What does diagnosis code R79 89 mean?
ICD-10 code R79. 89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the diagnosis code r74 8?
8: Abnormal levels of other serum enzymes.
What is the 2021 ICD 10 code for hypercalcemia?
ICD-10 code E83. 52 for Hypercalcemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
How do you code coronary artery calcification?
ICD-10-CM Code for Coronary atherosclerosis due to calcified coronary lesion I25. 84.
What does Abnormal levels of other serum enzymes mean?
What does it mean to have elevated liver enzymes? If you have high levels of liver enzymes in your blood, you have elevated liver enzymes. High liver enzyme levels may be temporary, or they may be a sign of a medical condition like hepatitis or liver disease. Certain medications can also cause elevated liver enzymes.
What is the ICD 10 code for elevated troponin?
Elevated Troponin should be coded to R74. 8 Abnormal levels of other serum enzymes. [Effective 11 Jul 2012, ICD-10-AM/ACHI/ACS 7th Ed.]
What is hypercalcemia caused by?
Hypercalcemia is usually a result of overactive parathyroid glands. These four tiny glands are situated in the neck, near the thyroid gland. Other causes of hypercalcemia include cancer, certain other medical disorders, some medications, and taking too much of calcium and vitamin D supplements.
What is DX code e8352?
E83. 52 - Hypercalcemia | ICD-10-CM.
Why do we get hypocalcemia?
Chronic hypocalcemia is commonly due to inadequate levels of parathyroid hormone or vitamin D, or due to resistance to these hormones. Treatment focuses on oral calcium and vitamin D supplements, as well as magnesium if deficiency is present.
What is cardiac calcification?
What is coronary artery calcification? Coronary artery calcification is a collection of calcium in your heart's two main arteries, also called your coronary arteries. This happens after you've had plaque (fat and cholesterol) forming in your arteries (atherosclerosis) for about five years.
What is ICD 10 code for mild coronary artery calcification?
I25. 84 - Coronary atherosclerosis due to calcified coronary lesion | ICD-10-CM.
Is calcification the same as atherosclerosis?
Calcification is a clinical marker of atherosclerosis. This review focuses on recent findings on the association between calcification and plaque vulnerability. Calcified plaques have traditionally been regarded as stable atheromas, those causing stenosis may be more stable than non-calcified plaques.
What does liver enzymes R74 8 mean?
ICD-10 code R74. 8 for Abnormal levels of other serum enzymes is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What causes an elevated alkaline phosphatase?
Causes of high ALP levels. ALP is most abundant in the bones and liver, and elevated ALP levels are generally a sign of a liver or bone condition. An obstruction of the liver or damage to it causes ALP levels to rise. Elevated levels can also result from an increase in bone cell activity.
What does a high alkaline phosphatase level indicate?
An alkaline phosphatase (ALP) test measures the amount of ALP in your blood. Although ALP exists throughout your body, the two main sources of ALP in your blood are your liver and bones. High levels of ALP may indicate liver disease or certain bone disorders, but an ALP test alone cannot diagnose a condition.
What does elevated Alk Phos indicate?
Higher-than-normal levels of ALP in your blood may indicate a health concern with your liver or gallbladder. This could include a blockage in your bile ducts, gallstones, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and some forms of hepatitis.
ICD-10 Codes for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease, also known as CAD, develops when the major blood vessels that supply your heart become damaged or diseased. Cholesterol-containing deposits (plaques) in your coronary arteries and inflammation are usually to blame for coronary artery disease.
Symptoms of CAD
If your coronary arteries narrow, they can’t supply enough oxygen-rich blood to your heart — especially when it’s beating hard, such as during exercise. At first, the decreased blood flow may not cause any symptoms.
Treatment for CAD
It’s important to reduce or control your risk factors and seek treatment to lower the chance of a heart attack or stroke, if you’re diagnosed with CAD. Treatment also depends on your current health condition, risk factors, and overall wellbeing.
Why does Aetna use calcium scoring?
Aetna considers calcium scoring (e.g., with ultrafast [electron-beam] CT, spiral [helical] CT, and multi-slice CT) experimental and investigational for all other indications because of insufficient evidence in the peer-reviewed published medical literature.
What voltage is used for atrial fibrillation?
Persons in atrial fibrillation (except when rate-controlled and 3rd generation Dual-Source CT (DSCT) 120-kv tube voltage is utilized).or with other significant arrhythmia.
What is CCTA in medical terms?
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is a noninvasive imaging modality designed to be an alternative to invasive cardiac angiography (cardiac catheterization) for diagnosing CAD by visualizing the blood flow in arterial and venous vessels. The gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery stenosis is cardiac catheterization.
Does Aetna recommend CT angiography?
Aetna considers cardiac computed tomography (CT) angiography medically necessary for evaluation of aortic erosion in symptomatic members (e.g., chest pain) who have been treated for atrial septal defect with an occlusive device.
Does Aetna use a single calcium score?
Aetna considers a single calcium scoring by means of low-dose multi-slice CT angiography, ultrafast [electron-beam] CT, or spiral [helical] CT medically necessary for screening the following:
Is repeat calcium scoring necessary?
Repeat calcium scoring is considered medically necessary only if the following criteria are met:
Is calcium scoring necessary for aortic valve?
Aetna considers calcium scoring of the aortic valve medically necessary in the setting of persons with suspected paradoxical low-flow, low-gradient symptomatic severe aortic stenosis when transthoracic echocardiography is inconclusive.
What is CACS in medical terms?
This coronary artery calcium score (CACS) noncontrasted electrocardiographically gated computerized tomographic (CT) single-plane view was obtained in a 52-year-old man with a family history of premature coronary artery disease. This view demonstrates extensive calcification in the left main coronary artery, the proximal left anterior descending coronary artery and the proximal circumflex coronary artery. The total CACS was 4,410 Agatston units.
What patient should not have a CACS?
The appropriate patient for CACS is still debated, and the answer to this question will likely continue to evolve as data accumulate. However, there is more agreement among experts in CVD prevention concerning patients for whom CACS is rarely indicated:
What is a high-risk imaging result?
This coronary artery calcium score (CACS) noncontrasted electrocardiographically gated computerized tomographic (CT) single-plane view was obtained in a 52-year-old man with a family history of premature coronary artery disease. This view demonstrates extensive calcification in the left main coronary artery, the proximal left anterior descending coronary artery and the proximal circumflex coronary artery. The total CACS was 4,410 Agatston units.
What is the risk of a 50 year old man with CVD?
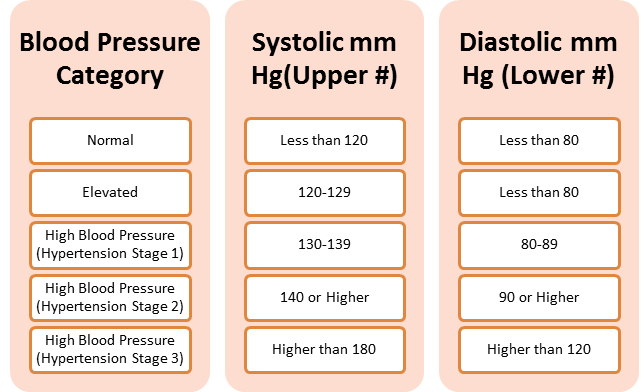
A 50-year-old African-American man, known in this case study as Smith, presents with concerns regarding cardiovascular risk. He has no personal history of CVD. He is active and asymptomatic and takes no medication. He is not a current smoker. His blood pressure is 134/82 mm Hg, and he has a total cholesterol level of 212 mg/dL, a high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level of 54 mg/dL, triglycerides of 92 mg/dL, and a calculated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level of 140 mg/dL. His 10-year risk, as determined by the ASCVD Pooled Cohort Risk Assessment Equations, is 5.7 percent.
Why is imaging important for CVD?
Because more-accurate means of determining individual CVD risk are needed , a search is ongoing for better tools to identify high-risk individuals before clinical events occur. One such tool is imaging for subclinical atherosclerosis, most commonly accomplished by quantifying the amount of calcium in the coronary arteries by computerized tomography.
Is CACS a risk factor?
The coronary artery calcium score (CACS) is strongly correlated with future risk of myocardial infarction and stroke, making it a potentially attractive tool to further clarify individual risk of CVD. Several large studies with long-term follow-up have shown that CACS adds incremental information in CVD risk identification and provides more-accurate CVD risk prediction compared with traditional risk factors in about 25 percent of individuals.
Is CVD preventable?
Despite these striking numbers, research data suggest that CVD is largely preventable.
What is HCC code?
For hierarchical condition categories (HCC) used in Medicare Advantage Risk Adjustment plans, certain diagnosis codes are used as to determine severity of illness, risk, and resource utilization. HCC impacts are often overlooked in the ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM conversion. The physician should examine the patient each year and compliantly document the status of all chronic and acute conditions. HCC codes are payment multipliers.
Is there an error in the prescription for Coumadin?
Note: There is nothing in the documentation that says that there was an error in the prescription for Coumadin or that the patient took it incorrectly. If the prescription was correctly prescribed and correctly administered/taken then it would be an adverse effect.
Ask the doctor
Q. I recently got a coronary artery calcium scan and the results showed that I have quite a bit of calcium in my heart arteries (my score was 900). Should I have an angiogram to confirm the results? I don't have any heart-related symptoms, but I'm worried about having a heart attack.
Disclaimer
As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
What happens if you submit a claim without a diagnosis code?
A claim submitted without a valid ICD-10-CM diagnosis code will be returned to the provider as an incomplete claim under Section 1833 (e) of the Social Security Act.
Does ICD-10-CM code cover a service?
The use of an ICD-10-CM code listed below does not assure coverage of a service. The service must be reasonable and necessary in the specific case and must meet the criteria specified in the attached determination.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for l acure renal failure
- 2. icd 10 code for hindfoot valgus
- 3. icd 10 code for cpt code 99385
- 4. icd 10 code for compound nevus back
- 5. icd 9 code for presence of picc line
- 6. icd code 10 for pulmonary nodules
- 7. icd 10 code for cms hcc
- 8. icd-10 code for pyelonephritis with sepsis
- 9. icd 10 cm code for medical renal disease
- 10. icd 9 code for vision check