What are the symptoms of elevated A1C?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R73 Elevated blood glucose level 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code R73 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R73 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are ICD 10 codes cover hemoglobin A1c?
Elevated blood glucose level (R73) R71.8 R73 R73.0 ICD-10-CM Code for Elevated blood glucose level R73 ICD-10 code R73 for Elevated blood glucose level is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What does an elevated A1c level mean?
ICD-10 Index. Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified (R00–R99) Abnormal findings on examination of blood, without diagnosis (R70-R79) Elevated blood glucose level (R73) R73 - Elevated blood glucose level NON-BILLABLE CODE; R73.0 - Abnormal glucose NON-BILLABLE CODE
What does elevated glucose level mean?
Consider using any of the following ICD-10 codes with a higher level of specificity when coding for elevated blood glucose level: NON-BILLABLE CODE - R73.0 for Abnormal glucose BILLABLE CODE - Use R73.01 for Impaired fasting glucose BILLABLE CODE - Use R73.02 for Impaired glucose tolerance (oral) BILLABLE CODE - Use R73.03 for Prediabetes
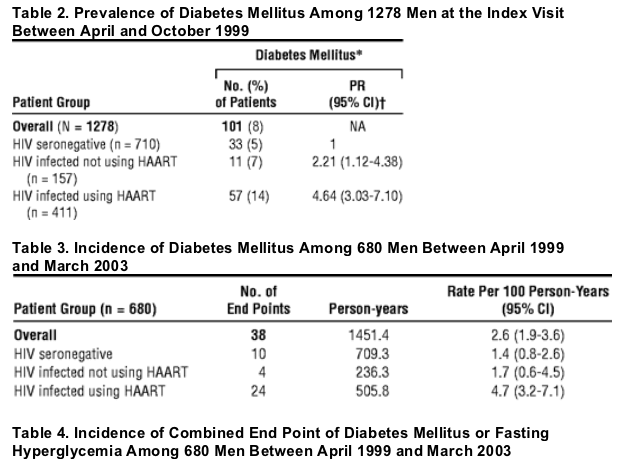
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated glucose?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R73: Elevated blood glucose level.
Is elevated glucose the same as hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia doesn't cause symptoms until glucose values are significantly elevated — usually above 180 to 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 10 to 11.1 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Symptoms of hyperglycemia develop slowly over several days or weeks.Jun 27, 2020
What is the ICD-10 code for glucose tolerance test?
02.
When do you use R73 09?
If a member has been diagnosed with prediabetes, or has had a previous diagnosis of diabetes and the disease is now considered latent or dormant (per the provider's documentation) the ICD-10 code R73. 09, Other abnormal glucose, should be assigned.
What is considered a high glucose level?
In general, high blood glucose, also called 'hyperglycemia', is considered "high" when it is 160 mg/dl or above your individual blood glucose target. Be sure to ask your healthcare provider what he or she thinks is a safe target for you for blood glucose before and after meals.
What is considered a glucose spike?
A glucose spike is that brief surge of energy that swells in us—especially in kids—after eating candy, cookies, or other sugary treats. In other words, a glucose spike is a temporary rise in blood sugar.Apr 2, 2020
How do you code an elevated glucose tolerance test?
09: Other abnormal glucose.
What is the ICD-10 code for elevated HGB?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R97 R97.
What diagnosis will cover 83036?
Diabetes Hemoglobin A1c Testing Claims including procedure code 83036 or 83037 should include a line item with the resulting CPT procedure code below and be billed with a zero charge.
Can you code E11 21 and E11 22 together?
The incorrect portion of the response came as an aside at the end, where it was stated that “it would be redundant to assign codes for both diabetic nephropathy (E11. 21) and diabetic chronic kidney disease (E11. 22), as diabetic chronic kidney disease is a more specific condition.” It is true you wouldn't code both.Nov 18, 2019
What is diagnosis code R53 83?
ICD-10 | Other fatigue (R53. 83)
When do you use E11 59?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other circulatory complications. E11. 59 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is it called when your blood sugar is too high?
Diabetes is a disease in which your blood sugar levels are too high. Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems. Even if you don't have diabetes , sometimes you may have problems with blood sugar that is too low or too high.
What is the name of the test that checks blood sugar?
Your health care provider will also do a blood test called an A1C. It checks your average blood sugar level over the past three months. If your blood sugar is too high, you may need to take medicines and/or follow a special diet. NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
How to keep blood sugar levels in target range?
Keeping a regular schedule of eating, activity, and taking any medicines you need can help. If you do have diabetes, it is very important to keep your blood sugar numbers in your target range. You may need to check your blood sugar several times each day.
Where does glucose come from?
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the main sugar found in your blood. It comes from the food you eat , and is your body's main source of energy. Your blood carries glucose to all of your body's cells to use for energy.
What is R73 code?
R73 is a non-specific and non-billable diagnosis code code, consider using a code with a higher level of specificity for a diagnosis of elevated blood glucose level. The code is not specific and is NOT valid for the year 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. Category or Header define the heading of a category ...
What does it mean when you have a high blood glucose level?
This condition is seen frequently in diabetes mellitus, but also occurs with other diseases and malnutrition. Pre-diabetes means you have blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes. Glucose comes from the foods you eat.
What is the state of latent impairment of carbohydrate metabolism in which the criteria for diabetes mellitus are
State of latent impairment of carbohydrate metabolism in which the criteria for diabetes mellitus are not all satisfied; sometimes controllable by diet alone; called also impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose. The time period before the development of symptomatic diabetes.
Can diabetes cause high blood glucose levels?
Too much glucose in your blood can damage your body over time. If you have pre-diabetes, you are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.most people with pre-diabetes don't have any symptoms. Your doctor can test your blood to find out if your blood glucose levels are higher than normal.
Popular Posts:
- 1. 2017 icd 10 diagnosis code for meningitis due to echovirus
- 2. icd 10 code for paratubal cyst of right fallopian tube
- 3. cpt code for single lead icd
- 4. icd 10 code for s/p gastric bypass
- 5. icd 10 code for glaucoma screening
- 6. icd 10 code for pharynogoconjuctival fever
- 7. icd 10 cm code for cellulitis left ear
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for acute renal insufficiency
- 9. what is icd 10 code z01.89 for
- 10. icd 10 code for dyslyndenia