How to Code Sepsis ICD 10?
• Septicemia – There is NO code for septicemia in ICD-10. Instead, you’re directed to a combination ‘A’ code for sepsis to indicate the underlying infection, such A41.9 (Sepsis, unspecified organism) for septicemia with no further detail. Note: ‘A’ codes for Sepsis in ICD-10 include both the underlying infection
What is the diagnosis code for E coli?
In the ICD-9-CM tabular the expanded category for 041.4, Escherichia coli, now includes the following specific STEC codes: 041.41, Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) O157 041.42, Other specified Shiga toxin-producing Escherich-ia coli (STEC)
What is the prevention of E coli?
To reduce your chance of being exposed to E. coli, avoid swallowing water from lakes or pools, wash your hands often, avoid risky foods, and watch out for cross-contamination. " E. coli stands for Escherichia coli, which is a type of bacteria."
Does ecoli cause wound infection?
If their skin is healthy and there are no wounds or irritated patches, this is unlikely to cause any problems. If E. coli gets into a wound or a sore patch on the skin, it may cause a local infection, but is unlikely to spread to other areas on the body from here.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for E. coli sepsis?
Sepsis due to Escherichia coli [E. coli] A41. 51 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is coli Septicaemia?
Septicemia caused by Escherichia coli is an incidental disease recognized in most mammalian and avian species. E coli strains of intestinal or extraintestinal origin reach the bloodstream, where they cause systemic disease, and from there may invade virtually every organ of the body.
How do you code E. coli bacteremia?
coli] as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere. B96. 20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Is E. coli in the blood the same as sepsis?
Most strains of E. coli are harmless but some strains can make you very sick and can cause sepsis. Sometimes incorrectly called blood poisoning, sepsis is the body's often deadly response to infection. Like strokes or heart attacks, sepsis is a medical emergency that requires rapid diagnosis and treatment.
Can E. coli go septic?
E coli bacteremia can lead to septic shock, manifesting as hypotension and fever (in some cases, with hypothermia rather than fever). It may be complicated by uremia, hepatic failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, stupor or coma, and death.
What causes E. coli blood infection?
It's usually spread by eating contaminated food or drinking contaminated water that contains illness-producing strains of E. coli.
How do you code septicemia?
Coding sepsis requires a minimum of two codes: a code for the systemic infection (e.g., 038. xx) and the code 995.91, SIRS due to infectious process without organ dysfunction. If no causal organism is documented within the medical record, query the physician or assign code 038.9, Unspecified septicemia.
Can sepsis and bacteremia be coded together?
81, Bacteremia, is a symptom code with an Exclude1 note stating it can't be used with sepsis and that additional documentation related to the cause of the infection, i.e., gram-negative bacteria, salmonella, etc., would be needed for correct code assignment.
What is the difference between bacteremia and sepsis?
Bacteremia is the presence of bacteria in the blood, hence a microbiological finding. Sepsis is a clinical diagnosis needing further specification regarding focus of infection and etiologic pathogen, whereupon clinicians, epidemiologists and microbiologists apply different definitions and terminology.
What is the difference between sepsis and Septicemia?
When bacteria invade the body, this can cause severe illnesses which may result in death. Septicaemia is when bacteria enter the bloodstream, and cause blood poisoning which triggers sepsis. Sepsis is an overwhelming and life-threatening response to infection that can lead to tissue damage, organ failure and death.
Is E. coli a blood infection?
The bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli), which grows naturally in the human digestive tract, is a leading cause of urinary tract infections. Medical researchers have long known that E. coli is also a cause of bloodstream infection.
What causes E. coli in blood and urine?
coli often gains entry into the urinary tract via stool. Women are particularly at risk for UTIs because their urethra sits close to the anus, where E. coli is present. It's also shorter than a man's, giving the bacteria easier access to the bladder, where the majority of UTIs occur, and the rest of the urinary tract.
How to get e. coli infection?
Cook meat well, wash fruits and vegetables before eating or cooking them, and avoid unpasteurized milk and juices. You can also get the infection by swallowing water in a swimming pool contaminated with human waste .most cases of e. Coli infection get better without treatment in 5 to 10 days.
When will the ICd 10 B96.20 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B96.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the name of the bacteria that lives in your intestines?
Approximate Synonyms. E coli infection. Escherichia coli urinary tract infection. Infection due to escherichia coli. Clinical Information. e. Coli is the name of a type of bacteria that lives in your intestines. Most types of e.
Can you get e. coli from eating?
Coli causes bloody diarrhea, and can sometimes cause kidney failure and even death. These problems are most likely to occur in children and in adults with weak immune systems. You can get e. Coli infections by eating foods containing the bacteria. To help avoid food poisoning and prevent infection, handle food safely.
What is the ICd 10 code for Sepsis?
A41.51 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Sepsis due to Escherichia coli [E. coli] . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also:
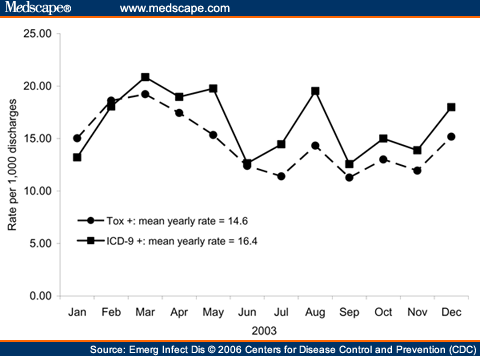
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for left pca occlusion
- 2. icd 10 code for history of abortion
- 3. icd 10 code for obstructive pneumonia
- 4. icd 10 code for white coast syndrome
- 5. icd 10 code for history of iufd in prior pregnancy
- 6. screening for unspecified immunity disorder icd 9 cm code
- 7. encounter for diabetic foot care icd 10 code
- 8. icd 10 code for insect bite forearm
- 9. icd 10 code for lapidus bunionectomy
- 10. icd 10 code for cabg x 5