How to classify distal radius fractures?
- Aged
- Clinical Competence / standards*
- Consensus*
- Europe
- Fracture Fixation, Internal / methods
- Fracture Fixation, Internal / standards*
- Fracture Healing
- Humans
- Intra-Articular Fractures / classification*
- Intra-Articular Fractures / surgery
What does distal radius fracture mean?
A distal radius fracture is a common bone fracture of the radius in the forearm. Because of its proximity to the wrist joint, this injury is often called a wrist fracture. Treatment is usually with immobilization, although surgery is sometimes needed for complex fractures. Specific types of distal radius fractures are Colles' fracture; Smith's fracture; Barton's fracture; Chauffeur's fracture.
Should angulated distal radius fractures be reduced?
When distal radius fractures are not simple fracture patterns, reduction may best be performed in the hands of an orthopedist or hand surgeon. Highly comminuted intra-articular fractures are unstable in anyone’s hands and will require surgery.
Do I need distal radial fracture surgery?
Surgery for Distal Radius Fractures This option is usually for fractures that are considered unstable or can’t be treated with a cast. Surgery is typically performed through an incision over the volar aspect of your wrist (where you feel your pulse). This allows full access to the break.
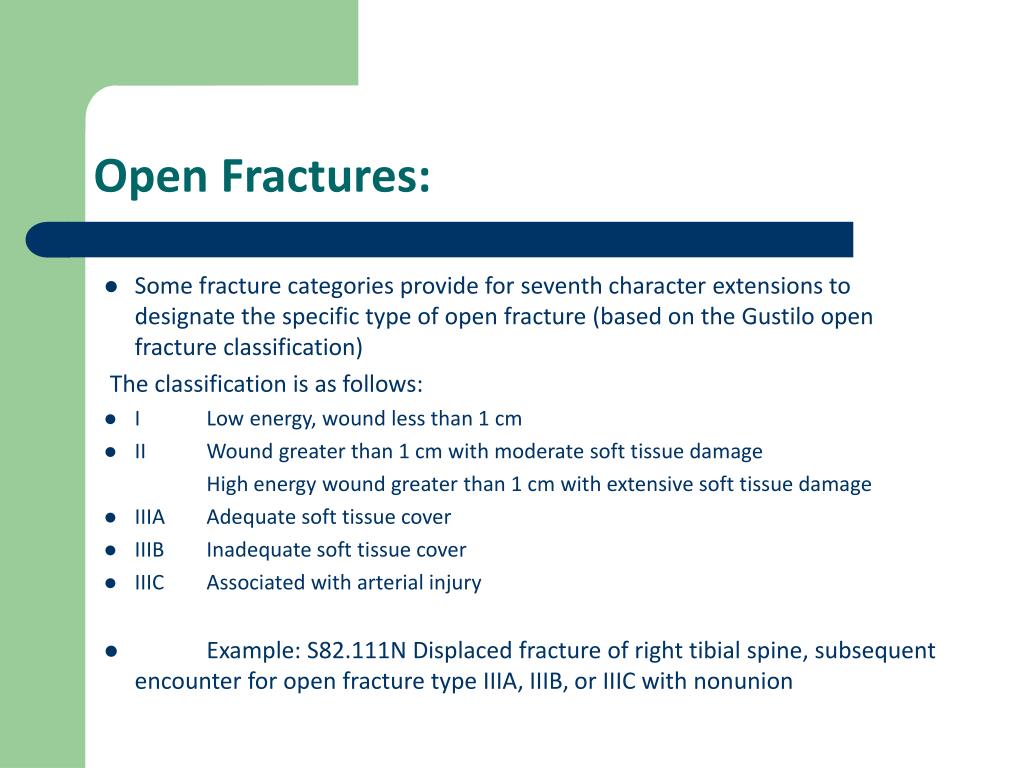
What is the ICD 10 code for displaced fracture?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S62. 329B: Displaced fracture of shaft of unspecified metacarpal bone, initial encounter for open fracture.
What is the ICD 10 code for fracture distal radius?
ICD-10 code S52. 5 for Fracture of lower end of radius is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
Where is the distal end of the radius?
The radius is one of two forearm bones and is located on the thumb side. The part of the radius connected to the wrist joint is called the distal radius. When the radius breaks near the wrist, it is called a distal radius fracture.
What is the ICD 10 code for left radial shaft fracture?
S52. 302A - Unspecified fracture of shaft of left radius [initial encounter for closed fracture] | ICD-10-CM.
What is a displaced fracture?
Displaced fractures: A gap forms where the bone breaks. Often, this injury requires surgery to fix. Partial fractures: The break doesn't go all the way through the bone. Stress fractures: The bone gets a crack in it, which is sometimes tough to find with imaging.
What is the code for closed fracture left distal radius and ulna?
Table: CodeICD10 Code (*)Code Description (*)S52.50Fracture of lower end of radius, closedS52.51Fracture of lower end of radius, openS52.6Fracture of lower end of both ulna and radiusS52.60Fracture of lower end of both ulna and radius, closed26 more rows
What is a displaced radial fracture?
The end of the radius is displaced or angled in the direction of the palm of the hand. It accounts for about 5% of all radial and ulnar fractures combined. Barton's Fracture. The most common cause of this fracture is a fall on an outstretched wrist. It is a compression injury that extends well into the wrist joint.
What type of fracture is a distal radius fracture?
The distal radius is a bone that is located in the forearm. The radius is the larger of the two bones in the area while the end portion towards the wrist is referred to as the distal end. Therefore, when the radius bone close to the wrist breaks its diagnosed as a distal radius fracture.
What is a closed fracture of distal end of radius?
A fracture of the distal radius occurs when the radius — one of the two long bones in the forearm — breaks close to the wrist. Distal radius fractures are very common. In fact, the radius is the most commonly broken bone in the arm.
What is the ICD-10 code for fracture?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S52. 501A: Unspecified fracture of the lower end of right radius, initial encounter for closed fracture.
What is the left radius?
It is located on the lateral side of the forearm parallel to the ulna (in anatomical position with arms hanging at the sides of the body, palms facing forward) between the thumb and the elbow.
What is ulna and radius?
The radius and ulna are long bones that make up the forearm, extending from the elbow to the wrist. In the anatomical position, the radius is found in the lateral forearm, while the ulna is found in the medial forearm.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for family history of glaucoma
- 2. icd 10 code for joint inflammation due to arthritis.
- 3. icd 10 code for pulmonary embolism
- 4. icd 10 cm code for worried well
- 5. icd 10 code for dislocation left shoulder
- 6. icd 10 code for episodic alcohol abuse how to code
- 7. icd 10 code for blunt force trauma to chest
- 8. icd code between patient and daughter for social work
- 9. icd 10 code for vascular peripherals
- 10. icd 10 diagnosis code for migraines