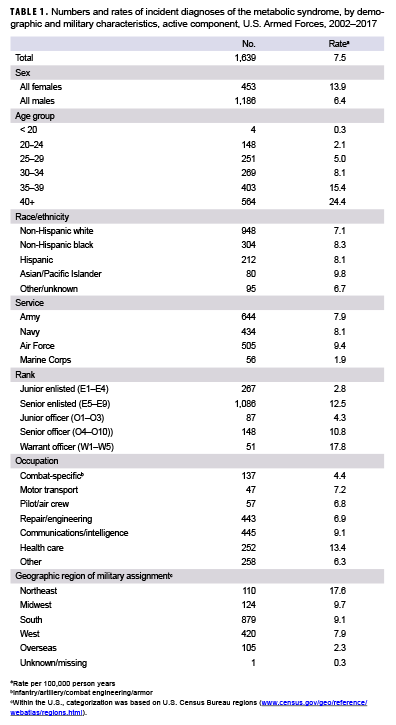
What is the ICD 10 code for diabetes with neurological complications?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with neurological complications. E11.4 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with neurological complications. It should not be used for HIPAA-covered transactions as a more specific code is available to choose from below.
What is the ICD 10 code for Neurologic diagnosis?
E09.42 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM E09.42 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E09.42 - other international versions of ICD-10 E09.42 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for Type 1 diabetes mellitus?
E10.49 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Type 1 diabetes mellitus with other diabetic neurological complication . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
What is the ICD 10 code for polyneuropathy?
E09.42 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Drug/chem diabetes w neurological comp w diabetic polyneurop. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM E09.42 became effective on October 1, 2018.
See more
What is the diagnosis code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with neurological complications?
4 Type 2 diabetes mellitus With neurological complications.
Is diabetes mellitus a neurological disorder?
Diabetes is responsible for a wide range of neurological manifestations. These can be the direct result of the metabolic disorder or its treatment, or they can represent secondary manifestations.
How do you code diabetes and neuropathy?
ICD-9-CM Coding If either peripheral or autonomic neuropathy is caused by diabetes, then a code from subcategory 250.6 will be sequenced first followed by code 357.2 for polyneuropathy in diabetes or code 337.1 for peripheral autonomic neuropathy.
What is the ICD-10 code for neurological disorders?
Other disorders of nervous system G98. 8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G98. 8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the major neurological complication of Type I diabetes mellitus?
Abstract. Peripheral neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes and may appear as the first manifestation of the disease. It is likely to occur in even the mildest cases of diabetes. Careful regulation of diabetes is necessary for effective treatment of the neuropathy.
What are neurological disorders?
Neurological disorders are medically defined as disorders that affect the brain as well as the nerves found throughout the human body and the spinal cord. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms.
What is the ICD-10 code for dm2 with peripheral neuropathy?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic neuropathy, unspecified. E11. 40 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.
What is Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic neuropathy unspecified?
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), a common and troublesome complication in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), contributes to a higher risk of diabetic foot ulcer and lower limb amputation. These situations can negatively impact the quality of life of affected individuals.
Is peripheral neuropathy and polyneuropathy the same?
Polyneuropathy is when multiple peripheral nerves become damaged, which is also commonly called peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral nerves are the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord.
What is the ICD 10 code R29 818?
ICD-10 code R29. 818 for Other symptoms and signs involving the nervous system is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What does neurological deficit mean?
A neurologic deficit refers to abnormal function of a body area. This altered function is due to injury of the brain, spinal cord, muscles, or nerves. Examples include: Abnormal reflexes. Inability to speak.
What is diagnosis code F88?
F88: Other disorders of psychological development.
What is diabetes mellitus with neurological manifestations?
Neurological manifestations of diabetes mellitus comprise structural changes in both central and peripheral nervous system, as well as functional cerebral disturbances.
Which system is affected in diabetes mellitus?
Causes of Type 1 diabetes: This is an immune system disease. Your body attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in your pancreas. Without insulin to allow glucose to enter your cells, glucose builds up in your bloodstream. Genes may also play a role in some patients.
Which are the most common disorders associated with patients with diabetes?
Hearing problems are more common in people with diabetes. Alzheimer's disease. Type 2 diabetes may increase the risk of dementia, such as Alzheimer's disease. The poorer your blood sugar control, the greater the risk appears to be.
How does neuropathy occur in diabetes?
Neuropathy is one of the long-term complications of diabetes. Over time, high blood glucose (sugar) levels can damage the small blood vessels that supply the nerves in your body. This stops essential nutrients reaching the nerves. As a result, the nerve fibres can become damaged, and they may disappear.
What is the ICD-10 code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus?
E11.4 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with neurological complications. It should not be used for HIPAA-covered transactions as a more specific code is available to choose from below.
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. Section E08-E13 — Diabetes mellitus.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for healthy child
- 2. what is the icd 10 code for fibromyalgia
- 3. icd 10 procedure code for diverting transverse loop colostomy.
- 4. icd 9 code for right knee medial and lateral meniscal tear
- 5. icd 10 code for hyperbilirubinemia in newborn
- 6. icd 10 code for abscess chest wall
- 7. icd 10 code for incomplete emptying bladder
- 8. icd 10 code for urination problems
- 9. icd 10 code for elevated hiv 1/2
- 10. icd 10 code for acquired keratoderma