11.51 Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic peripheral angiopathy without gangrene Diabetes mellitus type 2 with complications Diabetes type 2 w ischemic ulcer of midfoot and heel Diabetes type 2 with circulation disorder Diabetes type 2 with ischemic ulcer of ankle Diabetes type 2 with ischemic ulcer of foot Diabetes type 2 with ischemic ulcer of toe Diabetes type 2 with small vessel disease DM 2 w diabetic ischemic heel and midfoot ulcer DM 2 w diabetic peripheral circulatory disorder DM 2 W diabetic peripheral vascular disease Gangrene associated with type II diabetes mellitus Ischemic ankle ulcer due to type 2 diabetes mellitus Ischemic foot ulcer due to type 2 diabetes mellitus Ischemic heel AND/OR midfoot ulcer due to type 2 diabetes mellitus Peripheral circulatory disorder associated with type II diabetes mellitus Peripheral circulatory disorder due to type 2 diabetes mellitus Small vessel disease due to type 2 diabetes mellitus Ulcer of toe due to type 2 diabetes mellitus Continue reading >>
What is the ICd 10 code for a non-pressure ulcer of the lower limb?
L00-L99 Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue L80-L99 Other disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissue L97- Non-pressure chronic ulcer of lower limb, not elsewhere classified Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of unspecified foot with unspecified severity L9 7.509 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Non-pressure chronic ulcer oth prt unsp foot w unsp severity The 2018 edition of ICD-10-CM L97.509 became effective on October 1, 2017. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L97.509 - other international versions of ICD-10 L97.509 may differ. The following code (s) above L97.509 contain annotation back-references In this context, annotation back-references refer to codes that contain: Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue certain conditions originating in the perinatal period ( P04 - P96 ) certain infectious and parasitic diseases ( A00-B99 ) complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium ( O00-O9A ) congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities ( Q00-Q99 ) endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases ( E00 - E88 ) symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified ( R00 - R94 ) systemic connective tissue disorders ( M30-M36 ) Non-pressure chronic ulcer of lower limb, not elsewhere classified 2016 2017 2018 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code any associated underlying condition, such as: specific infections classified to A00-B99 Non-pressure chronic ulcer of lower limb, not elsewhere classified Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of foot 2016 2017 2018 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of foot Atherosclerosis native artery of leg, foot ulcer Diabetes t Continue reading >>
Is diabetes a coding change?
Diabetic coding in ICD-10 has changed significantly from ICD-9. The requirement for documenting the type of diabetes and linking it to any complications still exist. However, in ICD-10, there are very few diabetic codes that require an additional code for the manifestation.
What causes ulcers in the body?
Ulceration caused by prolonged pressure in patients permitted to lie too still for a long period of time; bony prominences of the body are the most frequently affected sites; ulcer is caused by ischemia of the underlying structures of the skin, fat, and muscles as a result of the sustained and constant pressure. Codes.
What does type 2 exclude note mean?
A type 2 excludes note represents "not included here". A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( L89) and the excluded code together.

Terminology
Diagnosis
Clinical significance
Causes
Signs and symptoms
Epidemiology
- The American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society states that ulceration is an extremely common complication in diabetic patients (up to 12 percent of the population). The plantar surface is the most common site of ulceration, especially at areas of bony prominence. The Society also points out that the presence of neuropathy is the key factor in develo...
Society and culture
Treatment
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right metacarpal fracture
- 2. icd 10 code for acure rash
- 3. icd 10 code for right shoulder arthropathy
- 4. icd 10 code for breast pain lactation
- 5. icd-9-cm code for glaucoma
- 6. icd 10 cm code for grave's disease
- 7. icd 10 code for 72 year old gyn exam with abnormal findings
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for squamous cell carcinoma in situ nose
- 9. icd 10 code for radioculopathy right
- 10. icd 10 code for presence of penile prosthesis