What is the ICD 10 code for mood disorder?
What is ICD 10 code for mood disorder NOS? Unspecified mood [ affective] disorder F39 is a billable/specific ICD - 10 -CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is diagnosis code 10?
What is an ICD-10 diagnosis code? The ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification) is a system used by physicians and other healthcare providers to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms and procedures recorded in conjunction with hospital care in the United States.
What are the causes of DMDD?
What are the Causes of DMDD?
- Biological Causes of DMDD. While there are a few biological factors believed to contribute to the development of DMDD, the exact way in which they contribute remains unclear.
- Environmental Causes of DMDD. ...
- Prenatal and Perinatal Causes of DMDD. ...
Which disorders are considered moderate mood disorders?
Affiliations
- Instituto Nacional de Psiquiatría Ramón de la Fuente, Mexico.
- Global Mental Health Program, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, USA.
- Cátedra CONACYT (Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología), Mexico.
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Ansari Nagar, India.
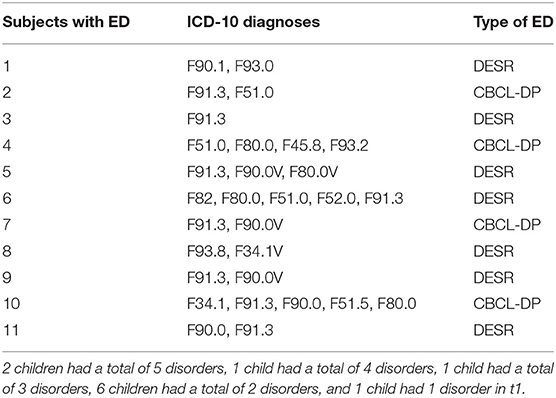
What is dysregulated mood disorder?
Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD) is a childhood condition of extreme irritability, anger, and frequent, intense temper outbursts. DMDD symptoms go beyond a being a “moody” child—children with DMDD experience severe impairment that requires clinical attention.
What is the DSM-5 code for disruptive mood dysregulation disorder?
Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder DSM-5 296.99(F34. 8) - Therapedia.
What is disruptive mood dysregulation disorder in adults?
Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD) defined by DSM-V is characterized by severe and recurrent temper outbursts and persistently irritable or angry mood. Objectives. Our aim is to attract attention to an adult case with DMDD since the literature is lacking adult manifestations.
What is the difference between disruptive mood dysregulation disorder and major depressive disorder?
Children and adolescents with depression may be sad, disinterested, and sluggish or overactive, aggressive, and irritable. Children with disruptive mood dysregulation disorder have frequent, severe temper outbursts and, between outbursts, are irritable and angry.
Is disruptive mood dysregulation disorder the same as bipolar?
What are the similarities and differences between DMDD and bipolar disorder? Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD) is a mental health condition that affects children between the ages of 6 and 18 years. Bipolar disorder (BD) is a condition that can cause extreme changes in mood.
Is emotional dysregulation a diagnosis?
Disorders Related to Emotion Dysregulation When emotional dysregulation appears as part of a diagnosed mental disorder, it typically involves a heightened sensitivity to emotional stimuli and a lessened ability to return to a normal emotional state within a reasonable amount of time.
What is the difference between IED and DMDD?
The primary difference between DMDD and IED is that the former represents a severe form of mood disorder in which anger is present most of time occurring before the age of ten while the latter describes individuals in whom aggressive outbursts are frequent but episodic and in whom anger is not present most of the time ...
What are three characteristics of disruptive mood dysregulation?
Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD) is a condition in which children or adolescents experience ongoing irritability, anger, and frequent, intense temper outbursts.
Is disruptive mood dysregulation disorder a depressive disorder?
The DSM-5 classifies DMDD as a type of depressive disorder, as children diagnosed with DMDD struggle to regulate their moods and emotions in an age-appropriate way. As a result, children with DMDD exhibit frequent temper outbursts in response to frustration, either verbally or behaviorally.
What triggers DMDD?
Genetic: A young person's genetic history is the strongest determining factor that could cause the onset of DMDD. In fact, among children and adolescents who meet criteria for this illness, all typically have a family history of depression, anxiety disorders, or substance use disorders in their backgrounds.
What is the best treatment for disruptive mood dysregulation disorder?
Risperidone and aripiprazole are FDA-approved for the treatment of irritability associated with autism and are sometimes used to treat DMDD.
What are the symptoms of emotional dysregulation?
Signs of emotional dysregulation include:Severe depression.Anxiety.High levels of shame and anger.Self-harm.Excessive substance use.High-risk sexual behaviors.Extreme perfectionism.Highly conflictual interpersonal relationships.More items...
Is DMDD a form of autism?
Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD) is a controversial new DSM-5 diagnosis. Mothers rated irritable-angry mood and temper outbursts in 1593 children. DMDD frequency was 45% autism, 39% ADHD-Combined, 12% ADHD-Inattentive, 3% typical. DMDD most common in autism, even controlling for oppositional behavior.
How many people have mood disorders?
Nearly one in ten people aged 18 and older have mood disorders. These include. major depressive disorder. dysthymic disorder (a chronic, mild depression) bipolar disorder (also called manic depression) mood disorders can increase a person's risk for heart disease, diabetes, and other diseases.
What is emotional disorder?
Emotional behavior inappropriate for one's age or circumstances, characterized by unusual excitability, guilt, anxiety, or hostility. Mental disorders characterized by a disturbance in mood which is abnormally depressed or elated. Compare emotional stability or emotionally disturbed.
What is the ICd 10 code for mood disorder?
F34.81 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also: Disorder (of) see also Disease. disruptive F91.9.
What is the ICd 10 code for mood disorder?
Mood disorder due to known physiological condition, unspecified 1 F06.30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 Short description: Mood disorder due to known physiological condition, unsp 3 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM F06.30 became effective on October 1, 2020. 4 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of F06.30 - other international versions of ICD-10 F06.30 may differ.
What is F05 dementia?
delirium due to known physiological condition ( F05) dementia as classified in F01 - F02. other mental disorders associated with alcohol and other psychoactive substances ( F10-F19) Other mental disorders due to known physiological condition.
What is the meaning of F10-F19?
mood disorders due to alcohol and other psychoactive substances ( F10-F19 with .14, .24, .94) mood disorders, not due to known physiological condition or unspecified ( F30-F39) Mood disorder due to known physiological condition. Approximate Synonyms. Organic mood disorder.
When does mood dysregulation occur?
According to the DSM-5, diagnosis of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder can only be made between the ages of 6 and 18 , but onset must occur before the age of 10. ...
What are some examples of disruptive mood dysregulation?
Common examples of self harm include cutting, burning, skin picking, carving, and pinching, biting, hitting, banging, stabbing, poking, ...
How often do disruptive moods occur?
The outbursts occur at least 3 times each week. Outbursts must occur both at two different locations, such as both home and school.
What is disruptive mood disorder?
New to the DSM-5, disruptive mood dysregulation disorder is a childhood disorder characterized by a pervasively irritable or angry mood. Symptoms include frequent angry or aggressive outbursts combined with an angry or irritable mood on days when outbursts do not occur. Although prevalence is low among the general population, disruptive mood disorder is common among children already being treated for psychiatric illness. Symptoms of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder are common to other disorders such a bipolar disorder, oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder. The disorder often co-occurs with depression, anxiety or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Although medication is available to treat symptoms of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder, family focused therapy typically has the best outcome.
Why is medication used to improve mood?
Because depression and suicidal behavior are often associated with disruptive mood dysregulation disorder, medication may be used to improve mood (Rutherford, 2010). Because children spend more time with their parents than with therapists, it is important that the entire family is involved in treatment. Parental involvement is important ...
What is low tolerance for frustration?
Low tolerance for frustration means that the child frequently loses his or her temper in class, during play and when interacting with family . They usually have few friends and other children typically avoid playing with the child after an outburst.
Is mood dysregulation disorder a comorbidity?
Comorbidity and Differential Diagnosis. According to the DSM-5, comorbidity among children diagnosed with disruptive mood dysregulation disorder is extremely common (American Psychiatric Association, 2013). As many as 92% of children diagnosed with disruptive mood dysregulation disorder also meet clinical criteria for another disorder.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for heart failure i i
- 2. icd 10 code for gastroenteritis unspecified
- 3. icd 10 code for laceration right thigh
- 4. icd 10 procedure code for wound care
- 5. icd-9 code for urinary retention
- 6. icd 10 code for impaired hearing
- 7. icd 10 cm code for deliberate self cutting
- 8. icd 10 code for left ankle effusion
- 9. icd 10 code for micrcytic anedmia
- 10. icd 10 code for abdominal infection unspecified