What is the ICD 10 code for diabetes mellitus with peripheral vascular disease?
Diabetic Peripheral Vascular Disease Icd 10 Nov 29, 2017 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Diabetic Peripheral Angiopathy Without Gangrene E11.51 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for small vessel disease of brain?
The 437 codes are the best codes to represent the "small vessel disease of the brain" scenario I have found in ICD9. Luckily, ICD 10 offers more options in the "I65- I68" section.
What is the ICD 10 code for diabetes mellitus with other complications?
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Other Circulatory Complications E11.59 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the latest ICD 10 version for Type 1 diabetes?
Short description: Type 1 diabetes w diabetic peripheral angiopath w/o gangrene The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM E10.51 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E10.51 - other international versions of ICD-10 E10.51 may differ.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes?
What type of diabetes codes should be used?
When to use unspecified ICD-10?
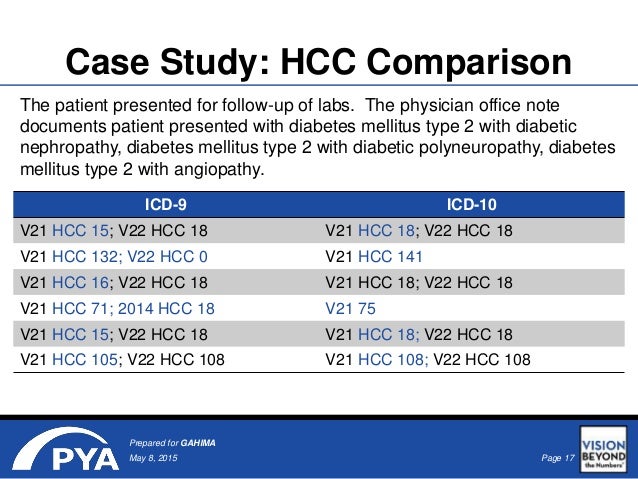
How do you code diabetes with PVD?
“Peripheral arteriosclerosis, peripheral vascular disease and peripheral arterial disease in a diabetic patient should be linked and coded as 'diabetic peripheral angiopathy. '" If diabetes (E11. 9) and peripheral artery disease (PAD) (I73.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes with vascular disease?
According to Coding Clinic, Third Quarter 2018, you should assign ICD-10-CM code E11. 51 (Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic peripheral angiopathy without gangrene) along with an additional code from subcategory I70. 2- to fully capture the patient's condition.
Do you code E11 51 and I73 9?
Document to the highest specificity and severity. E11. 51 Diabetes type II with PAD/PVD (no need to add code I73. 9) • Code I73.
When do you code E11 59?
ICD-10 Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other circulatory complications- E11. 59- Codify by AAPC.
What is diabetes with circulatory complications?
Diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis). If you have diabetes, you're more likely to have heart disease or stroke. Nerve damage (neuropathy).
What is mild peripheral vascular disease?
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a slow and progressive circulation disorder. Narrowing, blockage, or spasms in a blood vessel can cause PVD. PVD may affect any blood vessel outside of the heart including the arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels.
When do you use E11 51?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic peripheral angiopathy without gangrene. E11. 51 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.
What is the ICD 10 code for peripheral vascular?
ICD-10 code I73. 9 for Peripheral vascular disease, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is diabetes with peripheral angiopathy?
Diabetic peripheral angiopathy (DPA) is a blood vessel disease caused by high blood sugar levels (glucose). It is one of the most common complications of diabetes. It affects blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart.
What is the difference between E11 21 and E11 22?
The incorrect portion of the response came as an aside at the end, where it was stated that “it would be redundant to assign codes for both diabetic nephropathy (E11. 21) and diabetic chronic kidney disease (E11. 22), as diabetic chronic kidney disease is a more specific condition.”
When do you code E11 69?
ICD-10-CM Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other specified complication E11. 69.
What does E11 65 mean?
ICD-10 code E11. 65 represents the appropriate diagnosis code for uncontrolled type 2 diabetes without complications.
2022 ICD-10-CM Codes for Diabetes mellitus (E08-E13)
ICD-10 Codes used to specify 2022 ICD-10-CM Codes for Diabetes mellitus (E08-E13)
ICD-10 Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus- E11- Codify by AAPC
ICD-10-CM Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus E11 ICD-10 code E11 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E11: Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Free, official coding info for 2022 ICD-10-CM E11 - includes detailed rules, notes, synonyms, ICD-9-CM conversion, index and annotation crosswalks, DRG grouping and more.
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E11.65: Type 2 diabetes mellitus with ...
Free, official coding info for 2022 ICD-10-CM E11.65 - includes detailed rules, notes, synonyms, ICD-9-CM conversion, index and annotation crosswalks, DRG grouping and more.
Diabetes Coding Table
Diabetes outpatient self-management training services, group session (2 or more). ADCES Accredited or ADA Recognized ONLY and varies by provider type.
Common Diabetes ICD-10 Diagnosis Codes
Common Chronic Conditions ICD-10 Diagnosis Codes Amputations Z89.619 Lower Limb, Unspecified level Z89.419 Great Toe Z89.429 Toe Z89.439 Foot Z89.449 Ankle
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes?
For gestational diabetes (diabetes that occurs during pregnancy) women should be assigned a code under the 024.4 subheading and not any other codes under the 024 category.
What type of diabetes codes should be used?
If the type of diabetes that the patient has is not documented in the medical record, E11 codes for type 2 diabetes should be used as a default. If the medical record doesn’t say what type of diabetes the patient has but indicates that the patient uses insulin, the Type 2 diabetes codes should also be used.
When to use unspecified ICD-10?
The “unspecified” codes can be used when not enough information is known to give a more specific diagnosis; in that case, “unspecified” is technically more accurate than a more specific but as yet unconfirmed diagnosis. For more guidelines on using ICD-10 codes for diabetes mellitus, you can consult this document.
What is the ICd 10 code for Type 2 diabetes?
E11.51 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Type 2 diabetes w diabetic peripheral angiopath w/o gangrene This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.51 - other international versions of ICD-10 E11.51 may differ. Continue reading >>
What is the code for diabetes mellitus?
The body system (s) affected 3. The complications affecting the body system (s) When coding diabetes mellitus, you should use as many codes from categories E08-E13* as necessary to describe all of the complications and associated conditions of the disease.
What is the ICd 10 code for gangrene?
E10.51 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Type 1 diabetes w diabetic peripheral angiopath w/o gangrene This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E10.51 - other international versions of ICD-10 E10.51 may differ. Continue reading >>
What is the medical term for a shortage of oxygen and glucose?
The medical term for this condition is ischemia. The blood flow problem may be due to narrowing of the arteries by spasm or disease – or by some other form of arterial obstruction, such as pressure or trauma. Some serious health risks, including stroke, are associated with insufficient blood supply, depending upon where in the body the blood flow is restricted. When blood does not flow adequately to the capillary beds of the lower extremities, one of the most painful results may be an ischemic, or arterial, ulcer. These ulcers typically present on the lower leg or foot, particularly on the sides of the foot or the tips of a patient’s toes, where there is inadequate perfusion of skin and subcutaneous tissue. Clinicians generally recognize arterial ulcers by their “punched out” appearance. They are full thickness wounds with smooth edges. The appearance of the ulcer with regard to shearing and stretching of the tissue, whether dead tissue is sloughing off or whether there is eschar, a black tissue that can create a hard shell over an ulcer, is important to properly code an arterial ulcer. This is because ICD-10 classification requires documentation of the severity of the ulcer, even in the absence of documentation from the physician. We’ll take a look at the general stages of severity later in this article. Causes and relationships It is also important to note the underlying condition when coding arterial ulcers. Circulation problems which lead to ischemic, or arterial, ulcers may be caused by conditions such as coronary disease, artery disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, Pe Continue reading >>
What are the complications of diabetes?
Diabetes Complications Also called: Diabetic complications If you have diabetes, your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. Over time, this can cause problems with other body functions, such as your kidneys, nerves, feet, and eyes. Having diabetes can also put you at a higher risk for heart disease and bone and joint disorders. Other long-term complications of diabetes include skin problems, digestive problems, sexual dysfunction, and problems with your teeth and gums. Very high or very low blood sugar levels can also lead to emergencies in people with diabetes. The cause can be an underlying infection, certain medicines, or even the medicines you take to control your diabetes. If you feel nauseated, sluggish or shaky, seek emergency care. NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Diabetes - preventing heart attack and stroke (Medical Encyclopedia) Diabetes: Dental Tips - NIH (National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research) Diabetic hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome (Medical Encyclopedia) Diabetic ketoacidosis (Medical Encyclopedia) Long term complications of diabetes (Medical Encyclopedia) [Read More] Diabetes Type 2 Also called: Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes means your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood. Over time, high blood glucose can lead to serious problems with your heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and gums and teeth. You have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes if you are older, obese, have a family history of diabetes, or do not exercise. Having prediabetes also increases your risk. Continue reading >>
What happens if blood does not flow to the capillary beds of the lower extremities?
When blood does not flow adequately to the capillary beds of the lower extremities, one of the most painful results may be an ischemic, or arterial, ulcer.
Does type 2 diabetes have insulin?
With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood.
What is the ICd 9 code for small vessel disease?
I would verify with physician since this is not a heart scan/study. In ICD 9 "small vessel disease" is coded as 443.9: K.
What is the code for peripheral vessel?
The peripheral vessel code 443.9 can go for any vessel condition in which there is a deviation from or interruption of the normal structure or function of the blood vessels outside the heart; diseases of the peripheral as opposed to the cardiac circulation. It excludes : atherosclerosis of the arteries of the extremities (440.20-440.22)
Why is small vessel disease important?
Small vessel disease has an important role in cerebrovascular disease and is a leading cause of cognitive decline and functional loss in the elderly. Small vessel disease should be a main target for preventive and treatment strategies, but all types of presentation and complications should be taken into account].
What is 434.91 CVA?
434.91 is a CVA code . A CVA (Cerebral Vascular Accident) is commonly called a stroke. No I absolutely would not agree to 434.91. The question at hand asked about "small vessel disease in the brain" via an MRI result. Having small vessel disease MIGHT lead to a 434 code but it does not yet warrant one.
Is cerebrovascular disease a separate entity from PVD?
Yes I am sure and aware of that the cerebro vascular diseases are separate entity from PVD . But due to the inclusion of Carotid artery in classification in coding, it was a misconception. I could not find this particular disease in the broad listing of the CVD.
What is the ICd 10 code for Type 2 diabetes?
E11.51 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Type 2 diabetes w diabetic peripheral angiopath w/o gangrene This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.51 - other international versions of ICD-10 E11.51 may differ. Continue reading >>
What is the code for diabetes mellitus?
The body system (s) affected 3. The complications affecting the body system (s) When coding diabetes mellitus, you should use as many codes from categories E08-E13* as necessary to describe all of the complications and associated conditions of the disease.
What is the DCSI for diabetes?
The Diabetes Complications Severity Index (DCSI) converts diagnostic codes and laboratory results into a 14-level metric quantifying the long-term effects of diabetes on seven body systems. Adoption of the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) necessitates translation from ICD-9-CM and creates refinement opportunities. ICD-9 codes for secondary and primary diabetes plus all five ICD-10 diabetes categories were incorporated into an updated tool. Additional modifications were made to improve the accuracy of severity assignments. In the type 2 subpopulation, prevalence steadily declined with increasing score according to the updated DCSI tool, whereas the original tool resulted in an aberrant local prevalence peak at DCSI = 2. In the type 1 subpopulation, score prevalence was greater in type 1 versus type 2 subpopulations (3 versus 0) according to both instruments. Both instruments predicted current-year inpatient admissions risk and near-future mortality, using either purely ICD-9 data or a mix of ICD-9 and ICD-10 data. While the performance of the tool with purely ICD-10 data has yet to be evaluated, this updated tool makes assessment of diabetes patient severity and complications possible in the interim. Fig. 2. Prevalence and change in current-year admission risk by DCSI score; type 1 diabetes. NOTE: The intercept value for the admissions risk model, which is equivalent to admissions per 1000 for individuals with DCSI = 0, was 73.8 per 1000 (Young), 73.6 (updated DCSI, October 2014–September 2015), and 65.6 (updated DCSI, February 2015–January 2016). Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common form of diabetes and is currently a major worldwide cause of morbidity and mortality. This is likely to worsen, given th Continue reading >>
What is the medical term for a shortage of oxygen and glucose?
The medical term for this condition is ischemia. The blood flow problem may be due to narrowing of the arteries by spasm or disease – or by some other form of arterial obstruction, such as pressure or trauma. Some serious health risks, including stroke, are associated with insufficient blood supply, depending upon where in the body the blood flow is restricted. When blood does not flow adequately to the capillary beds of the lower extremities, one of the most painful results may be an ischemic, or arterial, ulcer. These ulcers typically present on the lower leg or foot, particularly on the sides of the foot or the tips of a patient’s toes, where there is inadequate perfusion of skin and subcutaneous tissue. Clinicians generally recognize arterial ulcers by their “punched out” appearance. They are full thickness wounds with smooth edges. The appearance of the ulcer with regard to shearing and stretching of the tissue, whether dead tissue is sloughing off or whether there is eschar, a black tissue that can create a hard shell over an ulcer, is important to properly code an arterial ulcer. This is because ICD-10 classification requires documentation of the severity of the ulcer, even in the absence of documentation from the physician. We’ll take a look at the general stages of severity later in this article. Causes and relationships It is also important to note the underlying condition when coding arterial ulcers. Circulation problems which lead to ischemic, or arterial, ulcers may be caused by conditions such as coronary disease, artery disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, Pe Continue reading >>
What happens if blood does not flow to the capillary beds of the lower extremities?
When blood does not flow adequately to the capillary beds of the lower extremities, one of the most painful results may be an ischemic, or arterial, ulcer.
What are the complications of diabetes?
Diabetes Complications Also called: Diabetic complications If you have diabetes, your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. Over time, this can cause problems with other body functions, such as your kidneys, nerves, feet, and eyes. Having diabetes can also put you at a higher risk for heart disease and bone and joint disorders. Other long-term complications of diabetes include skin problems, digestive problems, sexual dysfunction, and problems with your teeth and gums. Very high or very low blood sugar levels can also lead to emergencies in people with diabetes. The cause can be an underlying infection, certain medicines, or even the medicines you take to control your diabetes. If you feel nauseated, sluggish or shaky, seek emergency care. NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Diabetes - preventing heart attack and stroke (Medical Encyclopedia) Diabetes: Dental Tips - NIH (National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research) Diabetic hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome (Medical Encyclopedia) Diabetic ketoacidosis (Medical Encyclopedia) Long term complications of diabetes (Medical Encyclopedia) [Read More] Diabetes Type 2 Also called: Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes means your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood. Over time, high blood glucose can lead to serious problems with your heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and gums and teeth. You have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes if you are older, obese, have a family history of diabetes, or do not exercise. Having prediabetes also increases your risk. Continue reading >>
What is the term for a narrowing of the arteries in the heart?
Peripheral Artery Disease. Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a narrowing of the arteries other than those that supply the heart or the brain. [4] . When narrowing occurs in the heart, it is called coronary artery disease, while, in the brain, it is called cerebrovascular disease.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes?
For gestational diabetes (diabetes that occurs during pregnancy) women should be assigned a code under the 024.4 subheading and not any other codes under the 024 category.
What type of diabetes codes should be used?
If the type of diabetes that the patient has is not documented in the medical record, E11 codes for type 2 diabetes should be used as a default. If the medical record doesn’t say what type of diabetes the patient has but indicates that the patient uses insulin, the Type 2 diabetes codes should also be used.
When to use unspecified ICD-10?
The “unspecified” codes can be used when not enough information is known to give a more specific diagnosis; in that case, “unspecified” is technically more accurate than a more specific but as yet unconfirmed diagnosis. For more guidelines on using ICD-10 codes for diabetes mellitus, you can consult this document.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for dysphagia due to cva
- 2. icd 9 code for social phobia
- 3. icd 9 code for oa of hip
- 4. icd 10 cm code for /metastatic squamous cell cancer
- 5. icd 10 code for sarcoma of the inferior vena cava
- 6. icd 10 code for calcific tendinopathy
- 7. icd-10 code for abdominal wound
- 8. icd 10 code for diabetic nutrition counseling
- 9. icd 10 code for h66.02
- 10. icd 10 code for right homonymous hemianopia due to cva