What is optic disc elevation?
Understanding elevation Optic disc edema results from compression, infection, infiltration, inflammation, demyelinating disease or reduced perfusion to the nerve. These conditions slow normal axoplasmic flow, resulting in an accumulation of intracellular fluids within the ONH.
What is cupping of the optic nerve?
The optic nerve sits in the back of your eye, and it's surrounded by a dense network of other nerve fibers. When those smaller nerves die, the space they leave behind looks a bit like a cup. Doctors call this "optic nerve cupping." Cupping can be a sign of glaucoma, and this condition always needs treatment.
What is the ICD-10 code for optic disc edema?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H47. 13 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H47.
What is the ICD-10 code for Papilledema?
ICD-10 code H47. 11 for Papilledema associated with increased intracranial pressure is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the eye and adnexa .
What is cup and disc in eye?
The cup-to-disc ratio (often notated CDR) is a measurement used in ophthalmology and optometry to assess the progression of glaucoma. The optic disc is the anatomical location of the eye's "blind spot", the area where the optic nerve and blood vessels enter the retina.
Why does optic disc cupping happen?
Individuals with glaucoma have increased IOP or consequent loss of blood flow to some regions of the eye, resulting in the death of optic nerve cells. The center of the optic disc (known as the cup) becomes larger, and the cup to optic disc ratio increases alarmingly. This process is referred to as optic nerve cupping.
What is the ICD-10 code for optic nerve swelling?
H46. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is optic nerve hypoplasia?
Optic nerve hypoplasia (ONH) is a congenital disorder characterized by underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the optic nerves. The optic nerves transmit impulses from the nerve-rich membranes lining the retina of the eye to the brain.
What is optic nerve pallor?
Optic atrophy is a sign and typically is noted as optic nerve pallor. This is the end stage of a process resulting in optic nerve damage. Because the optic nerve fiber layer is thinned or absent the disc margins appear sharp and the disc is pale, probably reflecting absence of small vessels in the disc head.
What Papilledema means?
(PA-pil-eh-DEE-muh) Swelling around the optic disk, the area where the optic nerve (the nerve that carries messages from the eye to the brain) enters the eyeball.
What is unspecified Papilledema?
Papilledema is a serious medical condition in which the optic nerve at the back of the eye becomes swollen. The symptoms can include visual disturbances, headaches, and nausea. Papilledema occurs when there is a buildup of pressure in or around the brain, which causes the optic nerve to swell.
What is bilateral papilledema?
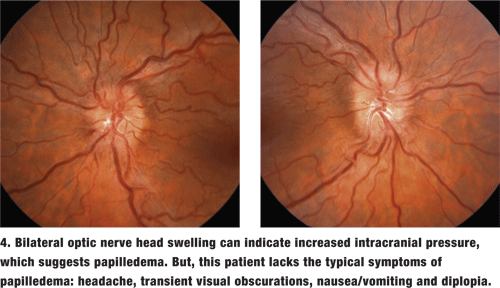
Papilledema is a sign of elevated intracranial pressure and is almost always bilateral. Causes include the following: Brain tumor. The tumors usually develop during early or middle adulthood but may develop at any age; they are... read more. or abscess.
Can you reverse optic nerve cupping?
Interpretation: Optic disc cupping can be reversed at an early stage of primary congenital glaucoma following successful reduction of IOP. Younger age at surgery was associated with reversal of cupping.
Is cupping good for eyes?
Facial cupping promotes circulation, which may help minimize the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, decrease puffiness, and more.
What are signs of optic nerve damage?
Symptoms of Optic Nerve DamageDecline in the field of vision.Distorted vision.Inflammation in the eye.Temporary or permanent vision loss.Unusual symptoms include numbness or weakness of the limbs, which may be a result of a neurological disorder.
What is physiological cupping of eyes?
Physiological cupping is a congenital disorder of optic cupping, which is caused by the scleral optic canal and pronounced glial atrophy of Bergmeister's papilla. GODC is a type of ascending optic nerve atrophy that is associated with the loss of retinal ganglion cell axons.
What is the ICd 10 code for optic nerve?
Disorders of optic nerve, not elsewhere classified 1 H47.0 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H47.0 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H47.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 H47.0 may differ.
Is H47.0 a reimbursement code?
H47.0 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H47.0 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H47.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 H47.0 may differ.
What is optic disk deficiency?
This condition indicates a deficiency in the number of nerve fibers which arise in the retina and converge to form the optic disk; optic nerve; optic chiasm; and optic tracts.
What is the disease of the eye and adnexa?
Diseases of the eye and adnexa. Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by loss of optic nerve fibers. It may be inherited or acquired. Acquired causes include ischemia, optic nerve neuropathy, glaucoma, trauma, radiation, brain tumors, and multiple sclerosis. It leads to vision disturbances.
What causes optic nerve pain?
A disorder characterized by inflammation of the optic nerve. Causes include autoimmune disorders, infections, toxins, drugs, and multiple sclerosis. It may manifest with acute loss of vision and pain. Inflammation of the optic nerve.
Where does inflammation occur?
Inflammation may occur in the portion of the nerve within the globe (neuropapillitis or anterior optic neuritis) or the portion behind the globe (retrobulbar neuritis or posterior optic neuritis).
Can optic neuritis be a sarcoidosis?
Why: optic neuritis may be present in patients with sarcoidosis or reiter's syndrome ( rarely). How: clinically, patients with optic neuritis present with sudden loss of central vision and pain on moving the eye. Opthalmoscopically there may be hyperemia of the optic disc and distention of the large retinal veins.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for left upper extremity pain
- 2. icd 10 pcs code for stenting of the lad
- 3. icd 10 code for follow up cva
- 4. 2019 icd 10 code for ventriculostomy shunt present
- 5. icd-10 code for hypothermia
- 6. icd 10 code for left medial thigh, lateral to and posterior to the vaginal introitus.
- 7. icd 10 code for rash and nonspecific skin eruption
- 8. icd 10 code for left foot mass
- 9. 2016 icd 10 code for osteoarthritis
- 10. icd 10 code for combined systolic and diastolic heart failure