What is the ICD 10 code for dyspnea?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50.3 Diastolic (congestive) heart failure 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code I50.3 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Jan 25, 2020 · Unspecified diastolic (congestive) heart failure I50. 30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM I50. 30 became effective on October 1, 2019. One may also ask, is diastolic dysfunction the same as heart failure?
What is diagnosis code 10?
Oct 01, 2021 · Unspecified diastolic (congestive) heart failure. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. I50.30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.30 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does Grade 1 diastolic dysfunction mean?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. I51.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I51.9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I51.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 I51.9 may differ.
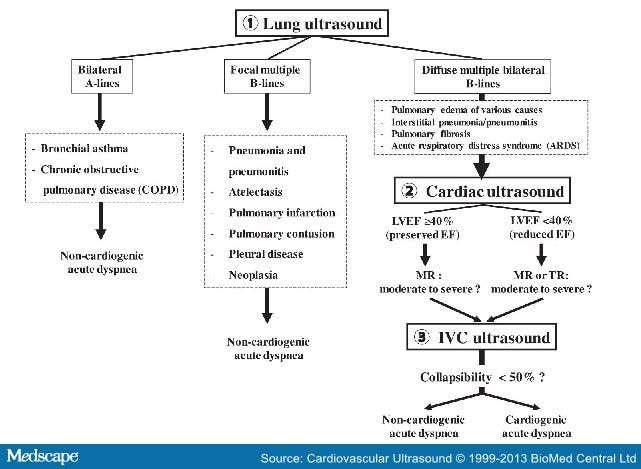
What is the ICD-10 code for diastolic dysfunction?
3.
Is grade 1 diastolic dysfunction the same as heart failure?
Grade I – The E/A ratio is reversed on the mitral inflow echocardiogram. This is the mildest form of diastolic heart failure and is referred to as an abnormal relaxation pattern. Patients are usually asymptomatic.
What is the difference between grade 1 and 2 diastolic dysfunction?
Patients with grade 1 DD can unexpectedly have elevated LVEDPs [15], while in patients with grade 2 DD, resting LV filling pressures may be elevated [16, 17], or within the normal range [18, 19].Jun 24, 2015
What is meant by diastolic dysfunction?
When the muscles of the heart become stiff, they can't relax properly, creating a condition known as diastolic dysfunction. This inflexibility prevents the heart's ventricles from filling completely, causing blood to back up in the organs.
What is a grade 1 diastolic dysfunction?
Grade 1 diastolic dysfunction occurs when the left lower chamber of the heart (the left ventricle) has trouble relaxing in between beats because it has stiffened over time. It interferes slightly with the heart's most important job—getting oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.Oct 8, 2021
Should I worry about grade 1 diastolic dysfunction?
The fact of the matter is true diastolic dysfunction is indeed dangerous, if not more dangerous than systolic dysfunction for the simple reason there is no specific treatment for this condition.Apr 16, 2016
What grade is mild diastolic dysfunction?
Diastolic dysfunction was graded on a four-point ordinal scale: 1) normal; 2) mild diastolic dysfunction = abnormal relaxation without increased LV end-diastolic filling pressure (decreased E/A ratio <0.75); 3) moderate or “pseudonormal” diastolic dysfunction = abnormal relaxation with increased LV end-diastolic ...
How many grades are there of diastolic dysfunction?
There are four grades of diastolic dysfunction, as described below. Clinical manifestations of congestive heart failure may start to occur once grade II diastolic dysfunction is present, but not in the presence of grade I diastolic dysfunction (impaired relaxation).
How many grades are there in diastolic dysfunction?
There are four grades of diastolic dysfunction as described below. Echocardiography is the gold standard to diagnose diastolic dysfunction.
How is diastolic dysfunction diagnosed?
Diastolic dysfunction, a type of heart failure in which the heart isn't able to fully relax after each beat, is diagnosed with an echocardiogram (ECG) and, sometimes, other imaging tests.Jun 10, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for heart failure?
I50.30 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of unspecified diastolic (congestive) heart failure. The code I50.30 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code I50.30 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like at high risk for heart failure, at high risk for heart failure, at risk for heart failure, at risk for heart failure, diastolic heart failure , diastolic heart failure stage a, etc.#N#The code is commonly used in cardiology medical specialties to specify clinical concepts such as heart failure.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like I50.30 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
When to use unspecified codes?
Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record. ICD-10: I50.30. Short Description:
How do doctors diagnose heart failure?
Your doctor will diagnose heart failure by doing a physical exam and heart tests. Treatment includes treating the underlying cause of your heart failure, medicines, and heart transplantation if other treatments fail. NIH: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for personal history of cellulitis
- 2. icd 10 code for healing post op abdominal wound icd 10
- 3. icd 10 code for subgaleal hematoma
- 4. icd 10 cm code for thyrotoxicosis
- 5. icd 9 code for pacemaker check
- 6. what is the icd code for quest
- 7. icd 10 code for r heel pain
- 8. icd 10 code for instability of ankle
- 9. icd 10 code for chronic myofascial pain
- 10. icd-code for left wrist fracture