What to eat after a duodenal ulcer?
- cauliflower
- cabbage
- radishes
- apples
- blueberries
- raspberries
- blackberries
- strawberries
- cherries
- bell peppers
What is a clean-based duodenal ulcer?
A, Anterior clean-based duodenal ulcer. The duodenal folds are markedly edematous at the superior duodenal angle . A speckled pattern is on the gastric body, suggesting gastritis (inset, top). The antrum appears normal endoscopically (inset, bottom).
Is duodenal cancer curable?
not curable, but it’s certainly treatable. The goal of treatment is to ease symptoms and control the cancer’s growth. Your doctor will recommend therapies based on your age and overall health, including any other health conditions you may have.
What is the appearance of duodenal ulcers on endoscopy?
The endoscopic appearance of an ulcer provides important prognostic information. Endoscopic intervention is indicated in active bleeding, non-bleeding visible vessel, and active bleeding or visible vessel exposed after adherent clot removal.
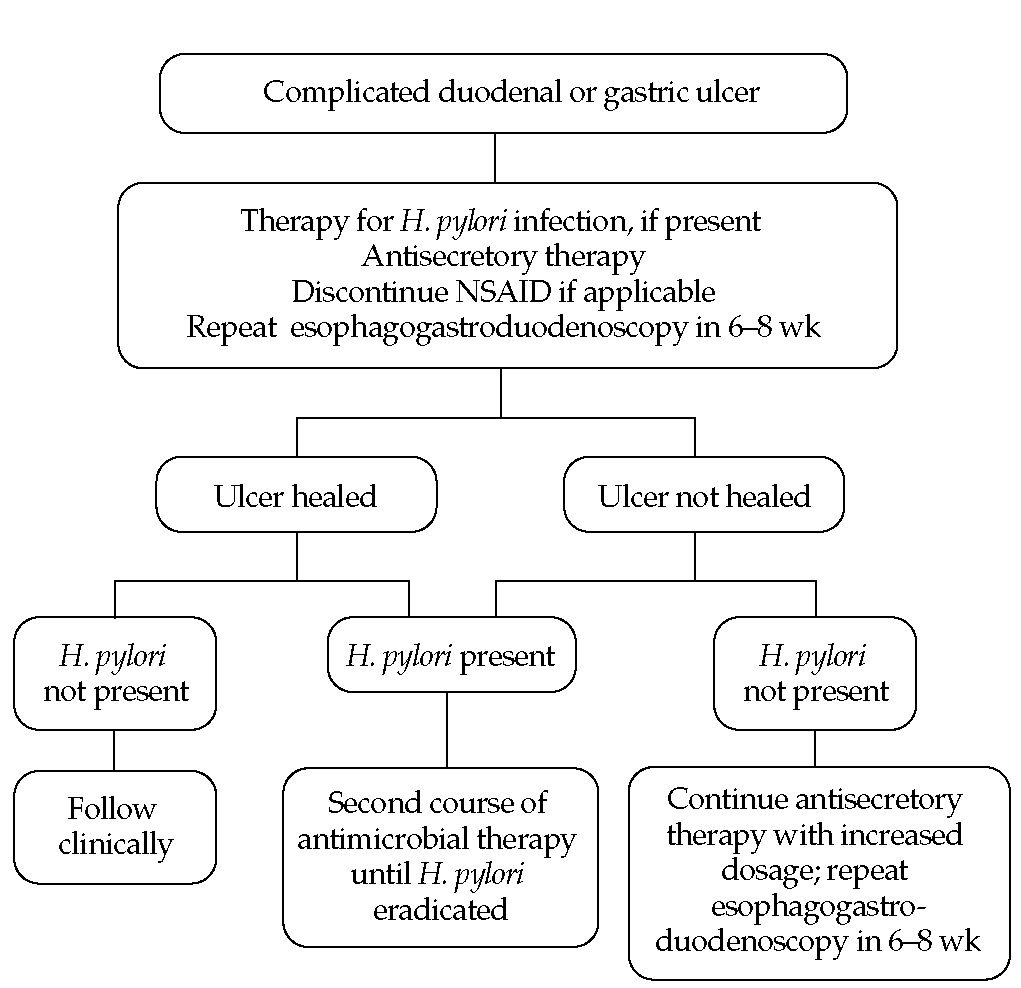
What is the ICD-10 code for duodenal ulcer with bleeding?
ICD-10-CM Code for Chronic or unspecified duodenal ulcer with hemorrhage K26. 4.
What is perforated duodenal ulcer?
Perforation of a duodenal ulcer allows egress of gastric and duodenal contents into the peritoneal cavity with a resulting initial chemical peritonitis. If there is continuing leakage of gastroduodenal contents, bacterial contamination of the peritoneal cavity can occur.
What are the symptoms of a duodenal ulcer?
What are the symptoms of a duodenal ulcer?Pain in the upper tummy (abdomen) just below the breastbone (sternum) is the common symptom. It usually comes and goes. ... Other symptoms which may occur include bloating, retching and feeling sick. ... Complications occur in some cases and can be serious.
What is the code for Duodenitis without bleeding?
ICD-10-CM Code for Duodenitis without bleeding K29. 80.
What causes duodenal ulcers?
The main cause of this damage is infection with bacteria called Helicobacter pylori, or H. pylori. The bacteria can cause the lining of your duodenum to become inflamed and an ulcer can form. Some medications can also cause a duodenal ulcer, particularly anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and aspirin.
What are the two types of stomach ulcers?
There are two different types of peptic ulcers. They are: Gastric ulcers, which form in the lining of the stomach. Duodenal ulcers, which form in the upper small intestine.
What is the ICD 10 code for duodenal ulcer?
Duodenal ulcer, unspecified as acute or chronic, without hemorrhage or perforation. K26. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the difference between gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer?
A peptic ulcer is a sore on the lining of your stomach, small intestine or esophagus. A peptic ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer. A duodenal ulcer is a peptic ulcer that develops in the first part of the small intestine (duodenum).
What is the most reliable symptom of duodenal ulcer?
The most common complaint is a burning pain in the stomach. Duodenal ulcers may also cause abdominal pain a few hours after eating. This pain tends to respond well to medications or foods that reduce stomach acid, but as the effects of these wear off, the pain usually returns.
What is the ICD-10 code for duodenitis?
ICD-10 code K29 for Gastritis and duodenitis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is chronic duodenitis?
Duodenitis is an intestinal condition caused by inflammation in your duodenum lining. It can sometimes happen along with gastritis, which is inflammation in your stomach lining.
What is erythema in the duodenum?
Erythematous means redness. So, having erythematous mucosa means the inner lining of your digestive tract is red. Erythematous mucosa isn't a disease. It's a sign that an underlying condition or irritation has caused inflammation, which has increased blood flow to the mucosa and made it red.
How serious is a perforated duodenal ulcer?
Perforation is a serious complication of PUD and patients with perforated peptic ulcer (PPU) often present with acute abdomen that carries high risk for morbidity and mortality[6]. The lifetime prevalence of perforation in patients with PUD is about 5%[7]. PPU carries a mortality ranging from 1.3% to 20%[8-10].
How serious is a perforated duodenum?
Duodenal perforation is a rare, but potentially life-threatening injury. Multiple etiologies are associated with duodenal perforations such as peptic ulcer disease, iatrogenic causes and trauma.
How serious is a perforated ulcer?
Perforation. A rarer complication of stomach ulcers is the lining of the stomach splitting open, known as perforation. This can be very serious because it enables the bacteria that live in your stomach to escape and infect the lining of your abdomen (peritoneum). This is known as peritonitis.
Is a perforated ulcer life-threatening?
Perforated peptic ulcer (PPU) is relatively rare, but life-threatening with the mortality varying from 10% to 40% [2, 4–6].
What are the symptoms of erosive duodenitis?
Symptoms include vomiting and abdominal pain. Inflammation of the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine that connects to the stomach). Inflammation of the duodenum section of the small intestine (intestine, small). Erosive duodenitis may cause bleeding in the upper gi tract and peptic ulcer. Code History.
When will the ICD-10-CM K29.8 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K29.8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
History Of Ulcerative Colitis
ICD-10-CM. 11. Diseases of the digestive system K50-K52 Noninfective enteritis and colitis. K51 Ulcerative colitis. K51.9 Ulcerative colitis, unspecified.
Identification Of Uc And Cd Patients
Information in the NPR includes patients unique civil registration numbers, hospital, departments, dates of admission and discharge, procedures performed and up to 20 discharge diagnoses based on the ICD, 8th revision before 1994 and ICD, 10th revision from 1994 onward .
Study Population And Setting
In Denmark, all citizens have free access to a tax supported health care system throughout the study period. Its uniform organization allowed us to use a population-based setting using nationwide data.
Factors Influencing Health Status And Contact With Health Servicesnote
Z codes represent reasons for encounters. A corresponding procedure code must accompany a Z code if a procedure is performed. Categories Z00-Z99 are provided for occasions when circumstances other than a disease, injury or external cause classifiable to categories A00 -Y89 are recorded as ‘diagnoses’ or ‘problems’. This can arise in two main ways:
Specific Coding For Other Ulcerative Colitis
Non-specific codes like K51.8 require more digits to indicate the appropriate level of specificity. Consider using any of the following ICD-10 codes with a higher level of specificity when coding for other ulcerative colitis:
Patient Demographics And Clinical Presentation
The elderly IBD patients were more likely to present with decreased oral intake, while the younger IBD patients were more likely to have inflammatory arthritis as an extraintestinal manifestation of their IBD . There was a trend toward family history of IBD being more common in the younger population.
Extraintestinal Manifestations And Complications
UC is characterized by immune dysregulation and systemic inflammation, which may result in symptoms and complications outside the colon. Commonly affected organs include: eyes, joints, skin, and liver. The frequency of such extraintestinal manifestations has been reported as between 6 and 47%.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for eyelid lesion
- 2. icd 10 pcs code for i&d right tibial incision
- 3. icd 10 code for adhd hyperactive
- 4. icd 10 code for removal of rhino rocket
- 5. icd 10 code for sprain ankle
- 6. icd 10 code for right bakers cyst
- 7. icd 10 code for flutter
- 8. icd 10 code for sprain right internal oblique muscle
- 9. icd 10 code for r10.13
- 10. icd 9 code for dot physical exam