What is the ICD 10 code for diabetic foot ulcer?
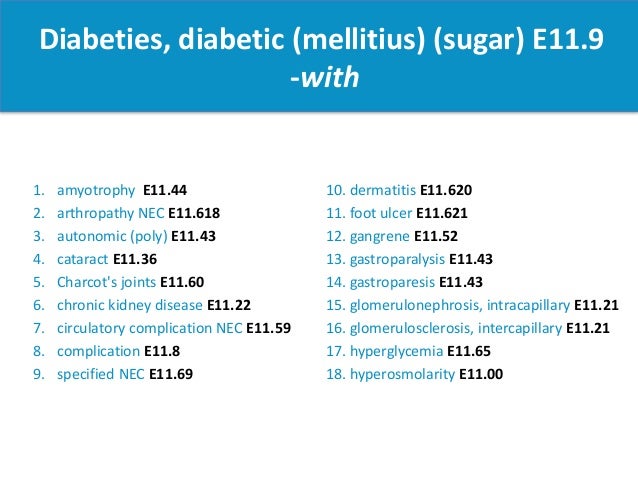
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E11.621 Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code E11.621 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.621 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for cellulitis of the foot?
Oct 01, 2021 · E11.628 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.628 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.628 - other international versions of ICD-10 E11.628 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for heel and midfoot ulcer?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M01.X7 Direct infection of ankle and foot in infectious and parasitic diseases classified elsewhere Direct infct of ank/ft in infec/parastc dis classd elswhr; Direct infection of tarsus, metatarsus and phalanges in infectious and parasitic diseases classified elsewhere ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S90.821A [convert to ICD-9-CM]
What is the ICD 10 code for skin infection?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M01.X7 Direct infection of ankle and foot in infectious and parasitic diseases classified elsewhere Direct infct of ank/ft in infec/parastc dis classd elswhr; Direct infection of tarsus, metatarsus and phalanges in infectious and parasitic diseases classified elsewhere ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S90.821A [convert to ICD-9-CM]

What is the ICD 10 code for diabetic foot infection?
What is the ICD 10 code for foot infection?
Is diabetic foot infection a diagnosis?
What is diabetic septic foot?
What is the ICD-10 code for infected wound?
What is the ICD-10 code for unspecified infection?
How is a foot infection diagnosed?
- Change in skin color.
- Rise in skin temperature.
- Swelling and pain.
- Open wounds that are slow to heal.
- Breaks or dryness in the skin.
- Drainage.
- Odor.
- Fever.
Why are foot infections common in diabetics?
Why do diabetics get foot infections?
Can diabetic foot infection lead to sepsis?
How do you treat a diabetic foot infection?
What is a diabetic foot ulcer?
Regarded as the most common reason for hospital stays among people with diabetes, a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is an open sore caused by neuropathic (nerve) and vascular (blood vessel) complications of the disease. Typically located on the plantar surface, or bottom/top of toes, pad of foot, or heel of foot, these complex, ...
Can diabetes cause foot ulcers?
Having too much glucose (sugar) in your blood can result in low blood flow to the affected areas and reduced white blood cell function. Poorly controlled diabetes often results in complications such as foot ulcers.
How many people with diabetes have foot ulcers?
According to the American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA), approximately 15 percent of people with diabetes suffer from foot ulcers. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, about 6 percent will be hospitalized due to serious infections or other ulcer-related complications.
Where are diabetic ulcers located?
Typically located on the plantar surface, or bottom/top of toes, pad of foot, or heel of foot , these complex, chronic wounds can affect people with both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. If left untreated, diabetic foot ulcers can have a permanent, long-term impact on the morbidity, mortality and quality of a patients’ life.
How many amputations are there for diabetics?
The risk of foot ulceration and limb amputations increases with age and duration of diabetes. In the United States, about 82,000 amputations are performed each year on persons with diabetes; half of those ages 65 years or older. Treatment for diabetic foot ulcers varies depending on their causes.
What are the risk factors for ulcers?
The most common risk factors for ulcer formation include – diabetic neuropathy, structural foot deformity, kidney disease, obesity and peripheral arterial occlusive disease. The condition can be effectively prevented if the underlying conditions causing it are diagnosed early and treated correctly.
Can diabetic neuropathy cause ulcers in feet?
Under the weight of the body, skin deteriorates and eventually becomes an open sore. These ulcers frequently form underneath calluses and cannot be felt due to diabetic neuro pathy. One of the initial signs of a foot ulcer is drainage from your foot (that might stain your socks or leak out in your shoe).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for vision screening
- 2. icd 9 code for gardasil vaccine
- 3. icd 10 code for claudication symptoms.
- 4. icd 10 cm code for rle nodule
- 5. icd -10 code for staphylococcus
- 6. icd 10 code for muscle tension dysphonia
- 7. icd 10 code for large uterine fibroids
- 8. icd-10 code for stage 4 pressure ulcer left ischium
- 9. icd 9 code for ligament laxity
- 10. icd code for left hand