What is the ICD 10 code for pyoderma gangrenosum?
Pyoderma gangrenosum 1 L88 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM L88 became effective on October 1, 2019. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L88 - other international versions of ICD-10 L88 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for gangrene?
2021 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I96 Gangrene, not elsewhere classified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code I96 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for ecthyma?
Ecthyma. L08.0. contagiosum B08.02. gangrenosum L08.0. infectiosum B08.02. ← Previous. Page 1. Next Page →. ICD-10 Code Lookup.
What is ecthyma gangrenosum (ECG)?
Ecthyma gangrenosum is a cutaneous infection most commonly associated with Pseudomonas bacteraemia. Ecthyma gangrenosum usually occurs in patients who are critically ill and immunocompromised.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for pyoderma Gangrenosum?
ICD-10 code L88 for Pyoderma gangrenosum is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is the ICD-10 code for pustular rash?
ICD-10-CM Code for Subcorneal pustular dermatitis L13. 1.
What is the ICD-10 code for skin infection?
ICD-10 Code for Local infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified- L08. 9- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for hidradenitis suppurativa?
ICD-10 code: L73. 2 Hidradenitis suppurativa | gesund.bund.de.
What is the ICD-10 code for skin lesion?
ICD-10-CM Code for Disorder of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified L98. 9.
What is pustular dermatitis?
Subcorneal pustular dermatosis (SPD), also known as Sneddon-Wilkinson disease, is a rare neutrophilic dermatosis in which recurrent crops of sterile pustules appear in the most superficial (subcorneal) layers of the skin (picture 1A-B).
What is the ICD-10 code for purulent drainage?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L08. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L08.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for wound culture?
Abnormal microbiological findings in specimens from other organs, systems and tissues. R89. 5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R89.
What is the CPT code for excision axillary hidradenitis complex repair?
11450CPT® Code 11450 in section: Excision of skin and subcutaneous tissue for hidradenitis, axillary.
What is axillary hidradenitis?
Hidradenitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by recurrent nodules and abscesses, typically of apocrine gland-bearing skin. Lesions can progress to sinus tracts and fistulae, and, when healed, can lead to severe scarring and fibrosis.
What is HS skin?
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a painful, long-term skin condition that causes abscesses and scarring on the skin. The exact cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is unknown, but it occurs near hair follicles where there are sweat glands, usually around the groin, bottom, breasts and armpits.
What is EG in medical terms?
Ecthyma gangrenosum (EG) is a cutaneous manifestation of gram-negative bacteremia, most commonly secondary to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It is seen predominantly in immunocompromised patients due to immunodeficiency syndromes or immunosuppressive therapy, or in chronic disease states such as severe burns, malnutrition, and diabetes mellitus. However, characteristic clinical lesions can also develop in immunocompetent individuals without associated sepsis.
What are the complications of gram negative sepsis?
Severe complications such as nephritis and osteomyelitis may occur. The course depends on the underlying disease, but once manifestations of shock appear, the patient may quickly and irreversibly decline. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) may appear with gram-negative sepsis.
What are the initial lesions of ecthyma gangrenosum?
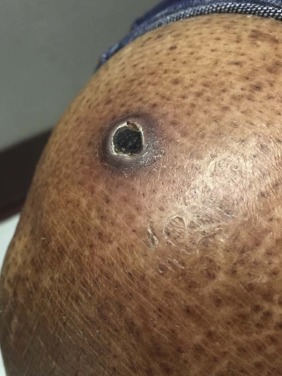
The initial lesions of ecthyma gangrenosum appear as painless, round, red patches in the skin which rapidly become pustular with surrounding redness. A haemorrhagic focus appears in the centre, forming a blister.
What is ecthyma gangrenosum?
Ecthyma gangrenosum is a cutaneous infection most commonly associated with Pseudomonas bacteraemia. Ecthyma gangrenosum usually occurs in patients who are critically ill and immunocompromised. The characteristic lesions of ecthyma gangrenosum are haemorrhagic (bloody) pustules that evolve into necrotic (black) ulcers.
What antibiotics are used for ecthyma gangrenosum?
Antibiotics which may be used include. Antipseudomonal penicillin such as piperacillin. Aminoglycosides. Fluoroquinolines. Third-generation cephalosporins. Aztreonam.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for unspecified arthritis
- 2. icd 10 code for history of parkinson's disease
- 3. icd 10 code for c79.51
- 4. icd 10 cm code for complete transposition of the great vessels with cyanosis
- 5. icd 10 code for biliary stent exchange
- 6. icd 10 pcs code for monitoring of central nervous electrical activity external approach
- 7. icd 10 code for family history of rectal cancer
- 8. icd 10 code for blunt trauma
- 9. icd 10 code for right hip cellulitis
- 10. icd 9 code for right hip fracture