What is the ICD 10 code for congenital malformations of diaphragm?
Other congenital malformations of diaphragm. Q79.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM Q79.1 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the new ICD 10 for diaphragm dome?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q79.1 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q79.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 Q79.1 may differ. A congenital abnormality characterized by the elevation of the diaphragm dome.
What is eventration ICD 10 Index?
Eventration ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index. The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index is designed to allow medical coders to look up various medical terms and connect them with the appropriate ICD codes. There are 2 terms under the parent term 'Eventration' in the ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index .
What causes diaphragm dome to be elevated?
A congenital abnormality characterized by the elevation of the diaphragm dome. It is the result of a thinned diaphragmatic muscle and injured phrenic nerve, allowing the intra-abdominal viscera to push the diaphragm upward against the lung.

What is diaphragmatic Eventration?
Diaphragmatic eventration (DE) is the abnormal elevation of a portion or entire hemidiaphragm due to a lack of muscle or nerve function while maintaining its anatomical attachments. The abnormality can be congenital or acquired, thus presenting in both the pediatric and adult populations.
What is diaphragmatic plication?
Diaphragmatic plication is a procedure used to surgically treat diaphragmatic eventrations/paralysis. The procedure involves repositioning and/or reshaping the diaphragm to expand lung capacity and ultimately, improve breathing difficulties caused by these conditions.
What is elevated diaphragm?
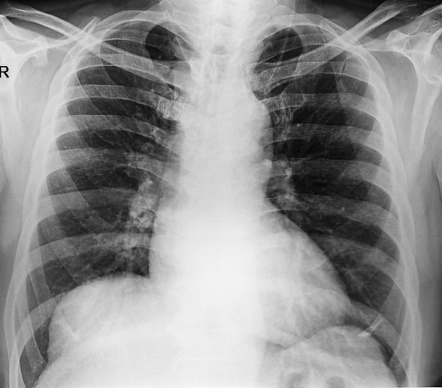
[1] Elevated hemidiaphragm occurs when one side of the diaphragm becomes weak from muscular disease or loss of innervation due to phrenic nerve injury. Patients may present with difficulty breathing, but more commonly elevated hemidiaphragm is found on imaging as an incidental finding, and patients are asymptomatic.
What is paralyzed diaphragm?
Patients with a paralyzed diaphragm experience weakness of the diaphragm and have reduced breathing capabilities or are unable to control their voluntary breathing. They also have difficulty maintaining adequate gas exchange, as the lungs are not able to inhale and exhale outside air as efficiently.
What is plication mean?
1 : the tightening of stretched or weakened bodily tissues or channels by folding the excess in tucks and suturing plication of the neck of the bladder. 2 : the folding of one part on and the fastening of it to another (as areas of the bowel freed from adhesions and left without normal serosal covering)
What is a plication operation?
Laparoscopic gastric plication is a newer minimally invasive weight-loss surgery technique that reduces the size of the stomach capacity to approximately 3 ounces. It is a restrictive weight-loss surgery, meaning that it restricts the amount of food the stomach can hold.
What causes eventration?
Most cases of diaphragm eventration can be present at birth (congenital) or develop due to injury, trauma, or an infection.
What causes diaphragm elevation?
Temporary elevation of the diaphragm occurs in pneumonia, lung abscess, subphrenic abscess, liver abscess, diabetes, Banti's disease, during digestion, and normally at full expiration.
What causes a tilted diaphragm?
The right hemi-diaphragm usually lies at a level slightly above the left. There are many possible causes of a raised hemidiaphragm such as damage to the phrenic nerve, lung disease causing volume loss, congenital causes such as a diaphragmatic hernia, or trauma to the diaphragm.
What is the difference between paresis and Plegia?
Paresis is a reduction in muscle strength with a limited range of voluntary movement. Paralysis (-plegia) is a complete inability to perform any movement.
How is diaphragm paralysis diagnosis?
Computed tomography scanning of the chest, abdomen or both. Magnetic resonance imaging to determine if there is an underlying condition involving the spinal column or nerve roots. Ultrasound to see the activity of the diaphragm and to identify any unusual movement or lack of movement.
What does a positive sniff test mean?
A sniff test shows if there are problems with the phrenic nerve, which controls movement of the diaphragm.
What is billable code?
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. The Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) requires medical coders to indicate whether or not a condition was present at the time of admission, in order to properly assign MS-DRG codes.
Is diagnosis present at time of inpatient admission?
Diagnosis was present at time of inpatient admission. Yes. N. Diagnosis was not present at time of inpatient admission. No. U. Documentation insufficient to determine if the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for detrusor instability
- 2. icd 10 code for left upper lobe lung nodule
- 3. icd 10 code for bronchial pneumonia
- 4. icd 10 code for /acute arterial occlusion
- 5. icd-10 code for metastatic lung cancer
- 6. icd 10 code for hemoglobin a1c
- 7. icd 10 code for muscle strain of upper back
- 8. icd 10 code for iud strings lost
- 9. icd 10 code for encounter for blood sugar check
- 10. icd 9 code for cystoid macular edema