What is the ICD 10 code for gastrostomy tube placement?
Oct 01, 2021 · Short description: Displacement of gastrointestinal prosth dev/grft The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM T85.528 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of T85.528 - other international versions of ICD-10 T85.528 may differ. The following code (s) above T85.528 contain annotation back-references
What is the ICD 10 code for nasogastric tube?
Oct 01, 2021 · Displacement of nephrostomy catheter, initial encounter. 2017 - New Code 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. T83.022A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM T83.022A became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for gastrointestinal prosth Dev/GRFT?
Consider using any of the following ICD-10 codes with a higher level of specificity when coding for displacement of gastrointestinal prosth dev/grft: BILLABLE CODE - Use T85.528A for initial encounter. BILLABLE CODE - Use T85.528D for subsequent encounter. BILLABLE CODE - Use T85.528S for sequela.
What is the ICD 10 code for nephrostomy?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K94.23 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K94.23 Gastrostomy malfunction 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code K94.23 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K94.23 became effective on October 1, 2021.

What is the ICD-10 code for G tube?
Z93.1ICD-10-CM Code for Gastrostomy status Z93. 1.
What is the ICD-10 code for PEG tube malfunction?
Valid for SubmissionICD-10:K94.23Short Description:Gastrostomy malfunctionLong Description:Gastrostomy malfunction
What happens when a PEG tube becomes dislodged?
If the tube is dislodged within 4 weeks of initial placement, patients are at significant risk of peritonitis and perforation due to peritoneal spillage of gastric contents through the immature track, and replacement should not be attempted without surgical consultation.Jul 18, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for leaking PEG tube?
0318/30 PEG infection/leaking gastrostomy tube In ICD-10-AM/ACHI/ACS Tenth Edition, new codes were created at K91. 4 Malfunction of stoma of the digestive system including stoma haemorrhage, infection, leak, and malfunction.
What is the CPT code for replacement of gastrostomy tube?
For CPT code 43762, the physician replaces a gastrostomy tube via percutaneous approach that does not require revision (simple) of the gastrostomy tract.Mar 3, 2022
What is gastrostomy mean?
noun, plural gas·tros·to·mies. Surgery. the construction of an artificial opening from the stomach through the abdominal wall, permitting intake of food or drainage of gastric contents.
How do I know if my G tube is in place?
Checking GJ Placement Simply insert about 15ml of dyed formula or Kool Aid into the J-port and allow the G-tube to drain into a diaper, basin, or bag. If the colored formula or Kool Aid immediately flows out of the G-port, the tube may be out of place.Mar 13, 2020
How do you know if a PEG tube is in place?
0:421:46How often do I need to check tube placement? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou can confirm placement of a gastric tube by checking the fluids drawn out of the stomach.MoreYou can confirm placement of a gastric tube by checking the fluids drawn out of the stomach.
How do you know if an NG tube is properly positioned?
Correct NG tube positionCheck the tube passes vertically in the midline, or near the midline, below the level of the carina (red ring)The tube MUST NOT follow the course of the right or left main bronchi.More items...
Why does a PEG tube leak?
Leakage. Leakage of feed/gastric contents around the PEG site can occur due to poor positioning of the external fixation plate (it is not flush to the skin) after insertion. Leakage may also occur if the tube is too small for the stoma, as gastric contents can leak around the tube.Oct 31, 2014
Is a PEG tube a gastrostomy?
A PEG (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy) feeding tube insertion is the placement of a feeding tube through the skin and the stomach wall. It goes directly into the stomach. PEG feeding tube insertion is done in part using a procedure called endoscopy. Feeding tubes are needed when you are unable to eat or drink.Jul 1, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for Transaminitis?
R74.0ICD-10-CM Code for Nonspecific elevation of levels of transaminase and lactic acid dehydrogenase [LDH] R74. 0.
What is the ICd 10 code for displacement of nephrostomy catheter?
Displacement of nephrostomy catheter, initial encounter 1 T83.022A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM T83.022A became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of T83.022A - other international versions of ICD-10 T83.022A may differ.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. code to identify any retained foreign body, if applicable ( Z18.-)
Coding Guidelines
The appropriate 7th character is to be added to each code from block Complications of internal prosth dev/grft (T85). Use the following options for the aplicable episode of care:
Index to Diseases and Injuries
The Index to Diseases and Injuries is an alphabetical listing of medical terms, with each term mapped to one or more ICD-10 code (s). The following references for the code T85.528 are found in the index:
Approximate Synonyms
The following clinical terms are approximate synonyms or lay terms that might be used to identify the correct diagnosis code:
What are the different types of stents?
The following clinical terms are approximate synonyms or lay terms that might be used to identify the correct diagnosis code: 1 Accidental removal of nasogastric tube 2 Device withdrawn and / or removed 3 Disorder of pancreatic stent 4 Displacement of pancreatic stent 5 Migration of implant or internal device 6 Migration of nasogastric tube 7 Migration of percutaneous transhepatic biliary drain catheter
When is T85.528A valid?
The code T85.528A is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. T85.528A is an initial encounter code, includes a 7th character and should be used while the patient is receiving active treatment for a condition like displacement of other gastrointestinal ...
What is the procedure called when a tube is inserted into the intestines?
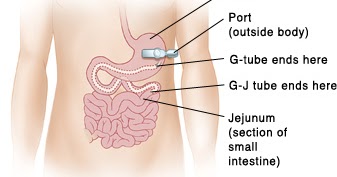
Gastro Jejunostomy Tube (GJ-Tube) Procedure. This is a feeding tube which is inserted through the gastrostomy stoma in the abdominal wall, passes through the stomach and advanced into the jejunum. This tube feeding directly into the intestines is called Gastrojejunostomy tube (GJ-Tube).
What is a gastrostomy tube?
Gastrostomy Tube (G-Tube) Procedure. This is a tube inserted into the stomach through a small incision in the abdomen. The tube goes through the skin (percutaneous) to the stomach wall and then into the stomach. This tube feeding into the stomach is called gastrostomy tube (G-Tube).
Why do doctors insert G tubes?
The physician inserts G-tube in those patients so that they can take adequate nutrition by mouth. However, some patients (mostly children) are unable to tolerate feeding of food directly into the stomach. The G-tube is required to be converted into GJ tube in these cases. This article covers all the ICD Codes and CPT Codes required for ...
Where is the tube placed for gastric tube placement?
Gastrostomy Tube Placement Procedures. The patient is placed supine on the procedure table and prepped and draped sterilely. The physician places a tube through the skin and into the stomach and uses x-rays to make sure it is in the right place.
Can a G tube be converted to a GJ tube?
The G-tube is required to be converted into GJ tube in these cases. This article covers all the ICD Codes and CPT Codes required for the medical billing of this conversion procedure under fluoroscopic guidance. There are some adult patients, who cannot take enough food through the mouth or have swallowing food problems, ...
How long does a NG tube last?
When an NG tube is used for nutrition alone, it either runs continuously, 16 hours on and eight hours off, or by bolus feedings, meaning feeding is delivered en masse at one time. Bolus feedings are tantamount to eating meals three to five times a day. A Look at the Codes.
How big is a Dobhoff tube?
A Dobhoff tube is a small-bore, flexible tube that typically has an inside diameter of about 0.15 inches (4 mm) that is inserted into the stomach by way of the nasal passage. Use of this particular type of NG tube is considered a best practice. Following insertion, correct placement is confirmed by X-ray.
What is NG tube?
For inpatients, the NG tube (NGT) is generally used to aspirate stomach contents or administer nourishment and medicine to people who cannot ingest anything by mouth.
Why is NG intubation necessary?
NG intubation is medically necessary for a variety of clinical situations, including: Patients who can’t eat or swallow. Cases of neck or facial injuries. When mechanical ventilation is required or the patient is comatose. To relieve pressure on intestinal obstruction or blockage.
Who is Kim Carr?
Kim Carr brings more than 30 years of health information and clinical documentation improvement management experience and expertise to her role as Director of Clinical Documentation, where she provides oversight for auditing and documentation improvement for HRS clients. Prior to joining HRS, Kim worked as a consultant implementing CDI programs in varied environments such as level-one trauma centers, small community hospitals and all levels in between.#N#Before joining the consultant arena, Kim served as Manager of CDI in an academic level-one trauma center. She was responsible for education and training for physicians and clinical documentation specialists. Over the past 30 years, Kim has held several HIM positions; including HIM Coding Educator, Quality Assurance/Utilization Management Coordinator, DRG Coding Coordinator and Coding Manager. Kim holds a degree in Health Information Management and is a member of AHIMA, THIMA, ACDIS and AAPC.
Does the stomach make a lot of its own secretions?
Also, the stomach makes a lot of its own secretions that need to be suctioned out in patients whose stomachs are not performing normal digestive functions. Buildup of normal stomach secretions can lead to an erosive event in the stomach or esophagus (or aspiration of stomach acid into the trachea or lungs).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd code 10 for hypoglycemia
- 2. icd 10 code for rt knee baker's cyst
- 3. whats the icd 10 code for localized edema, right foot
- 4. icd 9 code for myopia
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for hypertensive emergency
- 6. icd 10 code for shingles in left flank area
- 7. icd 10 code for bariatric surgery status
- 8. icd-10 code for depo provera injection
- 9. what is right icd 10 code for tpi injection
- 10. icd 10 code for unspecified internal derangement of left knee