What are the new ICD 10 codes?
Empyema (acute) (chest) (double) (pleura) (supradiaphragmatic) (thorax) J86.9ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J86.9Pyothorax without fistula2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 …
What is difference between ICD9 and ICD10?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J43 Emphysema 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code J43 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J43 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · Emphysema, unspecified. J43.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J43.9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J43.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 J43.9 may differ.
How many ICD 10 codes are there?
Jun 12, 2020 · ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J01. 8); acute abscess of sinus; acute empyema of sinus; acute infection of sinus; acute inflammation of sinus; acute suppuration of sinus; code (B95-B97) to identify infectious agent. Click to see full answer.
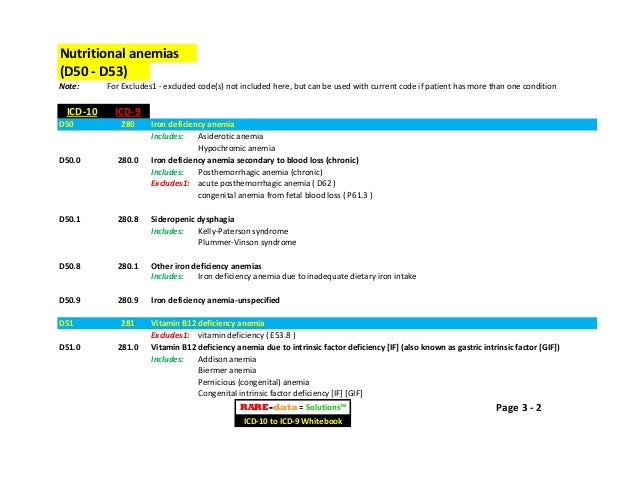
What is the ICD-10 code for left sided empyema?
J86. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J86. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is an empyema?
Empyema is a collection of pus in the cavity between the lung and the membrane that surrounds it (pleural space).
What's the other term used for empyema?
Empyema is also called pyothorax or purulent pleuritis. It's a condition in which pus gathers in the area between the lungs and the inner surface of the chest wall. This area is known as the pleural space. Pus is a fluid that's filled with immune cells, dead cells, and bacteria.
What is the pathology empyema?
empyema, accumulation of pus in a cavity of the body, usually in the pleura, which are the serous membranes covering the lungs. Empyema is the result of a microbial, usually bacterial, infection in a body cavity.
How is empyema diagnosis?
The first step to diagnosing empyema is a chest X-ray. An X-ray can only identify empyema when there is a specific amount of fluid in the pleural cavity, however. If the doctor suspects there is liquid in the pleural cavity after a chest X-ray, they will carry out an ultrasound.
What are the three stages of empyema pathophysiology?
Three stages in the natural course of empyema have long been described: the exudative, fibrinopurulent, and organizing phases.Jun 17, 2010
What is the root word of empyema?
Empyema: Empyema is a condition in which pus and fluid from infected tissue collects in a body cavity. The name comes from the Greek word empyein meaning pus-producing (suppurate).Mar 29, 2021
What is the treatment for empyema?
The goal of treating empyema is to remove the infection from the lung and cure the infection. Your doctor will prescribe antibiotics to get rid of the infection and use a chest tube to drain the pus.Jun 2, 2021
How is empyema pronounced?
0:051:00How To Say Empyema - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipEncima encima encima encima encima encima.MoreEncima encima encima encima encima encima.
What organism is responsible for empyema?
Most empyemas are parapneumonic, and the most commonly involved organisms are Staphylococcus aureus, enteric gram-negative bacilli, and anaerobes.
How does an empyema form?
Empyema is usually caused by an infection that spreads from the lung. It leads to a buildup of pus in the pleural space. There can be 2 cups (1/2 liter) or more of infected fluid. This fluid puts pressure on the lungs.Aug 25, 2019
Is empyema transudate or exudate?
Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural space that is classified as transudate or exudate according to its composition and underlying pathophysiology. Empyema is defined by purulent fluid collection in the pleural space, which is most commonly caused by pneumonia.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for history of bilateral lower extremity weakness
- 2. icd 10 code for moderate protein calorie malnutrition
- 3. icd 10 cm code for cataract due to type 2 diabetes mellitus
- 4. icd 10 code for abp pain
- 5. icd 10 code for circulation
- 6. icd 10 code for right of
- 7. icd 9 code for psa total
- 8. icd 10 code for acute bacterial bronchitis
- 9. icd 10 code for aortic mitral valve
- 10. icd 10 code for mild achilles tendon tightness