What is the ICD 10 code for congenital malformations of diaphragm?
Other congenital malformations of diaphragm. Q79.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM Q79.1 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the new ICD 10 for diaphragm dome?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q79.1 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q79.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 Q79.1 may differ. A congenital abnormality characterized by the elevation of the diaphragm dome.
What is diaphragm dome dysplasia?
A congenital abnormality characterized by the elevation of the diaphragm dome. It is the result of a thinned diaphragmatic muscle and injured phrenic nerve, allowing the intra-abdominal viscera to push the diaphragm upward against the lung. A congenital or acquired abnormality characterized by elevation of the hemidiaphragm.
What causes diaphragm dome to be elevated?
A congenital abnormality characterized by the elevation of the diaphragm dome. It is the result of a thinned diaphragmatic muscle and injured phrenic nerve, allowing the intra-abdominal viscera to push the diaphragm upward against the lung.
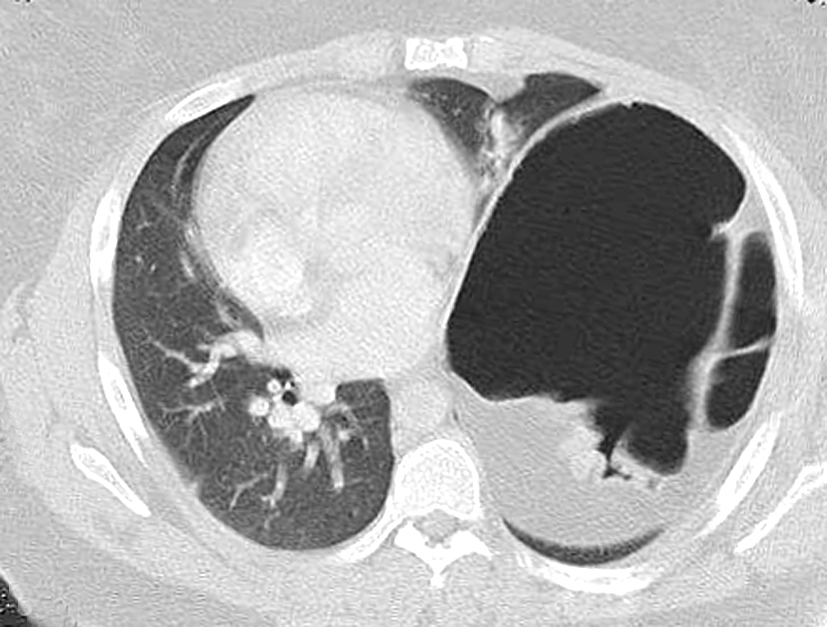
What is diaphragm eventration?
Diaphragmatic eventration (DE) is the abnormal elevation of a portion or entire hemidiaphragm due to a lack of muscle or nerve function while maintaining its anatomical attachments. The abnormality can be congenital or acquired, thus presenting in both the pediatric and adult populations.
What is congenital eventration of diaphragm?
Eventration of the diaphragm in infants is an uncommon disorder in which all or part of the diaphragmatic muscle is replaced by fibroelastic tissue, leading to a thinned and pliable central portion of the diaphragm. It is a result of either inadequate development (congenital) or atrophy (acquired) of the diaphragm.
What is eventration of the right hemidiaphragm?
Eventration of the diaphragm is a term used to describe an abnormal elevation of part or whole of the hemidiaphragm, where the whole or part of the diaphragm is made up of a thin fibro membranous sheet replacing normal diaphragmatic musculature.
Is diaphragmatic Eventration common?
It is a condition in which all or part of the diaphragm is largely composed of fibrous tissue with only a few or no interspersed muscle fibers. It can be complete or partial. Complete eventration of the right diaphragm, as seen in this adult patient, is relatively rare.
What is the meaning of eventration?
eventration. / (ˌiːvɛnˈtreɪʃən) / noun. pathol protrusion of the bowel through the abdomen.
What is the Definition of eventration?
Medical Definition of eventration : protrusion of abdominal organs through the abdominal wall.
Is eventration the same as hernia?
Abstract. Background: A hernia is due to a defect in the diaphragm. An eventration is due to a thinned diaphragm with no central muscle.
Is diaphragmatic Eventration serious?
According to most authors, 'true' eventration is always a congenital condition due to a defect of development of one portion or the entire central part of the diaphragm [1-4] and is characterized by a membranous appearance of the muscle with a marked decrease in muscle fibers compared to the normal muscle [4, 5].
What causes elevated right hemidiaphragm?
Raised hemidiaphragm The right hemi-diaphragm usually lies at a level slightly above the left. There are many possible causes of a raised hemidiaphragm such as damage to the phrenic nerve, lung disease causing volume loss, congenital causes such as a diaphragmatic hernia, or trauma to the diaphragm.
Can an elevated diaphragm heal itself?
However, most patients with elevated hemidiaphragm are asymptomatic. Asymptomatic patients with idiopathic etiology may not require any intervention. Elevated hemidiaphragm caused by phrenic nerve impairment can be transient and may resolve without further intervention.
What are the symptoms of an elevated diaphragm?
SymptomsDiscomfort or difficulty breathing.Pain in the chest, shoulder or abdominal area.Hypoxemia (a lack of oxygen in the blood)Fewer breath sounds.Paralysis, in rare cases.
Why is the right side of the diaphragm higher than the left?
Over the past three decades, the classic teaching has been that the diaphragm is elevated in the right side because the liver is in the right side.
How serious is an elevated diaphragm?
Complications of elevated hemidiaphragm related to neuropathic or muscular causes can lead to respiratory distress, which can progress to respiratory failure or heart failure.
Is eventration the same as hernia?
Abstract. Background: A hernia is due to a defect in the diaphragm. An eventration is due to a thinned diaphragm with no central muscle.
Why is congenital diaphragmatic hernia on left?
A left-sided CDH allows for the possibility of the stomach, intestines, and sometimes the liver to move (herniate) up into the baby's chest. The other 17% of babies with CDH have a defect on the right side of the diaphragm. A right-sided CDH almost always allows the liver to move into the chest.
What causes raised diaphragm?
Temporary elevation of the diaphragm occurs in pneumonia, lung abscess, subphrenic abscess, liver abscess, diabetes, Banti's disease, during digestion, and normally at full expiration.
What is the cause of the elevation of the diaphragm?
A congenital abnormality characterized by the elevation of the diaphragm dome. It is the result of a thinned diaphragmatic muscle and injured phrenic nerve, allowing the intra-abdominal viscera to push the diaphragm upward against the lung.
When will the ICD-10-CM Q79.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q79.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for prosthetic cardiac valve
- 2. icd 9 code for spastic hemiparesis
- 3. icd 10 code for low b12
- 4. icd 9 code for open surgical wound
- 5. icd-10 code for hot flashes menopause
- 6. icd 10 code for history of red man's syndrome due to vancomycin
- 7. icd 10 code for peripheral arterial occlusive disease
- 8. icd 10 cm code for laceration of cervix (obstetrics)
- 9. icd 10 cm code for thrombocytopenia
- 10. icd 10 code for pah