Other specified diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer. E13.621 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM E13.621 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the best treatment for a diabetic ulcer?
Oct 01, 2021 · Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other skin ulcer E00-E89 2022 ICD-10-CM Range E00-E89 Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases Note All neoplasms, whether... E11 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E11 Type 2 diabetes mellitus 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific...
Can a diabetic ulcer heal by itself?
Oct 01, 2021 · Non-pressure chronic ulcer of right heel and midfoot with unspecified severity L97.419 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Non-prs chr ulcer of right heel and midfoot w unsp severt The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM ...
What is the prognosis of diabetic ulcers?
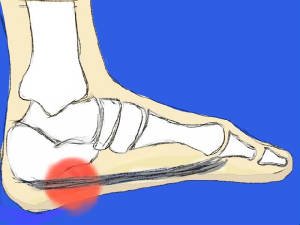
Oct 22, 2018 · A “diabetic foot ulcer,” which is caused exclusively by hyperglycemia, in the absence of neuropathy or ischemia, is a rarity. That term almost always refers to an ulcer on the foot of a diabetic that derives from neuro/ischemic etiology, as opposed to being strictly and principally due to pressure injury. Heel ulcers, however, are usually a ...
Which is the most common type of diabetic ulcer?
Aug 09, 2019 · The coder would then report ICD-10-CM code L89.623 (pressure ulcer of left heel, stage 3), as a secondary diagnosis. The coder would assign codes E11.51 (Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic peripheral angiopathy without gangrene) and E11.40 (Type 2 diabetes mellitus with neurological complications) as additional diagnoses. In this case, gangrene is …

What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic foot wound?
What is ICD-10 code for diabetic wound infection?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11. 622 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How do you code a diabetic foot infection?
How do you code a diabetic with a pressure ulcer?
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic foot foot ulcer?
What is the icd10 code for diabetes?
What is the ICD-10 code for foot ulcer?
Is diabetic foot ulcer a pressure ulcer?
What is the difference between pressure ulcer and non-pressure ulcer?
What is a diabetic pressure ulcer?
Can you link a pressure ulcer to diabetes?
Is a diabetic ulcer a stasis ulcer?
What is the code for diabetic foot ulcer?
Example: Diabetes with heel ulcer of the right foot, fat layer exposed, would be coded E11.621 and L97.412. Note the additional code for the ulcer and the increase in specificity with this diagnosis.
What is the ICd 10 code for a non-pressure ulcer of the lower limb?
L00-L99 Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue L80-L99 Other disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissue L97- Non-pressure chronic ulcer of lower limb, not elsewhere classified Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of unspecified foot with unspecified severity L9 7.509 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Non-pressure chronic ulcer oth prt unsp foot w unsp severity The 2018 edition of ICD-10-CM L97.509 became effective on October 1, 2017. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L97.509 - other international versions of ICD-10 L97.509 may differ. The following code (s) above L97.509 contain annotation back-references In this context, annotation back-references refer to codes that contain: Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue certain conditions originating in the perinatal period ( P04 - P96 ) certain infectious and parasitic diseases ( A00-B99 ) complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium ( O00-O9A ) congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities ( Q00-Q99 ) endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases ( E00 - E88 ) symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified ( R00 - R94 ) systemic connective tissue disorders ( M30-M36 ) Non-pressure chronic ulcer of lower limb, not elsewhere classified 2016 2017 2018 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code any associated underlying condition, such as: specific infections classified to A00-B99 Non-pressure chronic ulcer of lower limb, not elsewhere classified Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of foot 2016 2017 2018 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of foot Atherosclerosis native artery of leg, foot ulcer Diabetes t Continue reading >>
Can diabetes cause heel ulcers?
Heel ulcers, however, are usually a consequence of a pressure injury, although it is also possible to have another mechanism cause a non-pressure injury involving the heel. Diabetes may accelerate or complicate the injury. Neuropathy results in malum perforans pedis (a.k.a. bad perforating foot) ulcers.
What causes diabetic foot ulcers?
A “diabetic foot ulcer,” which is caused exclusively by hyperglycemia, in the absence of neuropathy or ischemia, is a rarity. That term almost always refers to an ulcer on the foot of a diabetic that derives from neuro/ischemic etiology, as opposed to being strictly and principally due to pressure injury.
What are the symptoms of ischemia?
They often overlie a metatarsal head. Ischemic wounds manifest local signs of ischemia such as thin, shiny, hairless skin with pallor and coldness. These are often found at areas of friction and may be painful.
Can diabetics get foot ulcers?
Diabetics are prone to foot ulcers, often with contributions from neuropathic, ischemic, and most commonly, neuro-ischemic (both) etiologies. Neuropathy occurs due to damage to the nerves and causes impaired sensation. After 10 years, ~90 percent of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics have some degree of neuropathy, most commonly affecting ...
What causes neuropathy in diabetics?
Neuropathy occurs due to damage to the nerves and causes impaired sensation. After 10 years, ~90 percent of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics have some degree of neuropathy, most commonly affecting the feet and legs, and 90 percent of diabetic foot ulcers have diabetic neuropathy as a contributing factor. If the diabetic doesn’t recognize discomfort due ...
Where do pressure ulcers form?
Pressure ulcers form in sites that experience shear or pressure, typically in tissue overlying bony prominences such as elbows, the sacrum, hips, or heels. After sacral, heel ulcers are the second most common type of pressure injury. The etymology of the term “decubitus ulcer” is from the Latin, decumbere, which means “to lie down,” ...
Is diabetes mellitus a secondary condition?
There are medical diagnoses that predispose patients to develop secondary conditions. Diabetes mellitus is a pervasive endocrinopathy whereby hyperglycemia affects every organ and system in the body, including the nerves and blood vessels. It makes a patient more prone to infection and poor healing.
What is the best foot protection for diabetics?
The GRADE 0 foot has intact skin. It has been found that this is the greatest protection to the diabetic foot. There may be bony deformities such as bunions, claw toes, depressed metatarsal heads and Charcot breakdown with bony prominences. There may be hyperkeratotic lesions around or under bony deformities.
What is the IDSA?
Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) [4]: for people with diabetes with suspected foot infections, with or without ulcers. [8] Does not include other elements such as ulcer, ischemic rest pain, ischemia or gangrene. The IDSA classification of diabetic foot infection was incorporated into the WIfI system, which includes these other elements and are more suited for patients with diabetic foot ulcers.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hemorrhoids
- 2. icd 10 code for submandibular gland swelling
- 3. icd-10 code e code for wasp bite
- 4. new icd 10 code for crohn's disease
- 5. icd 10 code for left knee total arthroplasty
- 6. icd 10 code for thrush, oral
- 7. icd 10 code for compound melanocytic nevus back
- 8. icd 10 code for breast cancer with mets
- 9. icd 9 code for sports massage
- 10. icd-9cm code for sterilization